What Is The Most Abundant Gas In Earth's Atmosphere
Juapaving
Apr 07, 2025 · 6 min read
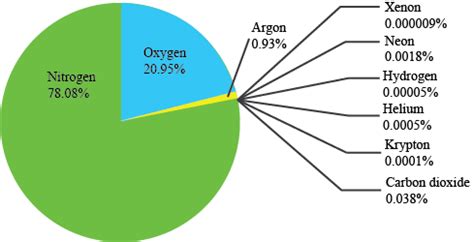
Table of Contents
What is the Most Abundant Gas in Earth's Atmosphere?
The Earth's atmosphere is a dynamic and complex mixture of gases that plays a crucial role in supporting life. Understanding the composition of this atmosphere, particularly the most abundant gases, is fundamental to comprehending weather patterns, climate change, and the overall habitability of our planet. While a myriad of gases exist in trace amounts, the answer to the question, "What is the most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere?" is clear: nitrogen (N₂). This article delves deep into the properties of nitrogen, its abundance, its role in the atmosphere, and its importance to life on Earth.
The Dominance of Nitrogen: A Closer Look
Nitrogen accounts for approximately 78% of the Earth's atmosphere by volume. This staggering percentage highlights its overwhelming dominance compared to other atmospheric constituents. While oxygen, the next most abundant gas, is crucial for respiration, nitrogen’s role is less direct, but no less significant. This seemingly inert gas plays a vital, albeit subtle, role in various atmospheric and biological processes.
The Inert Nature of Nitrogen
Nitrogen's chemical inertness is a key characteristic. Its strong triple bond (N≡N) requires considerable energy to break, making it relatively unreactive under normal atmospheric conditions. This inertness is both a blessing and a curse. While it prevents it from readily participating in many atmospheric reactions, it also means that nitrogen gas is not directly usable by most organisms. This leads us to the fascinating processes that convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms.
The Nitrogen Cycle: Transforming Inert Gas into Life's Building Blocks
The inert nature of atmospheric nitrogen highlights the importance of the nitrogen cycle, a biogeochemical process that converts inert nitrogen gas into biologically available forms, such as ammonia (NH₃) and nitrates (NO₃⁻). This cycle is essential for life because nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids—the fundamental building blocks of life.
Stages of the Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle comprises several crucial stages:
-
Nitrogen Fixation: This is the initial and perhaps most crucial step, where atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) is converted into ammonia (NH₃) or other nitrogenous compounds. This process is primarily carried out by specialized bacteria, known as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which possess the unique enzyme, nitrogenase. These bacteria are often found in the soil, living in symbiotic relationships with plants (e.g., legumes) or free-living in the environment. Industrial processes, such as the Haber-Bosch process, also contribute to nitrogen fixation, albeit on a much larger scale.
-
Nitrification: Once ammonia is formed, it undergoes nitrification. This process involves the conversion of ammonia to nitrites (NO₂⁻) and then to nitrates (NO₃⁻) by different groups of nitrifying bacteria. Nitrates are highly soluble and readily absorbed by plants through their roots.
-
Assimilation: Plants absorb nitrates from the soil and incorporate them into their organic molecules, such as amino acids and proteins. Animals then obtain nitrogen by consuming plants or other animals.
-
Ammonification: When plants and animals die, decomposers (bacteria and fungi) break down organic matter, releasing nitrogen back into the soil as ammonia.
-
Denitrification: In oxygen-poor environments, denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas (N₂), which is then released back into the atmosphere. This completes the cycle, maintaining the balance of atmospheric nitrogen.
The Significance of Nitrogen in the Atmosphere Beyond the Nitrogen Cycle
While the nitrogen cycle emphasizes the biological importance of nitrogen, its presence in the atmosphere also has broader climatic and atmospheric impacts:
-
Atmospheric Pressure: Given its abundance, nitrogen significantly contributes to the overall atmospheric pressure. This pressure is essential for maintaining the Earth's temperature and preventing the boiling away of water.
-
Temperature Regulation: While nitrogen itself doesn't directly absorb or emit significant amounts of infrared radiation, its presence, alongside other greenhouse gases, influences the Earth's overall temperature. The composition of the atmosphere directly impacts how effectively heat is trapped and distributed.
-
Ozone Layer Protection: While not directly involved, nitrogen oxides (NOx) play a complex role in ozone layer chemistry. NOx can catalytically destroy ozone, particularly in the stratosphere. However, their role is intertwined with other factors, highlighting the intricate nature of atmospheric processes.
Other Atmospheric Gases: A Comparative Analysis
While nitrogen reigns supreme, it's important to consider the other significant components of the Earth's atmosphere:
-
Oxygen (O₂): At approximately 21%, oxygen is the second most abundant gas. It is essential for respiration in most living organisms and plays a critical role in combustion processes.
-
Argon (Ar): Argon makes up around 0.93% of the atmosphere. It's a noble gas, meaning it's chemically inert and doesn't participate in many atmospheric reactions.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): While present in a relatively small amount (currently around 0.04%), carbon dioxide is a crucial greenhouse gas that plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's temperature. Increases in CO₂ levels are directly linked to climate change.
-
Water Vapor (H₂O): The concentration of water vapor varies significantly depending on location and weather conditions, ranging from near zero to around 4%. It's a powerful greenhouse gas and plays a vital role in the water cycle.
The Future of Atmospheric Nitrogen: Implications and Concerns
Human activities have significantly impacted the nitrogen cycle. The widespread use of nitrogen-based fertilizers in agriculture has led to an increase in nitrogen runoff into waterways, causing eutrophication and harming aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, industrial nitrogen fixation associated with the production of fertilizers and other nitrogen-containing compounds has increased the amount of reactive nitrogen in the environment. These changes are causing significant environmental concerns including:
-
Eutrophication: Excess nitrogen in waterways fuels algal blooms, depleting oxygen levels and harming aquatic life.
-
Acid Rain: Nitrogen oxides contribute to acid rain, which can damage forests and aquatic ecosystems.
-
Greenhouse Effect: While nitrogen itself is not a potent greenhouse gas, the altered nitrogen cycle can indirectly affect greenhouse gas concentrations.
-
Ozone Depletion: Although nitrogen oxides can contribute to ozone depletion, strategies to mitigate these impacts are in place.
Conclusion: Understanding the Atmosphere's Foundation
Nitrogen's dominance in the Earth's atmosphere is a fundamental aspect of our planet's composition and habitability. Its inert nature, coupled with the intricate nitrogen cycle, ensures the availability of nitrogen for life while maintaining atmospheric balance. However, the human impact on the nitrogen cycle necessitates a deeper understanding of the intricate processes involved. Continued research and sustainable practices are crucial to mitigate the negative impacts of human activities on the nitrogen cycle and maintain the delicate balance of Earth’s atmosphere for future generations. Protecting the delicate equilibrium of atmospheric gases is vital for preserving the health of our planet and ensuring its continued habitability. The abundance of nitrogen, while seemingly passive, underscores the profound interconnections between atmospheric composition, biological processes, and the overall well-being of our planet.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cm In 2 M
Apr 09, 2025
-
Why Is A Production Possibility Curve Concave
Apr 09, 2025
-
How Many Sides Do Pentagons Have
Apr 09, 2025
-
How Many Mm Is 6 Cm
Apr 09, 2025
-
A Pencil Is About How Long
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Most Abundant Gas In Earth's Atmosphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.