Different Or Alternative Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
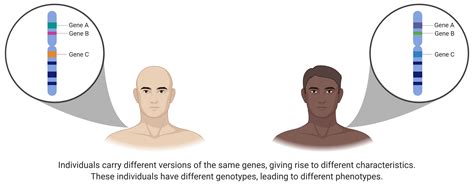
Table of Contents
Different or Alternative Forms of the Same Gene are Called Alleles: A Deep Dive into Genetics
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of life, our genes, is crucial for grasping the complexities of heredity and evolution. Within this intricate world of genetics lies a key concept: alleles. This article delves deep into the definition, types, significance, and impact of alleles on an organism's traits and characteristics. We will explore how these alternative forms of the same gene contribute to genetic diversity and the inheritance of traits across generations.
What are Alleles?
At its core, an allele is one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome. Think of a gene as a recipe for a specific trait, like eye color. An allele is then a specific version of that recipe, such as the recipe for blue eyes or brown eyes. Each gene resides at a specific location on a chromosome called a locus. Alleles occupy the same locus on homologous chromosomes – matching chromosome pairs inherited from each parent.
Understanding the Relationship Between Genes, Alleles, and Chromosomes:
To fully grasp the concept of alleles, let's clarify the relationship between genes, alleles, and chromosomes.
- Chromosome: A long, thread-like structure made up of DNA and proteins that carries genetic information. Humans possess 23 pairs of chromosomes, one set inherited from each parent.
- Gene: A specific segment of DNA located on a chromosome that contains the instructions for building a protein or performing a particular function.
- Allele: Different versions of the same gene. These variations arise due to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence.
For example, the gene for eye color might have several alleles, such as one for brown eyes, one for blue eyes, and one for green eyes. An individual inherits one allele for each gene from each parent, resulting in a pair of alleles for each gene.
Types of Alleles: Exploring Dominant and Recessive Traits
Alleles are categorized based on their influence on phenotype (observable traits) when present in pairs. The most common classification divides them into:
1. Dominant Alleles:
A dominant allele exerts its effect even when paired with a different allele (a recessive allele). It masks the expression of the recessive allele. We represent dominant alleles with uppercase letters (e.g., B for brown eyes). If an individual possesses at least one dominant allele, that dominant trait will be expressed.
2. Recessive Alleles:
A recessive allele only expresses its effect when paired with another identical recessive allele. Its expression is masked by a dominant allele. We usually represent recessive alleles with lowercase letters (e.g., b for blue eyes). An individual needs two copies of the recessive allele to exhibit the recessive trait.
Understanding Genotype and Phenotype:
The combination of alleles an individual inherits for a specific gene is called its genotype. The observable characteristic resulting from that genotype is the phenotype.
For instance:
- BB: Homozygous dominant genotype (brown eyes)
- Bb: Heterozygous genotype (brown eyes, as B is dominant)
- bb: Homozygous recessive genotype (blue eyes)
In this example, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue eyes (b). Both BB and Bb genotypes will result in a brown-eyed phenotype, while only the bb genotype produces a blue-eyed phenotype.
Beyond Simple Dominance: More Complex Allelic Interactions
While the dominant-recessive model is a useful simplification, many traits exhibit more complex interactions between alleles.
1. Incomplete Dominance:
In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant over the other. The heterozygote displays an intermediate phenotype. A classic example is flower color in snapdragons, where a red flower (RR) crossed with a white flower (rr) produces pink flowers (Rr).
2. Codominance:
In codominance, both alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote. There is no blending; both traits are visible. A prime example is the ABO blood group system, where individuals with AB blood type express both A and B antigens.
3. Multiple Alleles:
Many genes have more than two alleles. The ABO blood group system again exemplifies this, featuring three alleles (IA, IB, and i) that determine blood type.
4. Pleiotropy:
Some genes have multiple phenotypic effects, a phenomenon called pleiotropy. A single gene can influence several seemingly unrelated traits. For example, a gene affecting collagen production can impact skin, bones, and joints.
The Significance of Alleles in Genetic Variation and Evolution
Alleles are the cornerstone of genetic variation, which fuels evolution. The variety of alleles within a population increases the adaptability of that population to environmental changes. Individuals with different allele combinations may possess traits that make them better suited to survive and reproduce in specific environments.
The Role of Alleles in Natural Selection:
Natural selection acts upon phenotypes, favoring individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success. The frequency of advantageous alleles increases in a population over time, while less advantageous alleles may decrease or disappear.
Genetic Drift and Allele Frequency:
Random fluctuations in allele frequencies, particularly significant in small populations, are known as genetic drift. These random changes can lead to the loss of some alleles and fixation of others, even if those alleles aren't inherently advantageous or disadvantageous.
Gene Flow and Allele Exchange:
Gene flow, the movement of alleles between populations, influences allele frequencies. Migration and interbreeding introduce new alleles or alter existing allele frequencies, increasing genetic diversity.
Applications and Importance of Understanding Alleles
The understanding of alleles has profound implications across various fields:
1. Medicine:
Genetic testing identifies alleles associated with diseases, allowing for early diagnosis, preventative measures, and personalized medicine approaches. Understanding allele interactions is crucial for developing effective treatments for genetic disorders.
2. Agriculture:
Breeders leverage knowledge of alleles to improve crop yields and disease resistance. They select plants with desirable allele combinations, leading to more productive and resilient crops.
3. Conservation Biology:
Allele frequency analysis helps monitor genetic diversity within endangered species. This information is crucial for designing conservation strategies to maintain genetic health and prevent inbreeding.
4. Forensic Science:
Allele analysis, particularly through DNA fingerprinting techniques, plays a vital role in criminal investigations, paternity testing, and identification of human remains.
Conclusion:
Alleles, the alternative forms of the same gene, are fundamental units of heredity that shape the diversity of life. From simple dominant-recessive interactions to complex patterns of inheritance, alleles drive genetic variation, influencing an organism's traits, shaping evolution, and having significant applications across various fields. A thorough understanding of alleles is paramount for advancements in medicine, agriculture, conservation, and forensic science. Continuous research into allele interactions and their effects on phenotypes will further unlock the secrets of life and pave the way for innovative applications across diverse domains. The study of alleles remains a cornerstone of modern genetics and will undoubtedly continue to yield valuable insights into the complexities of life itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Force Is A Scalar Or Vector Quantity
Apr 05, 2025
-
Are Diagonals Perpendicular In A Parallelogram
Apr 05, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Starts With Thi
Apr 05, 2025
-
Factors Of X 2 2x 3
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 77 Inches
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Different Or Alternative Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
