How Do You Subtract Rational Numbers
Juapaving
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
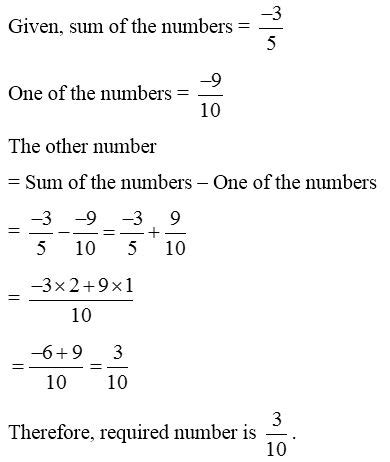
Table of Contents
How Do You Subtract Rational Numbers? A Comprehensive Guide
Subtracting rational numbers might seem daunting at first, but with a structured approach and a solid understanding of the underlying principles, it becomes a straightforward process. This comprehensive guide breaks down the process step-by-step, covering various scenarios and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We’ll delve into the core concepts, explore different methods, and address common pitfalls to ensure you master this essential arithmetic skill.
Understanding Rational Numbers
Before we dive into subtraction, let's refresh our understanding of rational numbers. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not zero. This includes:
- Integers: Whole numbers (positive, negative, and zero). Examples: -3, 0, 5.
- Fractions: Numbers expressed as a ratio of two integers. Examples: 1/2, -3/4, 7/1.
- Terminating Decimals: Decimals that end after a finite number of digits. Examples: 0.75, -2.5, 3.125.
- Repeating Decimals: Decimals that have a pattern of digits that repeats infinitely. Examples: 0.333..., 0.142857142857...
Numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers are called irrational numbers (e.g., π, √2). This guide focuses solely on rational numbers.
The Fundamental Principle: Adding the Opposite
The key to subtracting rational numbers lies in understanding that subtraction is the same as adding the opposite (or additive inverse). The additive inverse of a number is the number that, when added to the original number, results in zero. For example:
- The additive inverse of 5 is -5 (because 5 + (-5) = 0).
- The additive inverse of -3/4 is 3/4 (because -3/4 + 3/4 = 0).
Therefore, subtracting a rational number is equivalent to adding its additive inverse. This principle simplifies the subtraction process, particularly when dealing with negative numbers.
Example:
Instead of calculating 7 - 3, we can calculate 7 + (-3), which equals 4.
Subtracting Rational Numbers: Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a step-by-step guide to subtracting rational numbers, covering different scenarios:
1. Subtracting Fractions with a Common Denominator:
This is the simplest case. If the fractions have the same denominator, simply subtract the numerators and keep the common denominator.
Example:
5/8 - 2/8 = (5 - 2)/8 = 3/8
2. Subtracting Fractions with Different Denominators:
When the denominators are different, you must first find a common denominator (a number that is a multiple of both denominators). The most efficient common denominator is the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators. Once you have the common denominator, convert both fractions to equivalent fractions with that denominator, then subtract the numerators.
Example:
1/3 - 1/6
- Find the LCM of 3 and 6: The LCM is 6.
- Convert 1/3 to an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 6: 1/3 = 2/6
- Subtract: 2/6 - 1/6 = (2 - 1)/6 = 1/6
3. Subtracting Mixed Numbers:
Mixed numbers combine a whole number and a fraction (e.g., 2 1/2). To subtract mixed numbers, you can either convert them to improper fractions first or subtract the whole numbers and fractions separately.
Example (Converting to Improper Fractions):
3 1/4 - 1 3/4
- Convert to improper fractions: 3 1/4 = 13/4 and 1 3/4 = 7/4
- Subtract: 13/4 - 7/4 = 6/4 = 3/2 = 1 1/2
Example (Subtracting Separately):
3 1/4 - 1 3/4
- Subtract the whole numbers: 3 - 1 = 2
- Subtract the fractions: 1/4 - 3/4 = -2/4 = -1/2
- Combine: 2 - 1/2 = 1 1/2
4. Subtracting Decimals:
Subtracting decimals is similar to subtracting whole numbers. Align the decimal points vertically and subtract column by column, borrowing when necessary.
Example:
3.75 - 1.25 = 2.50
5. Subtracting Negative Rational Numbers:
Remember the principle of adding the opposite. Subtracting a negative number is the same as adding its positive counterpart.
Example:
5 - (-2) = 5 + 2 = 7
-3/4 - (-1/2) = -3/4 + 1/2 = -3/4 + 2/4 = -1/4
6. Subtracting Rational Numbers in Word Problems:
Many real-world problems involve subtracting rational numbers. Carefully analyze the problem to identify the numbers and the operation required.
Example:
A baker uses 2 1/2 cups of flour for one cake and 1 3/4 cups for another. How much more flour did the baker use in the first cake?
This problem requires subtraction: 2 1/2 - 1 3/4 = 3/4 cup.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
-
Using a Number Line: A visual aid like a number line can be helpful, especially for visualizing the subtraction of integers or visualizing the concept of adding the opposite.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Always simplify your final answer to its lowest terms. For example, 6/8 should be simplified to 3/4.
-
Dealing with Zero: Subtracting zero from any rational number leaves the number unchanged. Subtracting a number from zero results in the additive inverse of that number.
-
Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): If your problem involves multiple operations, remember to follow the order of operations (Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Forgetting to find a common denominator: This is a frequent error when subtracting fractions.
-
Incorrectly simplifying fractions: Always double-check your simplification.
-
Mixing up addition and subtraction: Pay close attention to the signs.
-
Ignoring negative signs: Carefully handle negative numbers and their additive inverses.
Practice Makes Perfect
The best way to solidify your understanding of subtracting rational numbers is through consistent practice. Work through various examples, involving fractions, decimals, mixed numbers, and negative numbers. You can find numerous practice problems online or in textbooks. The more you practice, the more confident and proficient you will become.
Conclusion
Subtracting rational numbers is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications in mathematics and various real-world scenarios. By mastering the techniques outlined in this guide and practicing regularly, you'll build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Remember the key principle: subtraction is the same as adding the opposite. With practice and attention to detail, you'll confidently tackle any rational number subtraction problem.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Reaction With Magnesium And Hydrochloric Acid
Mar 30, 2025
-
Round 728362 25369 To The Nearest Thousand
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root 72
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Elements Are Found In Glucose
Mar 30, 2025
-
Solid Changes To Liquid Is Called
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Subtract Rational Numbers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
