Lowest Common Multiple Of 2 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 4 min read
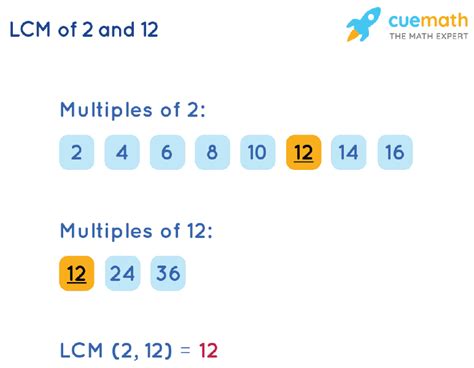
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 2 and 12: A Comprehensive Guide
The lowest common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to find the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. This article will delve deep into finding the LCM of 2 and 12, exploring multiple methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the broader context of LCMs and their significance in mathematics.
Understanding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific example of 2 and 12, let's solidify our understanding of the LCM. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into without leaving a remainder.
For instance, consider the numbers 4 and 6. The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20... and the multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24... The common multiples are 12, 24, 36... The smallest of these common multiples is 12, therefore, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method to find the LCM, especially for smaller numbers like 2 and 12, is by listing the multiples of each number.
Multiples of 2:
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
Multiples of 12:
12, 24, 36, 48, 60...
By comparing the lists, we can clearly see that the smallest common multiple of 2 and 12 is 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the concept. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors. Prime factors are prime numbers (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves) that multiply together to give the original number.
Prime Factorization of 2:
2 = 2¹ (2 is itself a prime number)
Prime Factorization of 12:
12 = 2² × 3¹
Now, to find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Multiply these highest powers together: 2² × 3¹ = 4 × 3 = 12
Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 12 is 12. This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or finding the LCM of more than two numbers.
Method 3: Using the Formula (LCM and GCD Relationship)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers are intimately related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
First, let's find the GCD of 2 and 12. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 2 and 12 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(2, 12) = 2.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(2, 12) × GCD(2, 12) = 2 × 12
LCM(2, 12) × 2 = 24
LCM(2, 12) = 24 / 2 = 12
Why is Understanding LCM Important?
The LCM has numerous applications across various mathematical fields and real-world scenarios:
-
Simplifying Fractions: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial for finding a common denominator. This simplifies the process significantly.
-
Solving Problems Involving Cycles or Periods: LCM is essential for solving problems involving repeating cycles or periods, such as determining when two events will occur simultaneously. For instance, if two buses leave a station at different intervals, the LCM helps determine when they'll depart at the same time again.
-
Scheduling and Planning: In project management and scheduling, LCM can help determine the optimal time intervals for various tasks or events.
-
Music Theory: LCM is used to calculate the least common multiple of different rhythmic patterns in music.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanics, LCM helps in calculating gear ratios for optimal power transmission.
LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, simply include all the prime factors of each number and take the highest power of each. For the listing method, it becomes more tedious, but the principle remains the same. Using the GCD-LCM relationship requires a slightly more complex iterative approach when dealing with multiple numbers.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
The lowest common multiple is a fundamental mathematical concept with far-reaching applications. Understanding how to calculate the LCM efficiently, whether through listing multiples, prime factorization, or the GCD-LCM relationship, is crucial for success in various mathematical endeavors and practical applications. This comprehensive guide has provided multiple methods for determining the LCM of 2 and 12, showcasing the versatility and importance of this essential mathematical tool. By mastering the LCM, you strengthen your mathematical foundation and enhance your problem-solving capabilities across various domains. Remember to practice these methods with different sets of numbers to build your proficiency and confidence in calculating LCMs. The more you practice, the easier it becomes to identify the most efficient method for solving any LCM problem.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Rusting Iron Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Stage Of Mitosis
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Find The Area And Perimeter Of A Triangle
Mar 09, 2025
-
Smallest Particle Of An Element That Retains Its Properties
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Know If A Number Is Divisible By 6
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 2 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
