Formula For Lateral Surface Area Of A Rectangular Prism
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
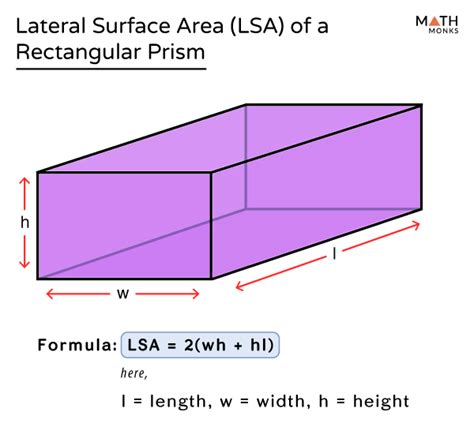
Table of Contents
The Comprehensive Guide to the Lateral Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The rectangular prism, a three-dimensional solid with six rectangular faces, is a fundamental shape in geometry. Understanding its properties, particularly its surface area, is crucial in various fields, from architecture and engineering to packaging and design. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the formula for calculating the lateral surface area of a rectangular prism, exploring its derivation, applications, and practical examples. We'll also look at how this concept connects to other geometrical concepts and problem-solving techniques.
Understanding the Rectangular Prism
Before diving into the formula, let's establish a clear understanding of a rectangular prism. It's a solid shape characterized by:
- Six rectangular faces: These faces are parallel to each other in opposite pairs.
- Twelve edges: These are the line segments where the faces meet.
- Eight vertices: These are the points where the edges intersect.
- Right angles: All angles formed by the edges are right angles (90 degrees).
Rectangular prisms are also known as cuboids. A special case of a rectangular prism is a cube, where all six faces are congruent squares.
Defining Lateral Surface Area
The total surface area of a rectangular prism encompasses the area of all six faces. However, the lateral surface area focuses specifically on the area of the four vertical faces – excluding the top and bottom faces. Imagine wrapping a rectangular box with wrapping paper; the lateral surface area is the amount of paper needed to cover the sides only, not the top or bottom.
The Formula for Lateral Surface Area
The formula for calculating the lateral surface area (LSA) of a rectangular prism is elegantly simple:
LSA = 2h(l + w)
Where:
- LSA represents the lateral surface area.
- h represents the height of the rectangular prism.
- l represents the length of the rectangular prism.
- w represents the width of the rectangular prism.
Derivation of the Formula
The formula isn't arbitrarily chosen; it's derived directly from the properties of rectangles. Let's visualize the four lateral faces:
- Two faces have dimensions h x l. Their combined area is 2 * h * l.
- Two faces have dimensions h x w. Their combined area is 2 * h * w.
Adding these areas together gives us:
2hl + 2hw = 2h(l + w)
This concisely represents the total area of the four lateral faces, hence the formula for the lateral surface area.
Practical Applications of the Lateral Surface Area Formula
The formula for lateral surface area finds applications in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Packaging and Shipping: Calculating the amount of material needed for the sides of boxes is crucial for packaging design and cost optimization. Knowing the LSA allows manufacturers to minimize material waste and improve efficiency.
-
Construction and Architecture: Architects and engineers use LSA calculations for estimating the amount of materials needed for exterior walls of buildings, providing crucial information for budgeting and material procurement. This is especially important in projects involving complex shapes that require breaking down into simpler rectangular prisms.
-
Civil Engineering: LSA calculations are useful in designing retaining walls, culverts, and other structures involving rectangular prisms. Knowing the surface area helps in estimating the amount of concrete or other materials needed for these projects.
-
Manufacturing and Fabrication: The LSA formula is essential in determining the surface area to be painted, coated, or treated in manufacturing processes. Accurate calculations ensure efficient use of materials and prevent wastage.
-
3D Printing and Modeling: In 3D modeling and additive manufacturing, determining the LSA is crucial for calculating the volume of material required and the time taken to complete a print job. This allows for better resource allocation and scheduling.
Solving Problems Involving Lateral Surface Area
Let's work through a few examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1:
A rectangular prism has a height of 10 cm, a length of 5 cm, and a width of 3 cm. Calculate its lateral surface area.
Using the formula:
LSA = 2h(l + w) = 2 * 10 cm * (5 cm + 3 cm) = 2 * 10 cm * 8 cm = 160 cm²
Example 2:
A storage container in the shape of a rectangular prism has a height of 2 meters and a lateral surface area of 24 square meters. If the length is twice the width, find the dimensions of the container.
Let's represent the width as 'x'. The length will be '2x'.
LSA = 2h(l + w) => 24 m² = 2 * 2 m * (2x + x)
24 m² = 4 m * 3x
6 m = 3x
x = 2 m (width)
2x = 4 m (length)
Example 3: A Real-World Scenario
A building contractor needs to estimate the cost of painting the exterior walls of a newly constructed building. The building's exterior walls form a rectangular prism with a height of 12 meters, a length of 20 meters, and a width of 15 meters. The cost of paint per square meter is $5. What is the total cost of painting the exterior walls?
First, calculate the lateral surface area:
LSA = 2h(l + w) = 2 * 12 m * (20 m + 15 m) = 24 m * 35 m = 840 m²
Next, calculate the total cost:
Total Cost = LSA * Cost per m² = 840 m² * $5/m² = $4200
Connecting Lateral Surface Area to Other Concepts
The concept of lateral surface area is intrinsically linked to other geometrical concepts:
-
Volume: While distinct, both LSA and volume calculations utilize the dimensions of the rectangular prism (length, width, and height). Understanding both is crucial in various applications, like determining the amount of material needed for a container, considering both its capacity and surface area.
-
Total Surface Area: The total surface area is simply the LSA plus the area of the top and bottom faces (2lw). This comprehensive measure is often necessary when considering the total material needed for a complete enclosure.
-
Nets: Visualizing the net of a rectangular prism (a 2D representation of the unfolded 3D shape) helps in understanding the individual faces and calculating their areas, contributing to a better grasp of the LSA calculation.
-
Surface Area of Other Shapes: The concept of lateral surface area extends to other 3D shapes such as cylinders and cones, although the formulas differ depending on the shape's properties.
Advanced Applications and Problem-Solving Techniques
Understanding the formula for lateral surface area is the first step. More complex problems might involve:
-
Composite Shapes: Dealing with structures that combine several rectangular prisms requires a systematic approach of breaking down the composite shape into individual rectangular prisms, calculating their individual LSA, and then summing them.
-
Optimization Problems: In scenarios where cost or material usage needs to be minimized, understanding LSA is vital in solving optimization problems related to dimensions and material use.
-
Calculus Applications: In advanced applications, concepts like integration can be used to determine the LSA of complex shapes that aren’t strictly rectangular prisms.
Conclusion
The formula for the lateral surface area of a rectangular prism – LSA = 2h(l + w) – is a fundamental concept with widespread practical applications across various fields. Mastering this formula and its derivation allows for efficient problem-solving in diverse contexts, from everyday tasks like calculating packaging needs to complex engineering projects involving structural design and resource management. By understanding the underlying principles and their connections to other geometrical concepts, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for tackling various mathematical challenges and real-world problems. Remember to always double-check your units and measurements to ensure accurate and reliable calculations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 25 And 35
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Are All The Factors Of 11
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Factors Of 25
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Much Electrons Does Sodium Have
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Is Larger 3 8 Or 1 2
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Formula For Lateral Surface Area Of A Rectangular Prism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
