Write 44 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
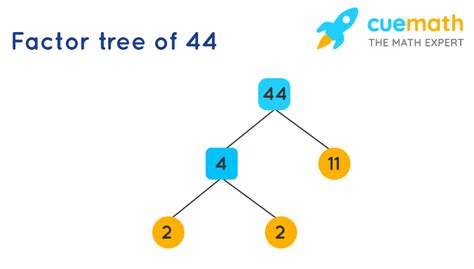
Table of Contents
Writing 44 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Comprehensive Guide
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This seemingly simple process unlocks deeper understanding in various mathematical fields, from cryptography to algorithm design. This article delves deep into the prime factorization of 44, explaining the method, its significance, and expanding on related concepts with practical examples.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before diving into the factorization of 44, let's establish a firm understanding of the fundamental concepts:
What are Prime Numbers?
Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. This means they cannot be expressed as a product of two smaller whole numbers. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Note that 1 is not considered a prime number.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal a given composite number. A composite number is a whole number greater than 1 that is not prime; it can be factored into smaller whole numbers. The prime factorization of a number is unique, meaning there's only one way to express it as a product of primes (ignoring the order of factors).
Finding the Prime Factors of 44: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's find the prime factors of 44. We'll use a method commonly known as the "factor tree."
-
Start with the number 44. Write it down at the top of your factor tree.
-
Find the smallest prime factor. The smallest prime number is 2. Since 44 is an even number, it is divisible by 2.
-
Divide 44 by 2. 44 divided by 2 is 22. Write 2 and 22 as branches from 44 in your factor tree.
-
Continue factoring. Now we need to factor 22. Again, 22 is divisible by 2. 22 divided by 2 is 11. Add branches from 22 to represent 2 and 11.
-
Identify the prime factors. We have reached 11, which is a prime number. The factorization process is complete.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 44 is 2 x 2 x 11, which can also be written as 2² x 11. This means that 2 multiplied by 2 multiplied by 11 equals 44.
Visualizing the Factor Tree for 44
Here's a visual representation of the factor tree:
44
/ \
2 22
/ \
2 11
This tree clearly shows the steps involved in breaking down 44 into its prime factors. Each branch represents a division by a prime number until only prime numbers remain at the bottom.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has profound implications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM):**
Prime factorization is crucial for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all given numbers without leaving a remainder. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all given numbers. By comparing the prime factorizations, we can easily find the GCD and LCM.
For example, let's find the GCD and LCM of 44 and 60:
- Prime factorization of 44: 2² x 11
- Prime factorization of 60: 2² x 3 x 5
GCD(44, 60) = 2² = 4 (The common prime factors raised to the lowest power) LCM(44, 60) = 2² x 3 x 5 x 11 = 660 (All prime factors raised to the highest power)
2. Cryptography:**
Prime numbers play a vital role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The security of these systems relies on the difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime factors. The larger the numbers, the more computationally intensive the factorization becomes.
3. Algorithm Design:**
Prime factorization algorithms are used in various computer science applications, including testing for primality and solving problems related to modular arithmetic.
4. Understanding Number Properties:**
Prime factorization helps us understand the properties of numbers, such as divisibility rules and identifying perfect numbers (numbers equal to the sum of their proper divisors).
Alternative Methods for Prime Factorization
While the factor tree is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers, other techniques can be employed for larger numbers:
1. Trial Division:**
This method involves systematically dividing the number by each prime number, starting from the smallest, until all prime factors are found. This can be tedious for large numbers.
2. Pollard's Rho Algorithm:**
This is a probabilistic algorithm that's more efficient than trial division for finding factors of larger composite numbers. It's particularly useful when dealing with numbers that have relatively small prime factors.
3. Sieve of Eratosthenes:**
The Sieve of Eratosthenes is not directly a prime factorization algorithm, but it's a powerful tool for finding all prime numbers up to a specified limit. This list of primes can then be used in the trial division method.
Practical Applications of Prime Factorization
Beyond theoretical mathematics, prime factorization finds practical applications in:
- Coding and Software Development: Understanding prime numbers and factorization is essential in various algorithms and data structures.
- Data Compression: Some compression algorithms leverage prime numbers to optimize data storage.
- Network Security: Prime numbers form the basis of several network security protocols.
- Scientific Computing: Prime factorization algorithms are used in various scientific computations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple task of writing 44 as a product of its prime factors (2² x 11) opens a gateway to a vast and fascinating world of number theory and its practical applications. From the fundamentals of GCD and LCM calculations to the complex realm of cryptography and algorithm design, prime factorization remains an essential concept with lasting relevance in mathematics and computer science. The ability to understand and apply prime factorization techniques enhances problem-solving skills and provides a solid foundation for further exploration in these fields. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for any student or professional working with numbers, algorithms, or security systems. The enduring importance of prime factorization lies in its ability to simplify complex mathematical problems and underpin many crucial aspects of modern technology and computation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Words That End With An S
Mar 18, 2025
-
Five Letter Words Starting With S A L
Mar 18, 2025
-
Volume Is The Amount Of Space A
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of These Is A Chemical Change
Mar 18, 2025
-
Write The Number 55 In Another Way
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write 44 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
