How Many Electrons In Double Bond
Juapaving
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
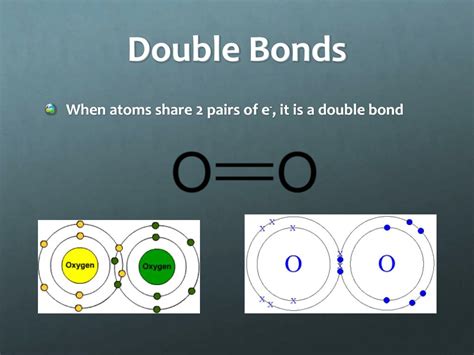
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons in a Double Bond? A Deep Dive into Chemical Bonding
Understanding chemical bonds is fundamental to grasping the behavior of matter. Among the various types of bonds, double bonds play a crucial role in the properties and reactivity of numerous molecules. This article will explore the fundamental question: how many electrons are involved in a double bond? We'll delve into the intricacies of covalent bonding, explore the implications of double bonds in different molecular structures, and examine how understanding electron count affects molecular geometry and reactivity.
Understanding Covalent Bonds
Before we tackle the specific case of double bonds, let's refresh our understanding of covalent bonding. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. These shared electrons are attracted to the positively charged nuclei of both atoms, creating a stable bond that holds the atoms together. The number of shared electron pairs determines the bond order.
Single Bonds: The Basics
A single bond involves the sharing of one electron pair (two electrons). Consider the simplest example: a hydrogen molecule (H₂). Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron to the bond, resulting in a shared pair that holds the two hydrogen atoms together.
Double Bonds: Sharing More Electrons
A double bond involves the sharing of two electron pairs (four electrons). This means each atom involved in the double bond contributes two electrons to the shared pool. The increased electron density in the double bond leads to a stronger and shorter bond compared to a single bond.
Key takeaway: A double bond always contains four electrons, shared equally between the two atoms involved.
Examples of Double Bonds in Organic Chemistry
Double bonds are prevalent in organic chemistry, significantly influencing the properties and reactivity of organic molecules. Let's examine some common examples:
Alkenes: The Carbon-Carbon Double Bond
Alkenes are hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond. The simplest alkene is ethene (C₂H₄), also known as ethylene. Each carbon atom in ethene is sp² hybridized, meaning it has three sp² hybrid orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital. One sp² hybrid orbital from each carbon atom overlaps to form a sigma (σ) bond. The remaining unhybridized p orbitals overlap laterally to form a pi (π) bond. This sigma bond and pi bond together constitute the double bond, containing a total of four electrons.
Visualizing the Electron Distribution: It's helpful to visualize the electron distribution in a double bond. The four electrons are not equally spaced between the two carbon atoms. The sigma bond concentrates electron density directly between the nuclei, while the pi bond has electron density above and below the plane of the sigma bond.
Carbonyl Compounds: Carbon-Oxygen Double Bonds
Carbonyl compounds contain a carbon-oxygen double bond (C=O). This functional group is present in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters. The carbon-oxygen double bond also comprises four electrons, with a sigma bond and a pi bond. The greater electronegativity of oxygen compared to carbon results in a polar bond, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and a partial positive charge on the carbon. This polarity significantly affects the reactivity of carbonyl compounds.
The Impact of Double Bonds on Molecular Geometry and Properties
The presence of a double bond significantly impacts the molecular geometry and other physical and chemical properties.
Molecular Geometry: Restricted Rotation
Unlike single bonds, double bonds exhibit restricted rotation. The pi bond restricts the rotation of the atoms around the double bond axis. This rigidity influences the overall shape and conformation of the molecule.
Reactivity: Electrophilic Addition Reactions
Double bonds are electron-rich regions in a molecule. Their reactivity is primarily due to the presence of the pi electrons. They undergo characteristic electrophilic addition reactions. In these reactions, electrophiles, which are electron-deficient species, attack the pi bond, leading to the formation of new sigma bonds. This opens a wide range of possibilities for chemical transformations involving molecules with double bonds.
Physical Properties: Boiling Points and Melting Points
Double bonds also affect the physical properties of molecules. The presence of a double bond often leads to higher boiling points and melting points compared to molecules with only single bonds. This is due to the stronger interactions between molecules caused by the increased electron density in the double bond.
Double Bonds in Inorganic Chemistry
While prevalent in organic chemistry, double bonds also exist in inorganic compounds.
Transition Metal Complexes
Many transition metal complexes involve metal-ligand double bonds. These bonds involve the donation of electrons from ligands to the metal, as well as back-donation from the metal to the ligand. This back-donation is crucial for the stability of these complexes.
Oxides and Other Inorganic Compounds
Several inorganic compounds exhibit double bonds. For instance, carbon dioxide (CO₂) contains two carbon-oxygen double bonds. Each oxygen atom contributes two electrons, and each carbon atom also contributes two electrons, resulting in four electrons in each double bond.
Beyond Double Bonds: Triple Bonds and Resonance
While this article focuses on double bonds, it's important to briefly mention higher-order bonds.
Triple Bonds: Six Electrons Shared
A triple bond involves the sharing of three electron pairs (six electrons). Triple bonds are even stronger and shorter than double bonds. A classic example is nitrogen gas (N₂), which is held together by a strong triple bond, accounting for its inert nature.
Resonance: Delocalized Electrons
Resonance structures describe molecules where electrons are delocalized across multiple atoms. Molecules exhibiting resonance might have partial double bond character, meaning the electron density isn't completely localized in one particular bond but distributed across multiple bonds.
Applications and Significance of Understanding Double Bonds
Understanding the number of electrons involved in a double bond and its impact on molecular properties is crucial in various fields:
Organic Synthesis
Chemists utilize this understanding to design synthetic routes for creating complex molecules with desired properties. This is critical in the pharmaceutical, materials, and agricultural industries.
Polymer Chemistry
The presence of double bonds in monomers is essential for polymerization reactions, enabling the synthesis of polymers with specific characteristics. This knowledge is fundamental in the production of plastics, fibers, and rubbers.
Biochemistry
Many biomolecules, including proteins and lipids, contain double bonds. Understanding their properties and reactivity helps us understand biological processes such as enzyme catalysis and membrane function.
Conclusion: The Importance of Electron Count in Chemical Bonding
In summary, a double bond always consists of four electrons shared between two atoms, creating a stronger and shorter bond than a single bond. Understanding this fundamental aspect of chemical bonding is essential for grasping the structure, properties, and reactivity of countless molecules in organic, inorganic, and biochemical contexts. The implications extend across various scientific disciplines and industrial applications, reinforcing the critical role of electron counting in our comprehension of the chemical world. The intricacies of double bonds, including their influence on molecular geometry, reactivity, and physical properties, continue to be a rich area of study and technological innovation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
One Pair Of Opposite Sides Are Parallel
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Relationship Between Density Mass And Volume
Mar 29, 2025
-
Difference Between Seed Germination And Seed Emergence
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 60
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Do You Turn A Ratio Into A Percent
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons In Double Bond . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
