Diff Between Renewable And Non Renewable
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 7 min read
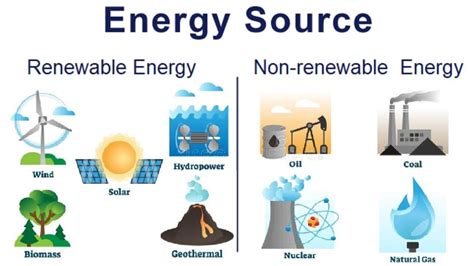
Table of Contents
The Great Divide: Understanding the Difference Between Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy
The world runs on energy. From the electricity powering our devices to the fuel driving our cars, energy is the lifeblood of modern civilization. But the sources of this energy are fundamentally different, categorized into two main groups: renewable and non-renewable. Understanding the crucial distinctions between these energy types is paramount, not just for scientific literacy but for shaping a sustainable future. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the differences, advantages, disadvantages, and environmental impact of both renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished over a relatively short period, making them sustainable and environmentally friendly options. These resources are virtually inexhaustible, constantly regenerating themselves through natural processes. This means their use doesn't deplete the Earth's finite resources. Key characteristics of renewable energy include:
Sustainability: The Core Principle
The core principle behind renewable energy is sustainability. It's about meeting our current energy needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own. This focus on long-term viability contrasts sharply with the finite nature of non-renewable resources.
Diverse Sources: A Multifaceted Approach
Renewable energy encompasses a diverse range of sources, each harnessing different natural processes:
-
Solar Energy: Harnessing the power of the sun through photovoltaic cells (solar panels) that convert sunlight directly into electricity or using concentrated solar power (CSP) to generate heat and electricity. Solar energy is abundant, particularly in sunny regions, and is becoming increasingly cost-effective.
-
Wind Energy: Capturing the kinetic energy of moving air using wind turbines. Wind farms, often located in areas with consistent strong winds, can generate significant amounts of electricity. Wind energy is a clean and sustainable source, but its output can be intermittent, depending on weather conditions.
-
Hydropower: Utilizing the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. Hydroelectric dams are a common method, harnessing the potential energy of water stored behind a dam. Hydropower is a reliable source of renewable energy, but large-scale dam projects can have significant environmental consequences.
-
Geothermal Energy: Tapping into the Earth's internal heat. Geothermal plants utilize steam or hot water from underground reservoirs to generate electricity or provide direct heating. Geothermal energy is a reliable and consistent source, but its geographical limitations restrict its widespread application.
-
Biomass Energy: Burning organic matter, such as wood, crops, or agricultural waste, to produce energy. Biomass energy is a renewable resource as long as the biomass is sustainably harvested and replanted. However, its use can contribute to air pollution if not managed properly.
What is Non-Renewable Energy?
Non-renewable energy sources are derived from finite resources that take millions of years to form. Once these resources are depleted, they are gone for good. The use of non-renewable energy contributes significantly to environmental problems and climate change. Key characteristics include:
Finite Resources: A Limited Supply
The defining characteristic of non-renewable energy is its finite nature. These resources exist in fixed quantities within the Earth's crust, and their extraction and consumption lead to their eventual depletion. This scarcity drives up prices and creates geopolitical instability.
Environmental Impact: A Major Concern
The extraction, processing, and combustion of non-renewable energy sources have severe environmental consequences:
-
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, contributing significantly to climate change.
-
Air Pollution: Combustion also releases other pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, leading to respiratory problems and acid rain.
-
Water Pollution: Oil spills and wastewater from extraction processes contaminate water sources, harming aquatic life and ecosystems.
-
Land Degradation: Mining for coal and other fossil fuels causes significant land degradation, disrupting ecosystems and impacting biodiversity.
Main Sources: Fossil Fuels Dominate
The primary sources of non-renewable energy are:
-
Coal: A solid fossil fuel formed from ancient plant matter. Coal is a relatively abundant and inexpensive energy source, but its combustion releases large amounts of greenhouse gases and pollutants.
