Explain The Function Of A Vacuole In Plant Cells.
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
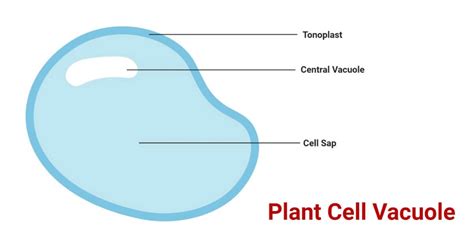
Table of Contents
The Crucial Role of Vacuoles in Plant Cell Function
Plant cells, the fundamental building blocks of the plant kingdom, possess a remarkable array of organelles that contribute to their unique characteristics and survival. Among these, the vacuole stands out as a particularly significant component, playing a multifaceted role in maintaining cell structure, regulating metabolism, and ensuring the overall health and functionality of the plant. This article delves deep into the intricacies of the plant cell vacuole, exploring its diverse functions and the profound impact it has on plant life.
What is a Plant Cell Vacuole?
A vacuole, in essence, is a membrane-bound organelle present in both plant and animal cells, but its prominence and function are vastly different in plants. In plant cells, the vacuole often occupies a substantial portion of the cell's volume, sometimes exceeding 90% in mature cells. This large, central vacuole is a fluid-filled sac enclosed by a single membrane called the tonoplast. The fluid within the vacuole, known as cell sap, is a complex solution containing a variety of substances, including water, dissolved salts, sugars, pigments, proteins, and waste products.
The Tonoplast: A Selective Barrier
The tonoplast isn't just a passive container; it's a highly selective membrane that plays a critical role in regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the vacuole. This selectivity is vital for maintaining the cell's internal environment and controlling the concentration of various substances within the vacuole and the cytoplasm. The tonoplast contains various protein pumps and channels that facilitate the active and passive transport of ions, metabolites, and other molecules. This precise control over the movement of substances is fundamental to many of the vacuole's key functions.
Key Functions of the Plant Cell Vacuole
The plant cell vacuole is far more than a simple storage container. Its functions are diverse and crucial for the plant's survival and overall well-being. Let's examine some of its most prominent roles:
1. Maintaining Turgor Pressure: The Foundation of Plant Structure
One of the most crucial functions of the vacuole is its contribution to turgor pressure. Turgor pressure is the hydrostatic pressure exerted by the cell contents against the cell wall. This pressure is generated primarily by the osmotic influx of water into the vacuole. As water enters the vacuole, it expands, pushing against the cell wall and creating turgor pressure. This pressure is vital for maintaining the plant's overall rigidity and structural integrity. Without adequate turgor pressure, plants would wilt and lose their shape.
Think of it like this: Imagine a balloon filled with water inside a rigid container. The water pressure against the container walls is analogous to turgor pressure. This pressure is essential for maintaining the balloon's shape and preventing it from collapsing. Similarly, turgor pressure keeps plant cells firm and upright.
2. Storage of Nutrients and Metabolites: A Cellular Warehouse
The vacuole serves as a vital storage compartment for a wide range of nutrients and metabolites. These include:
- Sugars: Vacuoles store sugars like sucrose and glucose, providing a readily available energy source for the cell. This stored energy is crucial during periods of low photosynthetic activity, such as at night or during unfavorable weather conditions.
- Amino acids and proteins: The vacuole can store amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and even proteins themselves. This storage ensures a ready supply of these essential molecules for cellular processes.
- Organic acids: Many organic acids, such as malic acid and citric acid, are stored in vacuoles. These acids play roles in various metabolic processes and can also contribute to the plant's overall pH balance.
- Pigments: The vibrant colors of many fruits and flowers are due to the presence of pigments stored in their vacuoles. Anthocyanins, for example, are responsible for the red, purple, and blue colors found in many plants. These pigments attract pollinators and seed dispersers.
3. Waste Product Sequestration: Detoxification and Protection
The vacuole acts as a central repository for waste products that could be harmful to the cell if left in the cytoplasm. These waste products are safely stored within the vacuole, preventing their interference with cellular processes. This sequestration is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and protecting the cell from potential damage.
4. Maintaining Cellular pH: Balancing the Internal Environment
The vacuole plays a critical role in maintaining the cell's internal pH. The concentration of various ions and organic acids within the vacuole helps buffer changes in pH, ensuring a stable cellular environment suitable for optimal enzyme activity and overall cellular function.
5. Hydrolysis and Recycling: Breaking Down and Reusing Components
The vacuole participates in the hydrolysis of macromolecules. The vacuole contains various hydrolytic enzymes that break down complex molecules into smaller, reusable components. This process of recycling is crucial for resource management within the plant cell.
6. Defense Against Pathogens: A Cellular Fortress
The vacuole can also contribute to plant defense against pathogens. Some vacuoles store defensive compounds, such as antimicrobial proteins and toxins, which can inhibit the growth of invading microorganisms. This internal defense system is a crucial component of the plant's overall immunity.
The Vacuole's Role in Plant Growth and Development
The vacuole's influence extends beyond its immediate cellular functions; it significantly impacts the plant's growth and development:
- Cell Expansion: The accumulation of water in the vacuole is a major driving force behind cell expansion during plant growth. As the vacuole swells, it pushes against the cell wall, causing the cell to enlarge. This cell expansion is essential for plant growth and development.
- Differentiation: The vacuole plays a role in cell differentiation, the process by which cells become specialized for specific functions. The accumulation of specific substances within the vacuole can influence the cell's fate and development.
- Senescence: During plant senescence, or aging, the vacuole plays a role in the breakdown of cellular components and the recycling of resources. The degradation of cellular materials within the vacuole helps the plant recycle nutrients and prepare for the eventual death of its cells.
Interplay with Other Organelles: A Coordinated Effort
The vacuole doesn't function in isolation; it interacts closely with other organelles within the plant cell, forming a complex network of communication and cooperation. For example, it works in conjunction with the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins and other molecules.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of vacuolar function. Scientists are employing advanced techniques like microscopy and proteomics to gain deeper insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying vacuole biogenesis, transport processes, and its multifaceted roles in plant growth, development, and stress response. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to strategies for improving crop yields, enhancing stress tolerance, and developing new approaches to plant biotechnology.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of the Plant Cell
The vacuole is an often-underappreciated but truly indispensable organelle within the plant cell. Its diverse functions, ranging from maintaining turgor pressure and storing nutrients to detoxifying waste products and contributing to plant defense, highlight its crucial role in the life of a plant. Further research will undoubtedly reveal even more about this remarkable organelle and its profound impact on the plant kingdom. By understanding the complexities of the vacuole, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that underpin plant life and its vital role in our ecosystem. This knowledge is also crucial for developing sustainable agricultural practices and improving crop resilience in the face of climate change and other environmental challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Three Examples Of Chemical Changes
Mar 31, 2025
-
Difference Between Genetic Map And Physical Map
Mar 31, 2025
-
Caso4 Xh2o Loses 6 2 Of Water
Mar 31, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 36
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Found In Prokaryotic Cells
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain The Function Of A Vacuole In Plant Cells. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
