Common Factors Of 4 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
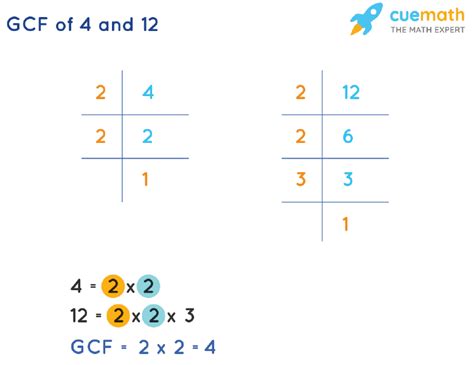
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Common Factors of 4 and 12: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple task, especially with smaller numbers like 4 and 12. However, understanding the underlying principles behind this seemingly basic concept opens doors to a deeper appreciation of number theory and its applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the common factors of 4 and 12, delving into the methods for finding them, their significance in mathematics, and practical examples showcasing their relevance.
Understanding Factors
Before we dive into the specifics of 4 and 12, let's establish a solid foundation. A factor of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6 because each of these numbers divides 6 without leaving a remainder.
Finding Factors: A Systematic Approach
There are several ways to find the factors of a number:
-
Listing Method: This straightforward method involves systematically checking each whole number to see if it divides the given number evenly. For example, to find the factors of 12, we would check 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12. Those that divide 12 evenly (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12) are its factors.
-
Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down a number into its prime factors. Prime factors are prime numbers (numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves). The prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3). Once you have the prime factorization, you can easily find all the factors by combining the prime factors in different ways.
-
Factor Tree: A visual representation of prime factorization. The number is broken down into smaller factors until all branches end in prime numbers.
Factors of 4 and 12: A Detailed Analysis
Now, let's apply these methods to find the factors of 4 and 12:
Factors of 4:
Using the listing method, we find the factors of 4 to be 1, 2, and 4.
Using prime factorization, we find that 4 = 2 x 2 = 2². This confirms the factors we found using the listing method.
Factors of 12:
Using the listing method, we find the factors of 12 to be 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Using prime factorization, 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3. From this, we can derive all the factors: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Notice how the combination of the prime factors gives us all possible factors. For example, 1 (2⁰ x 3⁰), 2 (2¹ x 3⁰), 3 (2⁰ x 3¹), 4 (2² x 3⁰), 6 (2¹ x 3¹), and 12 (2² x 3¹).
Identifying Common Factors
The common factors of two numbers are the numbers that are factors of both numbers. Comparing the factors of 4 (1, 2, 4) and the factors of 12 (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12), we can readily identify the common factors:
1, 2, and 4 are the common factors of 4 and 12.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
Among the common factors, the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. In the case of 4 and 12, the GCF is 4.
Finding the GCF: Different Methods
Several methods can be used to find the GCF:
-
Listing Method: This involves listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the largest common factor. This is effective for smaller numbers.
-
Prime Factorization Method: This method involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then identifying the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. For example, the prime factorization of 4 is 2² and the prime factorization of 12 is 2² x 3. The common prime factor is 2, and the lowest power is 2², thus the GCF is 2² = 4.
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This is a more efficient method for larger numbers. It involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCF.
The Significance of Common Factors
Understanding common factors and the GCF is crucial in various mathematical contexts:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the GCF allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 12/4 can be simplified to 3/1 by dividing both numerator and denominator by their GCF, which is 4.
-
Solving Equations: The concept of common factors plays a significant role in solving algebraic equations involving factorization.
-
Geometry: Common factors are useful in determining the dimensions of shapes. For example, if you have a rectangular area that can be divided into squares of side length 4 and squares of side length 12, the largest possible square would have side length 4.
-
Real-world Applications: Common factors are applied in various real-world scenarios such as dividing objects into equal groups, planning projects, and resource allocation. Imagine dividing 12 cookies evenly among 4 friends; each friend would get 3 cookies – this directly relates to the concept of common factors.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
The exploration of common factors extends beyond the simple examples like 4 and 12. Here are some advanced concepts and related ideas:
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both given numbers. It's closely related to the GCF. The product of the GCF and LCM of two numbers is always equal to the product of the two numbers.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Understanding factors is fundamental to modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus).
-
Number Theory: The study of common factors is a core component of number theory, a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of integers.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization and related concepts are crucial in modern cryptography, especially in securing online transactions and communications.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Common Factors
This in-depth exploration of the common factors of 4 and 12 reveals more than just a simple mathematical exercise. It highlights fundamental concepts within number theory, demonstrating their applicability in diverse fields. From simplifying fractions to solving complex equations and even contributing to the security of online transactions, the seemingly basic concept of common factors proves to be a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. By understanding and mastering these concepts, we enhance our problem-solving abilities and gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematics. The seemingly simple question of “what are the common factors of 4 and 12?” opens up a vast and fascinating world of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which State Of Matter Has Indefinite Shape And Is Compressible
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Diagonals Of An Isosceles Trapezoid Are Congruent
Mar 21, 2025
-
Composite Numbers And Prime Numbers Chart
Mar 21, 2025
-
Adjectives That Start With The Letter K
Mar 21, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 121
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 4 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