-
Oil: A liquid fossil fuel formed from ancient marine organisms. Oil is used for transportation, heating, and manufacturing. Its extraction and processing are associated with substantial environmental risks.
-
Natural Gas: A gaseous fossil fuel consisting mainly of methane. Natural gas is considered a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal and oil, but it still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Nuclear Energy: While not a fossil fuel, nuclear energy relies on uranium, a finite resource. Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear fission, a process that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions but poses risks associated with radioactive waste disposal and potential accidents.
Comparing Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy: A Head-to-Head Analysis
| Feature | Renewable Energy | Non-Renewable Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Naturally replenished (sun, wind, water, etc.) | Finite resources (fossil fuels, uranium) |
| Sustainability | Sustainable, virtually inexhaustible | Unsustainable, depletable |
| Environmental Impact | Generally low environmental impact | Significant greenhouse gas emissions and pollution |
| Cost | Initially higher investment, decreasing costs | Generally lower initial investment, increasing costs |
| Reliability | Intermittent for some sources (wind, solar) | Generally reliable, but subject to supply issues |
| Geopolitical Implications | Reduced dependence on foreign resources | Geopolitical implications due to resource scarcity |
| Energy Security | Enhanced energy security and independence | Vulnerability to supply disruptions and price volatility |
The Environmental Impact: A Crucial Difference
The most significant difference between renewable and non-renewable energy lies in their environmental impact. Renewable energy sources produce minimal or no greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet. Non-renewable energy sources, on the other hand, are the primary drivers of climate change and air pollution. The consequences of continued reliance on fossil fuels are far-reaching, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
Economic Considerations: A Shifting Landscape
While the initial investment for renewable energy technologies can be higher, costs are rapidly decreasing. Furthermore, the long-term economic benefits of renewable energy outweigh those of non-renewable sources, considering the environmental damage costs and the eventual depletion of fossil fuels. The shift toward renewable energy also creates new economic opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
The Future of Energy: A Transition in Progress
The world is undergoing a significant energy transition, shifting from reliance on non-renewable sources to increasingly adopting renewable energy technologies. This transition is driven by environmental concerns, economic factors, and the pursuit of energy security. While challenges remain, including grid integration and intermittency issues, the advancements in renewable energy technology and decreasing costs are paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
The Role of Technological Advancements
Technological innovation plays a crucial role in the advancement of both renewable and non-renewable energy sources. For renewable energy, advancements in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, and battery storage technologies are crucial for increasing reliability and decreasing costs. For non-renewable energy, technological advancements focus on improving extraction methods, increasing efficiency, and reducing environmental impact, but these advancements often come with their own set of environmental and social concerns.
Policy and Regulation: Shaping the Energy Landscape
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the energy landscape. Incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and renewable portfolio standards can accelerate the adoption of renewable energy technologies. Conversely, regulations that limit or discourage the use of non-renewable energy sources can also play a role in the energy transition. Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, can also encourage a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
Public Awareness and Engagement: A Crucial Factor
Public awareness and engagement are essential for successful energy transition. Educating the public about the benefits of renewable energy and the risks associated with non-renewable energy sources can drive demand for cleaner energy solutions. Increased public support for renewable energy policies and initiatives can lead to more rapid adoption and broader societal acceptance of the necessary changes.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future
The choice between renewable and non-renewable energy is not merely a technological one; it's a fundamental choice about our planet's future. While non-renewable energy has powered our civilization for centuries, its unsustainable nature and detrimental environmental impact necessitate a global shift towards renewable energy sources. Embracing renewable energy offers a path toward a cleaner, more sustainable, and more secure energy future for generations to come. This transition requires technological innovation, supportive policies, and widespread public engagement, but the benefits—a healthy planet and a thriving society—make the effort undeniably worthwhile.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Vertical Columns On The Periodic Table Are Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 1000
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Combination Of All The Forces Acting On An Object
Mar 15, 2025
-
Difference Between Laptop And Notebook Computer
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 42
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Diff Between Renewable And Non Renewable . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
