Fossil Fuels Are Classified As Non Renewable Because They
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 7 min read
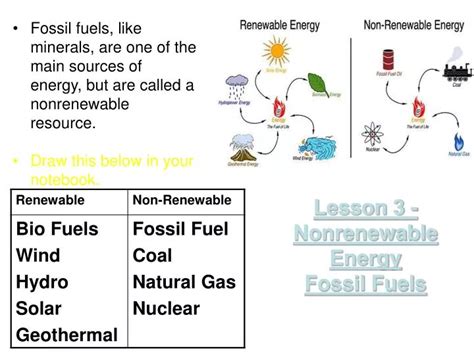
Table of Contents
- Fossil Fuels Are Classified As Non Renewable Because They
- Table of Contents
- Fossil Fuels Are Classified as Non-Renewable Because They… Take Millions of Years to Form
- The Geological Processes Behind Fossil Fuel Formation: A Slow and Steady Process
- Coal Formation: The Carbonization of Ancient Plants
- Oil and Natural Gas Formation: The Transformation of Marine Organisms
- The Time Factor: Why "Non-Renewable" is More Than Just a Label
- The Implications of Non-Renewable Fossil Fuels
- Climate Change: The Unmistakable Link
- Air and Water Pollution: Immediate Health Impacts
- Energy Security and Geopolitical Instability
- Transitioning to a Sustainable Future: The Urgency of Renewable Energy
- Renewable Energy Sources: A Diverse Portfolio
- Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
- Policy and Infrastructure Support
- Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Energy Future
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Fossil Fuels Are Classified as Non-Renewable Because They… Take Millions of Years to Form
Fossil fuels are a cornerstone of modern civilization, powering our transportation, industries, and homes. However, their finite nature poses a significant challenge to our future. The classification of fossil fuels as non-renewable resources stems from the incredibly long timeframe required for their formation—a process vastly exceeding human lifespans and even the timescale of recorded human history. This article delves deep into the reasons behind this classification, exploring the geological processes involved in fossil fuel creation, the implications of their non-renewable nature, and the urgent need for sustainable alternatives.
The Geological Processes Behind Fossil Fuel Formation: A Slow and Steady Process
The term "fossil fuels" itself hints at their origin: the fossilized remains of ancient organisms. These fuels—coal, oil (crude petroleum), and natural gas—are formed over millions of years through a complex interplay of geological processes. Understanding these processes is crucial to grasping why they are considered non-renewable.
Coal Formation: The Carbonization of Ancient Plants
Coal, the oldest fossil fuel, originates from vast, ancient swamps and forests. Millions of years ago, lush vegetation thrived in these environments. When these plants died, they sank into the oxygen-poor waters and sediments of swamps and bogs. The lack of oxygen prevented complete decomposition, allowing the organic matter to accumulate. Over time, layers of sediment buried these organic deposits, subjecting them to increasing pressure and heat.
This process, known as carbonization, gradually transformed the plant material into peat, then lignite (brown coal), sub-bituminous coal, bituminous coal (the most common type), and finally anthracite (the hardest and highest-grade coal). Each stage represents an increasing degree of carbon concentration, resulting from the loss of volatile compounds like water and hydrogen under intense pressure and heat. The entire process can take tens of millions of years, and the resulting coal seams are often found deep underground.
Oil and Natural Gas Formation: The Transformation of Marine Organisms
Oil and natural gas, primarily composed of hydrocarbons, originate from the remains of microscopic marine organisms—plankton and algae. These organisms, abundant in ancient oceans, died and sank to the seafloor. Similar to coal formation, the lack of oxygen in the deep-sea environment prevented their complete decay. Layers of sediment gradually buried these organic-rich deposits, again subjected to immense pressure and heat over millions of years.
Under these conditions, the organic matter underwent a complex series of chemical transformations. The process, known as catagenesis, involves the breakdown of complex organic molecules into simpler hydrocarbon molecules—the building blocks of oil and natural gas. These hydrocarbons then migrated through permeable rock layers, eventually accumulating in porous reservoir rocks, often trapped beneath impermeable layers like shale. The entire process from the deposition of organic matter to the formation of commercially viable oil and gas reserves can easily span tens of millions of years.
The Time Factor: Why "Non-Renewable" is More Than Just a Label
The sheer time scale involved in the formation of fossil fuels is the primary reason for their non-renewable classification. The geological processes described above—carbonization and catagenesis—are exceedingly slow. While new organic matter is continuously being produced, the rate of formation is dwarfed by the rate of consumption.
