What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 10
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
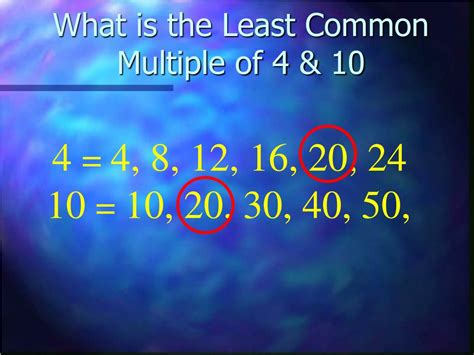
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 4 and 10? A Deep Dive into Finding LCMs
The question, "What is the least common multiple of 4 and 10?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding how to find the least common multiple (LCM) is crucial in various mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations. This article will not only answer that specific question but also provide a comprehensive guide to understanding LCMs, exploring different methods for calculation, and showcasing their real-world relevance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCMs)
Before diving into the specifics of finding the LCM of 4 and 10, let's establish a solid foundation. The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
Consider two numbers, 'a' and 'b'. Their multiples are the numbers obtained by multiplying each by consecutive integers (1, 2, 3, and so on). The LCM is the smallest number that appears in the list of multiples of both 'a' and 'b'.
Distinguishing LCM from Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
It's essential to distinguish the LCM from the greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF). While the LCM is the smallest multiple common to both numbers, the GCD is the largest divisor common to both. They are inversely related; understanding one helps understand the other.
Methods for Finding the LCM
Several methods can be used to determine the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common ones, focusing on their application to finding the LCM of 4 and 10.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32...
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50...
As you can see, the smallest common multiple of 4 and 10 is 20.
This method is effective for small numbers but becomes cumbersome with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Therefore, the LCM of 4 and 10 is 2² x 5 = 20.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the GCD. First, we need to find the GCD (greatest common divisor) of 4 and 10.
- Factors of 4: 1, 2, 4
- Factors of 10: 1, 2, 5, 10
The greatest common divisor of 4 and 10 is 2.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(4, 10) = (|4 x 10|) / GCD(4, 10) = 40 / 2 = 20
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding prime factorizations might be more challenging.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond abstract mathematical exercises. It finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses depart from a station at different intervals. Finding the LCM of their departure intervals helps determine when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
-
Construction and Engineering: In construction projects involving repetitive patterns (e.g., tiling or bricklaying), the LCM helps determine the optimal dimensions for materials to minimize waste and ensure seamless patterns.
-
Music: In music theory, the LCM helps determine when two musical notes with different frequencies will harmonize perfectly again. The LCM represents the time interval until the notes' waveforms coincide, creating a consonant sound.
Expanding on LCM Concepts: More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, we simply consider all the prime factors from all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the formula method, we can apply it iteratively, finding the LCM of two numbers first and then finding the LCM of the result with the next number, and so on. The listing multiples method becomes exponentially more difficult with more numbers.
For example, let's find the LCM of 4, 6, and 10:
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
The highest powers of the prime factors are 2², 3, and 5. Therefore, the LCM(4, 6, 10) = 2² x 3 x 5 = 60.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Finding the least common multiple is a fundamental skill in mathematics with far-reaching applications. Whether you use the listing multiples method, the prime factorization method, or the formula involving GCD, understanding the underlying concepts is key. The choice of method depends on the complexity of the numbers involved. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge and tools to confidently tackle LCM problems, no matter the scale. Remember, the LCM of 4 and 10, as demonstrated through various methods, is definitively 20. This understanding forms a crucial stepping stone for more advanced mathematical explorations. Continue practicing, and you'll quickly master the art of LCM calculation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All The Sides Of A Triangle Equal
Mar 08, 2025
-
How Many Black Cards Are In A Deck Of 52
Mar 08, 2025
-
What Is Word Form In Math
Mar 08, 2025
-
What Remains Constant In Charles Law
Mar 08, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factors Of 15
Mar 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
