Difference Between Ac And Dc Electric Motor
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
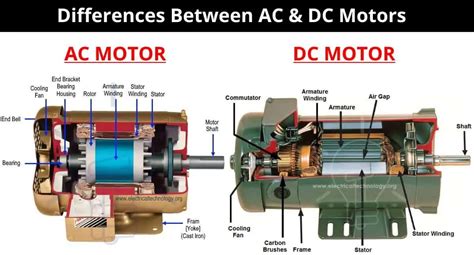
Table of Contents
AC vs. DC Electric Motors: A Comprehensive Comparison
Electric motors, the workhorses of modern industry and everyday life, come in two primary varieties: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). While both achieve the same fundamental goal – converting electrical energy into mechanical energy – their underlying mechanisms, applications, and characteristics differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right motor for a specific application. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of AC and DC motors, highlighting their key distinctions and advantages.
Fundamental Differences: AC vs. DC Power Supply
The most fundamental difference lies in the type of electricity they utilize. AC motors operate on alternating current, where the direction of current flow reverses periodically. This cyclical reversal is characterized by a sinusoidal waveform, resulting in a constantly changing voltage and current. Conversely, DC motors run on direct current, where the current flows consistently in one direction. This results in a constant voltage and current, simplifying certain aspects of motor control.
Construction and Working Principles: A Closer Look
The internal construction and operating principles of AC and DC motors are vastly different, leading to their distinct performance characteristics.
AC Motors: The Mechanics of Rotating Magnetic Fields
AC motors typically employ the principle of a rotating magnetic field. This field is generated by the interaction of stator windings (stationary coils) carrying alternating current and rotor windings (rotating coils) or a squirrel cage rotor (a simpler, more robust design). The alternating current in the stator windings creates a magnetic field that rotates, inducing current in the rotor windings. This induced current, in turn, generates a magnetic field in the rotor, causing it to align with the rotating magnetic field of the stator, resulting in continuous rotation.
Several types of AC motors exist, each with its own nuances:
-
Induction Motors (Asynchronous Motors): These are the most common type of AC motor, characterized by their simplicity, robustness, and low maintenance requirements. They don't require external excitation or brushes, making them highly reliable. The rotor speed is slightly less than the synchronous speed determined by the frequency of the AC power supply. This slip is crucial for torque generation. Different induction motor designs exist, including squirrel-cage and wound-rotor motors, each optimized for different applications based on their starting torque requirements and speed control capabilities.
-
Synchronous Motors: Unlike induction motors, synchronous motors run at a constant speed, synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply. They require some form of excitation (usually DC current) to their rotor windings, making their construction more complex. Synchronous motors are known for their high efficiency, constant speed operation, and power factor correction capabilities.
DC Motors: The Simplicity of Commutation
DC motors utilize the interaction between a magnetic field and current-carrying conductors to generate torque. They commonly employ a commutator, a segmented cylindrical component that reverses the current direction in the rotor windings at precisely the right time, ensuring continuous rotation. This process, known as commutation, is achieved through brushes that make contact with the commutator segments.
Several key types of DC motors cater to different needs:
-
Brushed DC Motors: These are the simplest type of DC motor, characterized by the use of brushes and a commutator for commutation. They offer high starting torque and good speed control, but have limitations due to brush wear and sparking, resulting in reduced lifespan and potential maintenance needs.
-
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): These motors eliminate the brushes and commutator, employing electronic commutation instead. This results in significantly longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and quieter operation compared to their brushed counterparts. However, they require more sophisticated control electronics.
Performance Characteristics: A Detailed Comparison
The performance characteristics of AC and DC motors significantly influence their suitability for various applications.
| Feature | AC Motor | DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Generally higher initial cost |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance requirements | Higher maintenance requirements (for brushed) |
| Efficiency | Generally high efficiency at rated load | High efficiency, especially brushless |
| Speed Control | Variable, but often less precise than DC | Highly precise speed control |
| Starting Torque | Varies greatly depending on the motor type | Typically high |
| Size & Weight | Can be larger and heavier for equivalent power | Can be smaller and lighter for equivalent power |
| Speed Regulation | Less precise than DC, prone to speed fluctuations with load changes | Excellent speed regulation |
| Noise Level | Can be noisy, especially at higher loads | Generally quieter, particularly brushless |
| Lifespan | Generally long lifespan | Brushed motors shorter lifespan, brushless longer |
Applications: Where Each Motor Excels
The choice between an AC or DC motor is largely determined by the specific application requirements.
AC Motor Applications:
- Industrial applications: Fans, pumps, compressors, conveyors, and other heavy-duty machinery. Their robustness and relatively low cost make them ideal for such applications.
- Household appliances: Refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and other appliances benefit from the simplicity and reliability of AC motors.
- Power generation: AC generators are the backbone of the electrical power grid.
DC Motor Applications:
- Precise motion control: Robotics, automation systems, and precision machinery benefit from the superior speed and torque control offered by DC motors.
- Electric vehicles: While AC motors are gaining traction, DC motors, especially brushless designs, have been dominant in electric vehicles due to their high efficiency and precise speed control.
- Computer peripherals: Many computer peripherals, such as printers and hard drives, use DC motors due to their compactness and controllability.
Advancements and Future Trends
Both AC and DC motor technologies continue to evolve. Developments in power electronics, materials science, and control algorithms are leading to significant improvements in efficiency, power density, and control precision.
Advancements in AC motor technology focus on improving efficiency through optimized designs, higher-performance materials, and advanced control strategies. The integration of intelligent sensors and predictive maintenance technologies is enhancing reliability and reducing downtime.
Advancements in DC motor technology are largely centered around brushless DC motors. Improvements in permanent magnets, electronic commutation techniques, and control systems are resulting in even higher efficiency, greater power density, and improved control capabilities. The development of high-power density brushless DC motors is driving their adoption in demanding applications such as electric vehicles and industrial robotics.
Conclusion: The Right Motor for the Right Job
The choice between an AC and DC motor is not a matter of one being inherently superior, but rather of selecting the optimal solution based on the specific application requirements. Factors to consider include power requirements, speed control needs, operating environment, cost constraints, maintenance requirements, and efficiency targets. By understanding the key differences between AC and DC motors, engineers and designers can make informed decisions to ensure optimal performance and longevity in their systems. The ongoing advancements in both technologies continue to expand their applications and enhance their capabilities, ensuring they remain essential components of a wide range of industrial and consumer products.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Words That End With An S
Mar 18, 2025
-
Five Letter Words Starting With S A L
Mar 18, 2025
-
Volume Is The Amount Of Space A
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of These Is A Chemical Change
Mar 18, 2025
-
Write The Number 55 In Another Way
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Ac And Dc Electric Motor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