The rate of consumption far exceeds the rate of natural replenishment. Humanity’s current extraction and usage of fossil fuels are depleting these resources at an alarming rate, far faster than the geological processes can replace them. To put this in perspective, the formation of a single barrel of oil can take millions of years, while we consume millions of barrels daily.
This imbalance is not just a theoretical concern; it’s a stark reality with far-reaching consequences. The finite nature of fossil fuels leads to:
- Resource depletion: Eventually, accessible reserves will be exhausted, leading to scarcity and price volatility.
- Geopolitical instability: Control over dwindling fossil fuel reserves can become a source of conflict and tension between nations.
- Environmental damage: The extraction, processing, and combustion of fossil fuels contribute significantly to environmental pollution, including air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction.
The Implications of Non-Renewable Fossil Fuels
The non-renewable nature of fossil fuels necessitates a fundamental shift in our energy paradigm. Continued reliance on these resources poses significant threats to both our environment and our long-term energy security. The consequences of neglecting this reality are multifaceted and profound.
Climate Change: The Unmistakable Link
The burning of fossil fuels is the primary driver of anthropogenic (human-caused) climate change. The release of massive amounts of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), into the atmosphere traps heat, leading to a global temperature increase and a cascade of related environmental problems, including:
- Rising sea levels: Melting glaciers and thermal expansion of seawater contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme weather events: Climate change intensifies extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, floods, and heatwaves, causing widespread damage and displacement.
- Ocean acidification: Increased CO2 absorption by the oceans leads to ocean acidification, harming marine life and ecosystems.
- Biodiversity loss: Changes in climate and habitat disrupt ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and the extinction of species.
Air and Water Pollution: Immediate Health Impacts
Beyond climate change, the extraction, processing, and combustion of fossil fuels cause significant air and water pollution. Air pollution contributes to respiratory illnesses and other health problems, while water pollution contaminates drinking water sources and harms aquatic life. The environmental damage associated with fossil fuel extraction, such as oil spills and coal mining, further exacerbates these issues.
Energy Security and Geopolitical Instability
Our dependence on fossil fuels for energy also creates vulnerabilities in energy security. Geopolitical factors, such as conflicts and trade disputes, can disrupt the supply of fossil fuels, impacting energy prices and overall economic stability. Diversifying our energy sources and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels are crucial for enhancing energy security.
Transitioning to a Sustainable Future: The Urgency of Renewable Energy
The non-renewable nature of fossil fuels necessitates a decisive shift towards sustainable energy alternatives. The transition to renewable energy sources is not merely an option; it’s a necessity for safeguarding our environment, ensuring our energy security, and promoting global stability.
Renewable Energy Sources: A Diverse Portfolio
Several renewable energy sources can effectively replace fossil fuels. These include:
- Solar energy: Harnessing the sun’s energy through photovoltaic cells or concentrated solar power plants is a clean and abundant source of electricity.
- Wind energy: Wind turbines capture wind energy to generate electricity, particularly effective in areas with consistent winds.
- Hydropower: Using the energy of flowing water to generate electricity is a mature technology, but its potential is limited by geographical constraints.
- Geothermal energy: Utilizing the Earth's internal heat to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling is sustainable and reliable.
- Biomass energy: Burning organic matter, such as wood or agricultural waste, to generate energy can be sustainable if managed properly.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
Technological advancements are continually improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy technologies. Innovations in battery storage, smart grids, and energy efficiency are also crucial for facilitating the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Policy and Infrastructure Support
Government policies and investments in renewable energy infrastructure are essential for driving the transition. Incentives for renewable energy development, carbon pricing mechanisms, and regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions can accelerate the shift away from fossil fuels.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Energy Future
The classification of fossil fuels as non-renewable resources is not a matter of debate. The geological processes involved in their formation take millions of years, making their replenishment far slower than our rate of consumption. Continued dependence on these resources has profound implications for our environment, our health, and our future. The urgent need to transition to sustainable energy alternatives is undeniable. Embracing renewable energy sources, coupled with technological advancements and supportive policies, is essential for creating a cleaner, healthier, and more secure future for generations to come. The time for decisive action is now; the future depends on it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 8 And 2
Apr 04, 2025
-
Define Conditions Under Which Linear Momentum Is Conserved
Apr 04, 2025
-
An Example Of An Unbalanced Force
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Mitotic Spindle Is Composed Of
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 3
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fossil Fuels Are Classified As Non Renewable Because They . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
