How Are Squares And Rectangles Alike
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
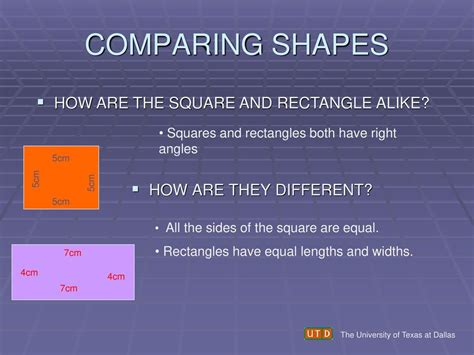
Table of Contents
How Are Squares and Rectangles Alike? Exploring Shared Properties and Differences
Squares and rectangles are fundamental geometric shapes that often appear together in discussions of geometry and mathematics. While distinct, they share a crucial underlying relationship, making them fascinating subjects for exploration. This article delves into the similarities and differences between squares and rectangles, emphasizing their shared properties and exploring how these properties contribute to their practical applications in various fields. We’ll uncover the mathematical underpinnings of their relationship and provide examples of where these shapes are used in the real world.
The Fundamental Similarities: A Family Resemblance
At their core, squares and rectangles belong to the same family of quadrilaterals – four-sided polygons. This shared characteristic gives them several common properties:
1. Four Sides and Four Angles: The Basic Framework
Both squares and rectangles possess four straight sides. This fundamental attribute defines them as quadrilaterals, differentiating them from triangles, pentagons, or other polygons. Moreover, both shapes have four angles, meaning that the sum of their internal angles is always 360 degrees. This consistent angle sum is a defining characteristic of all quadrilaterals.
2. Opposite Sides are Parallel and Equal: Defining Parallelism
A key feature shared by both squares and rectangles is the parallelism and equality of their opposite sides. This means that if you draw lines extending from opposite sides of either shape, these lines would never intersect. Furthermore, the lengths of opposite sides are identical. This parallelism is a fundamental concept in geometry, underpinning many geometric theorems and proofs. The property of parallel sides also contributes to the stability and practicality of rectangular and square structures in architecture and engineering.
3. Four Right Angles: The Cornerstone of Stability
Both squares and rectangles possess four right angles, each measuring exactly 90 degrees. This attribute is particularly important because right angles represent perfect corners – they are stable and easily constructed. This feature contributes significantly to the widespread use of these shapes in building construction, design, and various manufacturing processes. The precision and stability provided by right angles ensure that structures built using these shapes are robust and reliable. Consider the simple act of creating a rectangular frame – the 90-degree angles guarantee that the sides remain perpendicular, creating a sturdy structure.
4. Diagonals Bisect Each Other: A Shared Geometric Property
Another shared property lies in their diagonals. When you draw a line connecting two opposite corners of either a square or rectangle, you create a diagonal. In both shapes, these diagonals bisect each other – they intersect at their midpoints. This means that the point where the diagonals cross divides each diagonal into two equal segments. This property is often used in geometric proofs and constructions.
Where They Differ: Subtle Distinctions
Despite their shared properties, squares and rectangles are not identical. The key difference lies in the length of their sides:
1. Side Lengths: The Defining Distinction
In a square, all four sides are of equal length. This equal-sided nature is what distinguishes a square from other quadrilaterals. A square is a special case of a rectangle, a perfect and symmetrical form.
A rectangle, on the other hand, has only its opposite sides of equal length. This means that while opposite sides are equal, the adjacent sides can be of different lengths. This flexibility in side lengths is what allows rectangles to take on a wide variety of shapes and proportions.
2. Symmetry: A Square's Special Attribute
Squares exhibit higher levels of symmetry compared to rectangles. A square possesses both rotational and reflectional symmetry. It can be rotated 90, 180, and 270 degrees and still look identical. Similarly, it can be reflected across multiple axes and maintain its original form. Rectangles, while possessing reflectional symmetry along their axes of symmetry, lack the rotational symmetry of a square. They can only be rotated 180 degrees to appear identical.
3. Area and Perimeter Calculations: Formulas and Applications
While both shapes have formulas for calculating their area and perimeter, the formulas for a square are simpler due to its equal side lengths.
-
Square:
- Area: side * side (side²)
- Perimeter: 4 * side
-
Rectangle:
- Area: length * width
- Perimeter: 2 * (length + width)
The simpler formula for a square highlights the mathematical elegance and efficiency inherent in its symmetrical nature. The rectangle's formula, requiring both length and width, reflects its greater variability in shape and size.
Real-World Applications: Squares and Rectangles in Action
Squares and rectangles, due to their inherent stability and simplicity, find applications in countless aspects of our lives:
1. Architecture and Construction: Building Blocks of Structures
From the foundations of buildings to the designs of rooms and windows, squares and rectangles are the building blocks of architecture. Their right angles provide stability, making them ideal for creating sturdy and durable structures. The use of these shapes ensures that walls remain perpendicular to the ground, ensuring the overall integrity of the building.
2. Design and Art: Creating Visual Harmony
In graphic design, art, and even photography, the shapes create a sense of order and balance. The familiar proportions of rectangles are often used in layouts, creating visual harmony and readability. The use of squares often suggests stability and symmetry.
3. Manufacturing and Industry: Precision and Efficiency
In manufacturing, squares and rectangles are crucial for producing precise and consistent products. From cutting materials to assembling components, the precision of these shapes ensures accurate and reliable production. The use of these shapes allows for streamlined manufacturing processes, optimizing efficiency and reducing waste.
4. Everyday Objects: Practical and Functional Forms
Many everyday objects embody these shapes, from books and screens to boxes and tiles. Their simplicity and practicality make them ideal forms for various everyday items, demonstrating their importance in our daily lives.
Conclusion: A Unified Yet Diversified Family
In conclusion, squares and rectangles, while distinct geometric figures, share many fundamental properties that define them as quadrilaterals. Their shared attributes, including parallel sides, equal opposite sides, right angles, and bisecting diagonals, highlight their mathematical relationship. However, the key difference lies in the length of their sides, with the square's equal sides setting it apart from the rectangle’s variable side lengths. Understanding these similarities and differences provides insight into the practical applications and mathematical significance of these fundamental geometric shapes in various fields. Their widespread use in architecture, design, manufacturing, and countless everyday objects underscores their enduring importance and practical relevance. The elegance of their shared properties and the subtle distinction between a square and a rectangle reveal the beauty and versatility of fundamental geometric forms.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 15 And 24
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Factor Of 4 And 9
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Multiples Of 30
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 40 Percent Of 32
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Potassium
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Squares And Rectangles Alike . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
