An Element Is A Pure Substance
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
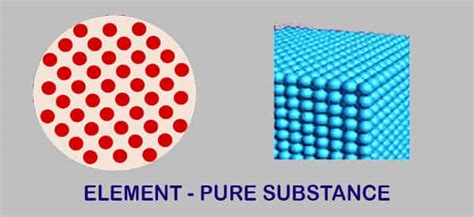
Table of Contents
An Element is a Pure Substance: Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter
The world around us is composed of countless substances, from the air we breathe to the ground beneath our feet. Understanding the fundamental building blocks of these substances is crucial to comprehending the nature of matter itself. At the heart of this understanding lies the concept that an element is a pure substance, meaning it's made up of only one type of atom. This seemingly simple definition opens the door to a vast and fascinating realm of chemical properties, reactions, and the organization of the periodic table. This article delves deep into the definition of an element as a pure substance, exploring its implications and significance in chemistry and beyond.
What is a Pure Substance?
Before we dive into the specifics of elements, let's clarify what constitutes a pure substance. A pure substance is a form of matter that has a constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. This means that no matter where you find a sample of a specific pure substance, its chemical makeup and physical attributes will remain consistent. Unlike mixtures, which are combinations of different substances, pure substances cannot be separated into simpler components through physical methods like filtration or distillation.
Pure substances are categorized into two main types: elements and compounds.
Elements: The Fundamental Building Blocks
Elements, as we've established, are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Each element is identified by its unique atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. This number dictates the element's position on the periodic table and governs its chemical behavior.
For instance, oxygen (O) is an element with an atomic number of 8, meaning each oxygen atom possesses 8 protons. Similarly, hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1, and gold (Au) has an atomic number of 79. These atomic numbers are fundamental and unchanging for each element.
Compounds: Combinations of Elements
Compounds, on the other hand, are pure substances formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. These bonds create entirely new substances with properties distinct from the elements that compose them. Water (H₂O), for example, is a compound formed from the elements hydrogen and oxygen. The properties of water are radically different from those of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. This demonstrates a key aspect of chemical bonding: the properties of the compound are often unrelated to the properties of its constituent elements.
The difference between elements and compounds is crucial. Elements are the fundamental building blocks, while compounds are combinations of those blocks. You can't break down an element into simpler substances through chemical means; however, you can decompose compounds into their constituent elements through chemical reactions.
The Periodic Table: Organizing the Elements
The periodic table is a powerful tool that organizes and displays all known elements. It's arranged according to increasing atomic number and groups elements with similar chemical properties together in columns called groups or families. This arrangement reflects the underlying electron configurations of the atoms, which significantly influence their chemical behavior.
The periodic table is instrumental in understanding the relationships between different elements. Elements within the same group tend to exhibit similar reactivity and form similar compounds. For instance, the alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive and readily form +1 ions. The halogens (Group 17) are also reactive, forming -1 ions. This predictable behavior stems from the similar arrangement of electrons in their outermost shells.
Properties of Elements: A Diverse Landscape
Elements exhibit a remarkable diversity of properties, ranging from highly reactive metals to inert gases. These properties are determined by their electronic structure and atomic number. Some key properties include:
-
Metallic Character: Metals generally exhibit luster, malleability (ability to be hammered into sheets), ductility (ability to be drawn into wires), and good conductivity of heat and electricity. Examples include iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and aluminum (Al).
-
Non-metallic Character: Nonmetals typically lack the characteristic properties of metals. They are often poor conductors of heat and electricity, and can exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature. Examples include oxygen (O), sulfur (S), and chlorine (Cl).
-
Reactivity: Some elements are highly reactive, readily participating in chemical reactions, while others are inert, showing little tendency to react. The reactivity of an element is largely determined by its electronic configuration.
-
Physical States: At room temperature, elements can exist as solids (e.g., iron), liquids (e.g., mercury), or gases (e.g., oxygen).
Isotopes: Variations within an Element
While an element is defined by its atomic number (number of protons), it's important to understand the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number results in variations in the atomic mass of the isotopes.
For example, carbon (C) has two naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12 (¹²C) and carbon-13 (¹³C). Both isotopes have 6 protons, but ¹²C has 6 neutrons, while ¹³C has 7 neutrons. Although isotopes have different masses, they exhibit similar chemical behavior because they have the same number of electrons, which determine chemical reactivity.
The Significance of Elements
Understanding elements as pure substances is fundamentally important for several reasons:
-
Foundation of Chemistry: Elements are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. Chemistry, at its core, is the study of the properties and interactions of elements and the compounds they form.
-
Technological Advancements: Our technological advancements rely heavily on the properties of different elements. Metals are used in construction, electronics, and transportation; gases are used in various industrial processes; and many elements are crucial in medical applications.
-
Understanding Natural Phenomena: Elements play a critical role in various natural processes, from photosynthesis (which relies on carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) to the formation of rocks and minerals.
-
Environmental Science: Understanding the behavior and interactions of elements is vital for environmental monitoring and remediation efforts. The cycling of elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in ecosystems is crucial for maintaining environmental balance.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Elements
In conclusion, the statement that "an element is a pure substance" encapsulates a fundamental concept in chemistry. It highlights the fact that elements are the foundational building blocks of all matter, each characterized by its unique atomic number and properties. The periodic table provides a systematic way to organize and understand the relationships between different elements. The diversity of properties exhibited by elements, along with the concept of isotopes, adds further complexity and richness to this foundational concept. Comprehending the nature of elements as pure substances is not just a theoretical exercise; it's essential for advancing our understanding of chemistry, technology, and the natural world around us. The ongoing research and discoveries in the field of chemistry continue to expand our knowledge of elements and their role in shaping our universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Planet Is Farthest From The Sun
Apr 07, 2025
-
Find Three Consecutive Even Integers Whose Sum Is 108
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is The Most Abundant Gas In Earths Atmosphere
Apr 07, 2025
-
Is Phosphorus A Metal Or Nonmetal
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 17 Inches
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Element Is A Pure Substance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
