54 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
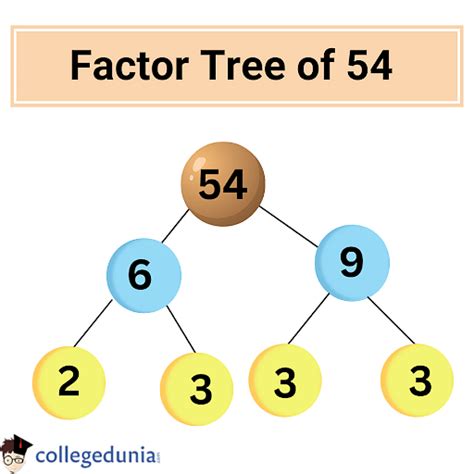
Table of Contents
54 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Understanding this process is crucial for various mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations. This article will delve deep into the prime factorization of 54, exploring the method, its significance, and its broader implications within the world of mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we embark on the prime factorization of 54, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental concepts. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Conversely, a composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. 54, the number we'll be focusing on, is a composite number.
Prime factorization, also known as integer factorization, is the process of decomposing a composite number into a unique set of prime numbers multiplied together. This set of prime numbers is called the prime factorization of the composite number. The fundamental theorem of arithmetic guarantees that every composite number has only one unique prime factorization, regardless of the method used to find it. This uniqueness is a powerful tool in various mathematical applications.
Methods for Finding Prime Factors
There are several methods to find the prime factors of a number. Let's explore a few, applying them to the number 54:
1. The Factor Tree Method
The factor tree method is a visual and intuitive approach. We start by finding any two factors of 54. Let's choose 2 and 27:
54
/ \
2 27
Now, 2 is a prime number, so we circle it. 27 is composite, so we continue the process by finding its factors. Let's choose 3 and 9:
54
/ \
2 27
/ \
3 9
9 is also composite (3 x 3), so we continue:
54
/ \
2 27
/ \
3 9
/ \
3 3
Now all the branches end in prime numbers (2, 3, 3, 3). Therefore, the prime factorization of 54 is 2 x 3 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3³.
2. Repeated Division by Prime Numbers
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly. We start with 54:
- 54 ÷ 2 = 27 (2 is a prime factor)
- 27 ÷ 3 = 9 (3 is a prime factor)
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3 (3 is a prime factor)
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1 (3 is a prime factor)
The prime factors are 2, 3, 3, and 3. Therefore, the prime factorization of 54 is 2 x 3³.
3. Using the Sieve of Eratosthenes (for larger numbers)
The Sieve of Eratosthenes is a powerful algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. While it's more suited for finding primes themselves, it can be indirectly used for prime factorization. By generating a list of primes, you can systematically check which primes divide your target number (54 in this case).
The Significance of Prime Factorization of 54
The prime factorization of 54, 2 x 3³, holds significance in several mathematical contexts:
-
Simplifying Fractions: When simplifying fractions, finding the prime factorization of the numerator and denominator allows us to identify common factors and cancel them out, reducing the fraction to its simplest form.
-
Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Using prime factorization, we can easily find the GCD by identifying the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
-
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. Prime factorization simplifies finding the LCM by identifying all prime factors present in the numbers, raising each to the highest power it appears in any of the numbers.
-
Modular Arithmetic: In modular arithmetic, prime factorization plays a crucial role in solving congruences and other related problems.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks in modern cryptography. Large prime numbers are used in algorithms like RSA to secure online transactions and data communication. The difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors forms the basis of the security of these cryptographic systems.
Beyond 54: Applications and Extensions
The concepts discussed concerning the prime factorization of 54 are applicable to any composite number. The process remains the same, whether dealing with small numbers like 54 or extremely large numbers encountered in advanced mathematical fields and cryptography.
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic assures us that every composite number has a unique prime factorization, making it a powerful tool in various mathematical areas, including:
- Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization helps understand concepts like prime ideals and unique factorization domains in abstract algebra.
- Number Theory: Many number-theoretic problems rely heavily on prime factorization, including finding perfect numbers, Mersenne primes, and solving Diophantine equations.
- Computer Science: Algorithms for prime factorization are essential in cryptography and computer security. Finding efficient algorithms for factoring large numbers remains an active area of research.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 54, while seemingly a simple exercise, represents a fundamental concept in number theory and has far-reaching implications. Understanding this process, along with the various methods for achieving it, provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. The uniqueness of prime factorization and its applications in various fields highlight its significance as a core component of mathematics. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, the concept of prime factorization continues to be an indispensable tool in mathematics and computer science. This deep dive into the prime factorization of 54 serves as a stepping stone to exploring the broader world of number theory and its applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Strontium
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Gold A Mixture Or Pure Substance
Mar 14, 2025
-
Cellulose Is An Example Of A
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Square
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Basic Building Block Of All Matter
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 54 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
