How Many Corners Does A Square Have
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
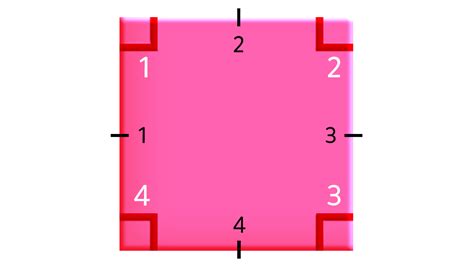
Table of Contents
How Many Corners Does a Square Have? A Deep Dive into Geometry
This seemingly simple question, "How many corners does a square have?", opens the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, spatial reasoning, and the very foundation of mathematical understanding. While the immediate answer is a straightforward "four," delving deeper reveals a rich tapestry of interconnected concepts. This article will not only answer the question definitively but also explore the related properties of squares, their place within broader geometric frameworks, and the implications of this seemingly basic concept in various fields.
Understanding Corners: Vertices and Angles
Before definitively answering the core question, let's clarify terminology. In geometry, the points where two or more lines meet to form an angle are called vertices. Therefore, when we talk about the "corners" of a square, we are referring to its vertices. A square, by definition, is a two-dimensional shape with four sides of equal length and four right angles (90-degree angles). Each vertex represents the meeting point of two adjacent sides, forming a corner.
Therefore, a square unequivocally has four corners or vertices.
Beyond the Obvious: Exploring the Properties of Squares
The seemingly simple four-cornered square is a cornerstone of geometry. Its properties are fundamental and serve as building blocks for more complex shapes and concepts. Let's examine some key characteristics:
1. Sides and Angles: The Defining Features
- Equal Sides: All four sides of a square are of equal length. This is a defining characteristic that distinguishes it from other quadrilaterals like rectangles (which only require opposite sides to be equal) or parallelograms (which require opposite sides to be parallel).
- Right Angles: Each of the four interior angles of a square measures exactly 90 degrees. This precise angular measurement contributes to the square's inherent symmetry and stability.
2. Symmetry: A Perfect Balance
Squares exhibit both rotational symmetry and reflectional symmetry.
- Rotational Symmetry: A square possesses rotational symmetry of order 4. This means it can be rotated around its center by 90 degrees, 180 degrees, 270 degrees, and 360 degrees (a full rotation), and still look identical.
- Reflectional Symmetry: A square has four lines of reflectional symmetry. These lines can be drawn vertically, horizontally, and diagonally through the center of the square, creating mirror images across each line.
3. Area and Perimeter: Quantifying the Square
- Area: The area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one side (side * side = area). This simple formula highlights the square's relationship to the concept of exponents and powers.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a square is the total length of its four sides, calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four (4 * side = perimeter).
Squares in Different Contexts: Applications and Significance
The humble square, with its four corners, is far more significant than its simplicity might suggest. It plays crucial roles across various disciplines:
1. Mathematics: A Foundation for Higher Concepts
Squares are foundational in:
- Plane Geometry: They are a key element in understanding quadrilaterals, polygons, and more complex geometric constructions. The properties of squares inform theorems and postulates in Euclidean geometry.
- Coordinate Geometry: Squares are easily represented on Cartesian coordinate systems, providing a concrete visual representation of algebraic concepts.
- Algebra: The area calculation (side squared) directly relates to algebraic concepts of exponents and polynomials.
2. Art and Design: Aesthetics and Structure
Squares are frequently used in:
- Architecture: From the perfectly symmetrical facades of buildings to the layout of rooms and spaces, squares provide a sense of order and stability. Many iconic buildings incorporate square elements in their designs.
- Graphic Design: Squares are used extensively in logos, layouts, and visual compositions to create balance and visual interest. Their symmetrical nature lends itself to clean and effective design solutions.
- Art: Artists have utilized squares in numerous works, both as the primary subject matter and as compositional elements to create structure and harmony.
3. Science and Engineering: Practical Applications
Squares find practical applications in:
- Engineering: Square shapes offer structural integrity and are used in building materials, components of machines, and various engineering structures.
- Physics: The concept of squares is fundamental in understanding areas, volumes, and other physical properties.
- Computer Science: Squares are integral in computer graphics, image processing, and algorithms related to spatial reasoning.
Misconceptions and Related Shapes
It's important to address potential misconceptions and related shapes:
- Squares vs. Rectangles: While all squares are rectangles (because they have four right angles), not all rectangles are squares (as rectangles only require opposite sides to be equal). This distinction highlights the importance of precise definitions in geometry.
- Squares vs. Rhombuses: A rhombus has four equal sides but doesn't necessarily have right angles. Therefore, all squares are rhombuses, but not all rhombuses are squares.
- Three-Dimensional Analogue: Cubes: The three-dimensional equivalent of a square is a cube. A cube has six square faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices (corners).
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the Square
The seemingly simple question of how many corners a square has leads us on a journey through the fundamentals of geometry, its applications in diverse fields, and the subtle nuances of mathematical definitions. The answer – four – is undeniable, but the implications and significance of this fundamental shape extend far beyond a simple numerical count. From its inherent symmetry to its practical applications in various disciplines, the square stands as a testament to the power and beauty of mathematical forms. The understanding of this basic shape lays the groundwork for comprehending more complex geometric concepts and their real-world applications. The four corners of a square represent not only a geometric reality but also a foundation upon which much of our understanding of the world is built.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 10
Mar 07, 2025
-
What Is Larger A Gigabyte Or A Megabyte
Mar 07, 2025
-
Which One Of The Following Statements Is True
Mar 07, 2025
-
How To Change Mole To Grams
Mar 07, 2025
-
How Many Acres Is In A Mile
Mar 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Corners Does A Square Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
