66 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
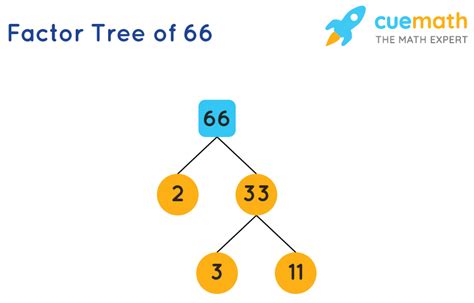
Table of Contents
66 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, the process of breaking down a number into its prime number components, is a fundamental concept in number theory. Understanding this process is crucial for various mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. This article delves deep into the prime factorization of the number 66, exploring the method, its significance, and its broader implications within the world of mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we embark on the factorization of 66, let's refresh our understanding of key terms.
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other natural numbers.
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, result in the original number. Every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Finding the Prime Factors of 66
Now, let's break down the number 66 into its prime factors. We can use a factor tree to visualize this process:
Method 1: Using a Factor Tree
-
Start with the number 66. We look for the smallest prime number that divides 66 evenly. This is 2.
-
Divide 66 by 2. 66 / 2 = 33. We now have 2 and 33 as factors.
-
Focus on 33. The smallest prime number that divides 33 is 3.
-
Divide 33 by 3. 33 / 3 = 11. We now have 2, 3, and 11 as factors.
-
11 is a prime number. This means we have reached the end of our factorization.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 66 is 2 x 3 x 11.
Method 2: Repeated Division
Alternatively, we can use repeated division by prime numbers.
-
Start with 66. Divide by the smallest prime number, 2: 66 / 2 = 33.
-
Divide 33 by the next smallest prime number that divides it, which is 3: 33 / 3 = 11.
-
11 is a prime number. We stop here.
Again, the prime factorization of 66 is 2 x 3 x 11.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 66, and indeed of any number, holds significant importance in various mathematical contexts:
1. Simplifying Fractions
Prime factorization is essential for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For instance, if we have the fraction 66/90, we can find the prime factorization of both the numerator (66 = 2 x 3 x 11) and the denominator (90 = 2 x 3² x 5). By canceling out common factors (2 and 3), we simplify the fraction to 11/15.
2. Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization is a powerful tool for determining the greatest common divisor (GCD) and the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
To find the GCD of 66 and 90, we compare their prime factorizations:
- 66 = 2 x 3 x 11
- 90 = 2 x 3² x 5
The common prime factors are 2 and 3. The GCD is the product of the lowest powers of the common prime factors: 2¹ x 3¹ = 6.
To find the LCM, we take the highest powers of all prime factors present in either factorization: 2¹ x 3² x 5¹ x 11¹ = 990.
3. Solving Diophantine Equations
Diophantine equations are algebraic equations where only integer solutions are sought. Prime factorization often plays a crucial role in solving these types of equations.
4. Cryptography
Prime factorization forms the backbone of many modern cryptographic systems, particularly those based on the RSA algorithm. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components makes these systems secure.
5. Number Theory Research
Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, with ongoing research exploring the distribution of prime numbers, the efficiency of factorization algorithms, and related topics. Understanding prime factorization is a stepping stone to more advanced concepts in number theory.
Extending the Concept: Exploring Larger Numbers
While we've focused on 66, the principles of prime factorization apply to all composite numbers, no matter how large. For larger numbers, more sophisticated algorithms are often employed, but the underlying concept remains the same: breaking the number down into its fundamental prime components. Consider the example of a much larger number, like 1001:
- 1001 is divisible by 7 (1001/7 = 143).
- 143 is divisible by 11 (143/11 = 13).
- 13 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 1001 is 7 x 11 x 13.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization in Mathematics
The prime factorization of 66, as a seemingly simple example, demonstrates the fundamental importance of this concept in mathematics. It provides a pathway to solving complex problems in areas ranging from basic arithmetic to advanced cryptography. The ability to efficiently find the prime factors of a number is a powerful tool for any mathematician or anyone interested in delving deeper into the fascinating world of numbers. This foundational concept underlies numerous more advanced mathematical concepts, emphasizing its lasting significance in the field. Understanding prime factorization is not just about finding the factors of a single number; it’s about unlocking a deeper understanding of the structure and behavior of numbers themselves. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, the impact of prime factorization is both profound and far-reaching.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Percentage Of One Sixth
Mar 18, 2025
-
Convert Kg M3 To G Cm3
Mar 18, 2025
-
Difference Between Ac And Dc Electric Motor
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are All Of The Factors Of 81
Mar 18, 2025
-
Write 44 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 66 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
