How Many Corners Does A Polygon Have
Juapaving
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
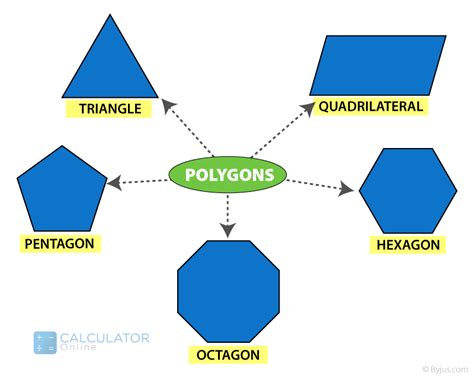
Table of Contents
How Many Corners Does a Polygon Have? A Deep Dive into Polygons and Their Properties
The seemingly simple question, "How many corners does a polygon have?" opens a fascinating exploration into the world of geometry. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, a deeper understanding requires delving into the definitions, classifications, and properties of polygons. This comprehensive guide will unpack this question, exploring different types of polygons, their applications, and the mathematical principles that govern them.
Understanding Polygons: Definitions and Basic Properties
A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a finite number of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the sides meet are called the vertices or corners. It's crucial to understand that a polygon must be a closed figure; open figures with straight lines are not considered polygons. The number of sides directly determines the number of corners; a polygon with n sides will always have n corners.
Key Characteristics of Polygons:
- Sides: Straight line segments forming the polygon.
- Vertices (Corners): Points where two sides intersect.
- Angles: Formed by the intersection of two adjacent sides at a vertex. The sum of interior angles of a polygon is dependent on the number of sides.
- Diagonals: Line segments connecting non-adjacent vertices.
Classifying Polygons: A Taxonomy of Shapes
Polygons are categorized primarily by the number of sides they possess. This classification leads to a rich variety of shapes, each with its unique properties and applications. Here are some key classifications:
Common Polygons and Their Corner Count:
- Triangle (3 sides): The simplest polygon, possessing 3 sides, 3 vertices, and 3 interior angles. Triangles are further classified into equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), and scalene (all sides unequal).
- Quadrilateral (4 sides): A polygon with four sides and four vertices. This category encompasses squares, rectangles, parallelograms, rhombuses, trapezoids, and kites – each with specific properties regarding side lengths, angle measures, and parallel sides.
- Pentagon (5 sides): A polygon with five sides and five vertices. Regular pentagons have all sides and angles equal.
- Hexagon (6 sides): A polygon with six sides and six vertices. Regular hexagons appear in nature, such as in honeycombs.
- Heptagon (7 sides): A polygon with seven sides and seven vertices.
- Octagon (8 sides): A polygon with eight sides and eight vertices. Stop signs are a common example of an octagon.
- Nonagon (9 sides): A polygon with nine sides and nine vertices.
- Decagon (10 sides): A polygon with ten sides and ten vertices.
- Undecagon (11 sides): A polygon with eleven sides and eleven vertices.
- Dodecagon (12 sides): A polygon with twelve sides and twelve vertices.
Beyond the Basics: Higher-Order Polygons
The number of sides in a polygon can extend infinitely. While the names for polygons beyond twelve sides become less common (tridecagon for 13 sides, tetradecagon for 14 sides, and so on), the fundamental principle remains: the number of corners always equals the number of sides.
Calculating Interior Angles of Polygons
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is directly related to the number of sides. The formula for calculating this sum is:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' is the number of sides (and therefore corners).
For example:
- Triangle (n=3): (3-2) * 180° = 180°
- Quadrilateral (n=4): (4-2) * 180° = 360°
- Pentagon (n=5): (5-2) * 180° = 540°
This formula is a fundamental concept in geometry and is crucial for solving various problems related to polygons.
Regular vs. Irregular Polygons: A Key Distinction
Polygons are further classified as either regular or irregular.
- Regular Polygons: Have all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure. Examples include a square (regular quadrilateral), equilateral triangle (regular triangle), and regular hexagon.
- Irregular Polygons: Have sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. Most polygons encountered in everyday life fall into this category.
Real-World Applications of Polygons
Polygons are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they are ubiquitous in the real world. Their applications span numerous fields:
- Architecture and Engineering: Polygons form the basis of building designs, from simple rectangular rooms to complex structures.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use polygons to create various shapes and patterns, showcasing their aesthetic appeal and versatility.
- Nature: Hexagons are commonly observed in natural structures like honeycombs. Many natural forms approximate polygons, demonstrating their presence in the natural world.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Polygons are fundamental to computer graphics, used to represent and render 3D objects and environments.
- Manufacturing and Industry: Polygons are crucial in designing and manufacturing various products, from simple nuts and bolts to intricate machine parts.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Polygon Properties
The relationship between the number of sides and corners is just the starting point. A deeper understanding of polygons involves exploring more advanced concepts:
- Area Calculation: Different formulas exist for calculating the area of various polygons, depending on their shape and the given dimensions.
- Perimeter Calculation: The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides.
- Tessellations: The ability of polygons to tile a plane without gaps or overlaps. Certain polygons, like squares and hexagons, tessellate perfectly.
- Symmetry: Polygons can exhibit various types of symmetry, such as rotational symmetry and reflectional symmetry.
- Convex vs. Concave Polygons: Convex polygons have all interior angles less than 180°, while concave polygons have at least one interior angle greater than 180°.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Polygons
The seemingly simple question of how many corners a polygon has leads us to a vast and fascinating realm of geometric exploration. From the fundamental relationship between sides and corners to the diverse applications of polygons in various fields, the subject matter is rich and rewarding. Whether you're a student of geometry or simply curious about the world around you, understanding the properties and characteristics of polygons provides valuable insights into the shapes that define our world. The seemingly simple polygon holds a complexity that is endlessly intriguing, making it a cornerstone of mathematical understanding and practical application alike. The number of corners, equal to the number of sides, serves as the foundation upon which a deeper understanding of these fundamental shapes is built.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is One Difference Between A Mixture And A Compound
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Are All Factors Of 40
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is 40 Hours
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is A Measure Of The Gravitational Force On An Object
Mar 28, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 3 And 9
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Corners Does A Polygon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
