How Do I Find The Perimeter Of A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
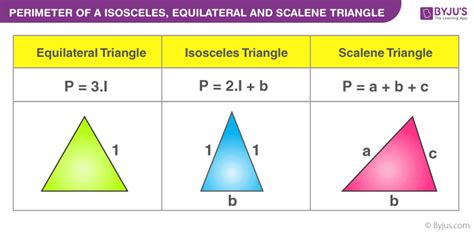
Table of Contents
How Do I Find the Perimeter of a Triangle? A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the perimeter of a triangle might seem like a simple task, especially compared to calculating its area. However, understanding the different approaches and nuances involved is crucial, particularly when dealing with various types of triangles – equilateral, isosceles, scalene, and right-angled triangles. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods, formulas, and practical applications of determining the perimeter of a triangle, equipping you with a thorough understanding of this fundamental geometric concept.
Understanding the Basics: What is Perimeter?
Before we dive into the specifics of triangle perimeters, let's establish a clear understanding of what perimeter means. The perimeter of any shape is the total distance around its outer boundary. Imagine walking along the edges of a triangle; the total distance you cover represents its perimeter. This concept applies to all polygons, not just triangles.
Calculating the Perimeter of a Triangle: The Fundamental Approach
The most fundamental method for finding the perimeter of a triangle involves simply adding the lengths of its three sides. Every triangle has three sides, conventionally labeled as a, b, and c. Therefore, the formula for the perimeter (P) of a triangle is:
P = a + b + c
This formula remains consistent regardless of the type of triangle. Whether it's an equilateral triangle (all sides equal), an isosceles triangle (two sides equal), a scalene triangle (all sides unequal), or a right-angled triangle (one angle is 90 degrees), the perimeter is always the sum of its three sides.
Example 1: A Simple Scalene Triangle
Let's say we have a triangle with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm. To find the perimeter, we simply add these values:
P = 5 cm + 7 cm + 9 cm = 21 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of this scalene triangle is 21 cm.
Example 2: An Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. Suppose we have an isosceles triangle with two sides measuring 6 cm each and a third side measuring 8 cm. The perimeter would be:
P = 6 cm + 6 cm + 8 cm = 20 cm
The perimeter of this isosceles triangle is 20 cm.
Example 3: An Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle possesses the simplest calculation. All three sides are equal in length. If each side of an equilateral triangle measures 4 cm, its perimeter is:
P = 4 cm + 4 cm + 4 cm = 12 cm
The perimeter of this equilateral triangle is 12 cm.
Finding the Perimeter Using Other Given Information
Sometimes, you might not be directly given the lengths of all three sides. You might have information about other aspects of the triangle, such as its area, angles, or a combination of side lengths and angles. Let's explore how to tackle these situations.
Using Heron's Formula (When Area and One Side are Known)
Heron's formula is a powerful tool that allows you to calculate the area of a triangle if you know the lengths of all three sides. While it's primarily used for area calculation, it can indirectly help you find the perimeter if you already know the area and one side length.
Heron's Formula for Area:
Area = √[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)]
where:
- s = (a + b + c) / 2 (the semi-perimeter)
- a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides.
If you know the area and two side lengths (a and b), you can solve this equation for c, and then find the perimeter using P = a + b + c. This method is particularly useful when dealing with complex triangles where direct measurement of all sides is difficult.
Using Trigonometry (When Angles and One Side are Known)
Trigonometry offers another powerful approach, especially when you're dealing with right-angled triangles or when you know some angles and side lengths. Using trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent, you can calculate the missing side lengths and then determine the perimeter.
For example, in a right-angled triangle, if you know the length of one side and one of the acute angles, you can use trigonometric ratios to find the lengths of the other two sides, thus enabling you to calculate the perimeter.
Using Coordinate Geometry (When Vertex Coordinates are Known)
If you know the coordinates of the three vertices of the triangle in a Cartesian plane, you can use the distance formula to calculate the lengths of the sides and then find the perimeter. The distance formula is:
Distance = √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
where (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) are the coordinates of two points. You would apply this formula for each pair of vertices to find the lengths of the sides and subsequently calculate the perimeter.
Practical Applications of Finding Triangle Perimeters
The ability to calculate the perimeter of a triangle extends far beyond the realm of theoretical mathematics. It has numerous practical applications across various fields:
-
Engineering and Construction: Determining the amount of material needed for fencing, building frameworks, or designing structural elements often requires calculating the perimeter of triangular components.
-
Surveying and Land Measurement: Surveyors utilize triangle perimeters to accurately measure land boundaries and calculate distances between points.
-
Cartography and Mapmaking: Precise perimeter calculations are crucial in creating accurate maps and geographical representations.
-
Computer Graphics and Design: In computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling, calculating perimeters is essential for creating and manipulating various shapes, including triangles.
-
Physics and Mechanics: Triangle perimeters can be relevant in calculating forces, moments, and other physical quantities in structural analysis.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While the concept of finding a triangle's perimeter is relatively straightforward, several common issues can arise:
-
Inaccurate Measurements: Errors in measuring the side lengths can lead to inaccurate perimeter calculations. It's crucial to use precise measurement tools and techniques.
-
Unit Consistency: Ensure that all side lengths are measured using the same units (e.g., centimeters, meters, inches). Mixing units will result in an incorrect perimeter.
-
Incorrect Formula Application: Always double-check that you are using the correct formula (P = a + b + c) and that you have correctly substituted the values of the side lengths.
-
Complex Triangle Types: When dealing with complex triangles or those defined indirectly (e.g., using Heron's formula or trigonometry), carefully review the steps involved to avoid errors.
Conclusion: Mastering Triangle Perimeter Calculations
Mastering the calculation of a triangle's perimeter is a fundamental skill in geometry and has far-reaching practical applications. By understanding the fundamental formula, and by learning to adapt your approach when given different information, you'll be equipped to confidently tackle perimeter problems in various contexts. Remember to always double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy. With practice, calculating the perimeter of any triangle will become second nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Mixture Is Air
Mar 05, 2025
-
Simplify To Create An Equivalent Expression
Mar 05, 2025
-
Is Water A Compound Element Or Mixture
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Roman Numeral For 11
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of Ten
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do I Find The Perimeter Of A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
