Is Sugar A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
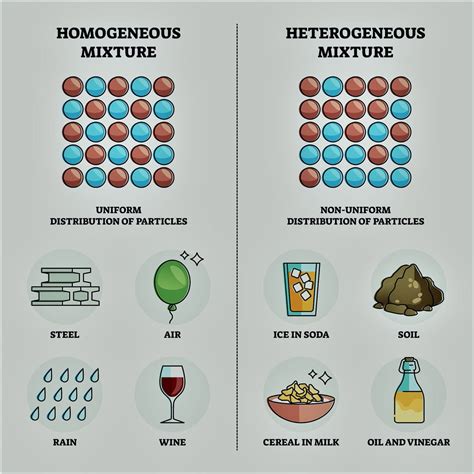
Table of Contents
Is Sugar a Pure Substance or a Mixture? A Deep Dive into Sucrose
The seemingly simple question, "Is sugar a pure substance or a mixture?" opens a fascinating exploration into the world of chemistry, encompassing concepts like purity, compounds, and the complexities of everyday materials. While table sugar might appear uniform, its classification requires a closer examination of its composition and properties. This article delves into the scientific definition of pure substances and mixtures, explores the chemical makeup of sugar, and ultimately answers the question definitively. We'll also look at different types of sugars and how their composition affects their classification.
Understanding Pure Substances and Mixtures
Before we classify sugar, it's crucial to define our terms. In chemistry, pure substances are materials composed of only one type of atom or molecule. They have a consistent and unchanging composition and a fixed set of properties. Examples include elements like gold (Au) or oxygen (O2), and compounds like water (H2O) or sodium chloride (NaCl). Pure substances have a defined melting point and boiling point.
Conversely, mixtures consist of two or more substances physically combined but not chemically bonded. Mixtures retain the individual properties of their components and can have varying compositions. Think of saltwater, where the salt (NaCl) and water (H2O) exist separately, or air, a mixture of various gases. Mixtures typically do not have sharp melting or boiling points.
The Chemical Composition of Table Sugar
Table sugar, also known as sucrose, is a pure substance—specifically, a compound. It's not a mixture of different sugars, but rather a single type of molecule with a specific chemical formula: C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁. This formula indicates that each molecule of sucrose is composed of 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms, arranged in a specific, well-defined structure.
This consistent molecular structure is the key to understanding why sucrose is classified as a pure substance. No matter where you source your table sugar – from sugarcane, sugar beets, or a supermarket shelf – the chemical composition remains the same. Each crystal is composed of identical sucrose molecules, strongly bound together by intermolecular forces. This uniformity in composition results in consistent properties, like a defined melting point (around 186°C) and sweetness.
Distinguishing Sugar from Mixtures
It's important to contrast sucrose with other sugary substances that are indeed mixtures. For instance, honey is a complex mixture of various sugars (fructose, glucose, sucrose), water, enzymes, and other organic compounds. The proportions of these components can vary depending on the floral source and processing. Similarly, maple syrup contains several sugars and other flavor compounds, resulting in a mixture rather than a pure substance. These mixtures don't have a consistent composition and exhibit a range of properties reflecting the contributions of their individual components.
The key difference lies in the chemical bonding. In a pure substance like sucrose, all the molecules are identical, held together by strong chemical bonds within the molecule and weaker intermolecular forces between molecules. In a mixture, the components remain distinct entities, with no chemical bonding between them.
Refining Sugar: The Journey from Mixture to Pure Substance
The sugar we use in our daily lives is often extracted from sugarcane or sugar beets. Initially, the raw material contains sucrose mixed with various impurities, such as water, fibers, and other plant components. The process of refining sugar involves a series of steps aimed at separating the sucrose from these impurities.
These processes include crushing the raw material, dissolving the sugar, filtration to remove solids, and crystallization to obtain pure sucrose crystals. Each step refines the mixture, gradually increasing the concentration of sucrose and removing impurities. The end product, refined table sugar, is considerably purer than the initial raw material.
Types of Sugars and Their Classification
While sucrose is a pure substance, it's crucial to acknowledge the existence of other types of sugars. These include:
-
Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): A simple sugar, also known as dextrose, found naturally in fruits and honey. Glucose is a pure substance.
-
Fructose (C₆H₁₂O₆): Another simple sugar, known as fruit sugar, also found in fruits and honey. It's a pure substance.
-
Lactose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁): Milk sugar, a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose. Lactose is also a pure substance.
Although these are all individually pure substances, a mixture can arise when they are combined. For example, a solution containing glucose, fructose, and sucrose would constitute a mixture, despite each sugar component being a pure substance in its isolated form.
Beyond Table Sugar: Other Aspects of Purity
The concept of purity in substances is context-dependent. While refined table sugar is considered a pure substance in a practical sense, it may contain trace amounts of other substances. The degree of purity is often specified by standards that define acceptable limits for impurities. For instance, pharmaceutical-grade sucrose has a far higher level of purity compared to table sugar intended for culinary purposes.
Conclusion: Sugar's Purity Confirmed
To conclude, table sugar (sucrose) is indeed a pure substance, a crystalline compound with a consistent chemical formula (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁). This composition is independent of its source or method of refinement. While the raw material might be a mixture, refining processes effectively isolate and purify the sucrose. The purity of a substance often depends on the context and acceptable thresholds for impurities, as highlighted by the differences between food-grade and pharmaceutical-grade materials. However, in its purest form, as found in granulated sugar, sucrose is definitively a pure compound, not a mixture. Understanding this distinction is vital for appreciating the chemical nature of common everyday materials.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons In P
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Composition Of Sulfur In H2so4
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Waste Products Of Cellular Respiration Include
Mar 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 3 5 7
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Spell 90 In English
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Sugar A Pure Substance Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
