Does The Orthocenter Have To Be Inside The Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
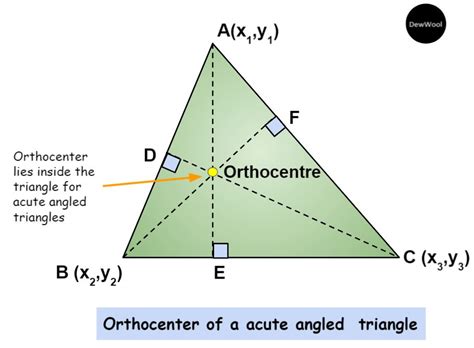
Table of Contents
Does the Orthocenter Have to Be Inside the Triangle? Exploring the Geometry of Orthocenters
The orthocenter, a fascinating point within (or sometimes outside!) a triangle, holds a unique position in geometry. Defined as the intersection of a triangle's altitudes, its location relative to the triangle itself is a key area of study. This article delves deep into the question: Does the orthocenter have to be inside the triangle? The short answer is no, and understanding why requires exploring the different types of triangles and the behavior of their altitudes.
Understanding the Orthocenter and Altitudes
Before we delve into the intricacies of orthocenter placement, let's establish a solid foundation. The orthocenter of a triangle is the point where the three altitudes of the triangle intersect. An altitude of a triangle is a line segment from a vertex perpendicular to the opposite side (or its extension). It's crucial to understand that the altitude doesn't necessarily fall within the triangle; it can extend beyond the triangle's sides.
Constructing Altitudes and Identifying the Orthocenter
To locate the orthocenter, you'd typically construct the altitudes one by one. Consider a triangle ABC:
- Altitude from Vertex A: Draw a line segment from vertex A perpendicular to side BC.
- Altitude from Vertex B: Draw a line segment from vertex B perpendicular to side AC.
- Altitude from Vertex C: Draw a line segment from vertex C perpendicular to side AB.
The point where these three altitudes intersect is the orthocenter, often denoted as H. This process holds true for all triangles, regardless of their shape or size.
Orthocenter Location: Inside, Outside, or On?
The crucial aspect is that the orthocenter's position isn't fixed within the triangle. Its location is entirely dependent on the type of triangle:
1. Acute Triangles: Orthocenter Inside
In an acute triangle (all angles less than 90°), the orthocenter lies comfortably inside the triangle. All three altitudes intersect within the confines of the triangle's vertices and sides. This is the most intuitive and commonly encountered scenario. The altitudes are entirely contained within the triangle, resulting in an orthocenter neatly positioned within its boundaries.
2. Right Triangles: Orthocenter at a Vertex
A right triangle presents a special case. One of its angles is exactly 90°. In a right-angled triangle, two of the altitudes are the legs (sides forming the right angle) themselves. The third altitude, drawn from the right angle vertex, intersects the hypotenuse at a point which is precisely the orthocenter. In essence, the orthocenter coincides with the right-angled vertex of the triangle. It lies on the triangle, rather than strictly inside or outside.
3. Obtuse Triangles: Orthocenter Outside
The most interesting situation arises with obtuse triangles (one angle greater than 90°). In an obtuse triangle, the orthocenter resides outside the triangle. The altitudes from the two acute angles extend beyond the opposite sides to intersect, forming the orthocenter beyond the triangle's boundaries. This is because the altitudes drawn from the acute angles extend outside the triangle before intersecting. This external location of the orthocenter adds a layer of complexity and intrigue to the geometric properties of obtuse triangles.
Why the Orthocenter's Position Varies
The location of the orthocenter is directly tied to the angles of the triangle. The altitudes' inclination relative to the triangle's sides dictates the orthocenter's position. In acute triangles, the altitudes intersect within the triangle's interior because the angles are all less than 90°. In obtuse triangles, the obtuse angle forces the altitudes to intersect outside the triangle's boundaries. The right-angled triangle acts as a transition point, where the orthocenter shifts from inside to a vertex.
Exploring the Properties of the Orthocenter
The orthocenter possesses some remarkable properties, regardless of its position:
- Centroid Connection: The orthocenter (H), centroid (G), and circumcenter (O) are collinear, lying on a single line known as the Euler line. This line has significant implications in triangle geometry.
- Distance Relationships: Specific distance relationships exist between the orthocenter and other notable points within the triangle, such as the vertices and circumcenter.
- Reflection Properties: The orthocenter plays a crucial role in various reflection properties related to the triangle's altitudes and sides.
Applications and Further Exploration
The orthocenter's position and properties are not merely abstract concepts; they have practical applications in various fields, including:
- Computer Graphics: Determining the orthocenter is crucial for certain geometric transformations and calculations in computer graphics.
- Engineering and Architecture: Understanding spatial relationships and geometric constructions is essential in engineering design and architectural planning.
- Advanced Geometry: The orthocenter forms a foundation for exploring more advanced geometric concepts and theorems.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Point in Triangle Geometry
The orthocenter's location is not fixed; it's dynamically determined by the triangle's angles. While it resides within acute triangles, it sits on a vertex for right triangles, and extends outside obtuse triangles. This variability makes the orthocenter a fascinating point to study, revealing further insights into the rich world of triangle geometry. Its properties and interactions with other notable points within the triangle open avenues for deeper exploration and a better understanding of geometric principles. The orthocenter isn't just a point; it's a key that unlocks many fascinating geometric secrets. Understanding its behavior, therefore, is crucial for anyone interested in a more complete understanding of triangle geometry and its numerous applications. Further exploration of its relationships with other triangle centers such as the centroid and circumcenter leads to even more fascinating and intricate aspects of geometry. Continued study will undoubtedly reveal further properties and applications of this dynamic and essential point within a triangle.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Base Of A Parallelogram
Mar 09, 2025
-
Fish That Does Not Have Scales
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is Sugar A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Mar 09, 2025
-
Unit Of Torque In Si System
Mar 09, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 2 And 12
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Does The Orthocenter Have To Be Inside The Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
