Molar Mass Of Ba Oh 2
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
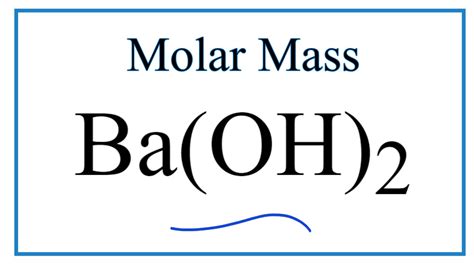
Table of Contents
Molar Mass of Ba(OH)₂: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the molar mass of a compound is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for various stoichiometric calculations and quantitative analyses. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calculating the molar mass of barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)₂, explaining the process step-by-step and highlighting its significance in different chemical contexts.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before we embark on calculating the molar mass of Ba(OH)₂, let's establish a clear understanding of the term itself. Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
The molar mass of an element is numerically equivalent to its atomic weight, as found on the periodic table. For compounds, the molar mass is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in the molecule or formula unit.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Ba(OH)₂
Barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)₂, is an ionic compound composed of barium (Ba), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms. To calculate its molar mass, we need to consider the atomic masses of each element and their respective quantities in the formula unit.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
-
Identify the elements and their quantities: Ba(OH)₂ contains one barium atom (Ba), two oxygen atoms (O), and two hydrogen atoms (H).
-
Find the atomic mass of each element: Referencing a periodic table, we find the following approximate atomic masses:
- Barium (Ba): 137.33 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1.01 g/mol
-
Calculate the total mass contribution of each element:
- Barium: 1 x 137.33 g/mol = 137.33 g/mol
- Oxygen: 2 x 16.00 g/mol = 32.00 g/mol
- Hydrogen: 2 x 1.01 g/mol = 2.02 g/mol
-
Sum the contributions: Add the mass contributions of all elements to find the molar mass of Ba(OH)₂:
137.33 g/mol + 32.00 g/mol + 2.02 g/mol = 171.35 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of Ba(OH)₂ is approximately 171.35 g/mol. Slight variations may occur depending on the source of atomic mass data used.
Significance of Molar Mass of Ba(OH)₂
The molar mass of Ba(OH)₂ is essential for various chemical calculations and applications, including:
1. Stoichiometric Calculations:
In chemical reactions, the molar mass allows us to convert between mass and moles of Ba(OH)₂. This is crucial for determining the amounts of reactants needed or products formed in a reaction. For example, if you need to react a specific mass of Ba(OH)₂ with another compound, knowing the molar mass helps you determine the number of moles involved, facilitating accurate calculations of reaction yield and limiting reagents.
2. Solution Concentration:
The molar mass is critical in preparing solutions of a known concentration. For instance, to prepare a 1 M (one molar) solution of Ba(OH)₂, you need to dissolve 171.35 grams of Ba(OH)₂ in enough solvent to make one liter of solution. Knowing the molar mass ensures the correct amount of solute is used to achieve the desired concentration.
3. Titration Analysis:
Titration is a common analytical technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. If you're titrating an acidic solution with a standard solution of Ba(OH)₂, knowing the molar mass of Ba(OH)₂ is crucial for calculating the concentration of the acid.
4. Gravimetric Analysis:
In gravimetric analysis, the mass of a precipitate is measured to determine the quantity of a substance in a sample. If Ba(OH)₂ is involved in forming a precipitate, its molar mass is needed to convert the mass of the precipitate to the amount of the original substance.
5. Understanding Chemical Properties:
The molar mass influences various chemical properties of Ba(OH)₂. For instance, it's relevant in calculating the density of a Ba(OH)₂ solution or determining the osmotic pressure of a solution containing Ba(OH)₂.
Practical Applications of Ba(OH)₂
Barium hydroxide finds diverse applications in various fields due to its strong basic nature and other unique properties:
-
Sugar Refining: Ba(OH)₂ is used in the purification of sugar beet juice. Its strong alkalinity helps to precipitate impurities, leading to a refined sugar product.
-
Chemical Synthesis: Ba(OH)₂ serves as a reactant or catalyst in many chemical syntheses. Its strong base character makes it useful in various organic reactions and inorganic preparations.
-
Wastewater Treatment: Its alkalinity can help neutralize acidic wastewater, contributing to environmental protection.
-
Lubricants: Specific applications utilize Ba(OH)₂ in the formulation of certain types of lubricants.
-
Laboratory Use: Ba(OH)₂ is commonly used in laboratories for various chemical experiments and titrations as a standard base.
Potential Hazards and Safety Precautions
Barium hydroxide is a caustic substance. Direct contact with skin, eyes, or ingestion can cause severe irritation, burns, and potential health issues. Therefore, it's imperative to follow strict safety protocols when handling Ba(OH)₂:
-
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE): This includes gloves, eye protection, and a lab coat.
-
Handle in a well-ventilated area: Barium hydroxide can release irritating vapors.
-
Avoid direct contact: Use appropriate tools and techniques to minimize direct contact.
-
Proper disposal: Dispose of Ba(OH)₂ and its waste according to established safety regulations.
Conclusion
The molar mass of Ba(OH)₂, approximately 171.35 g/mol, is a fundamental parameter in various chemical calculations and practical applications. Understanding its calculation and significance is essential for students and professionals alike. Accurate determination of molar mass is crucial for quantitative analysis, stoichiometric calculations, and various applications of barium hydroxide in diverse industrial and laboratory settings. Always remember to prioritize safety when handling this caustic chemical. Remember to always refer to up-to-date safety data sheets (SDS) for the most accurate and current information.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 29 C In Fahrenheit
Mar 20, 2025
-
How To Determine The Coordination Number
Mar 20, 2025
-
5 Letter Words With A And S
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factors Of 14
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 2
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molar Mass Of Ba Oh 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
