Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Working
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
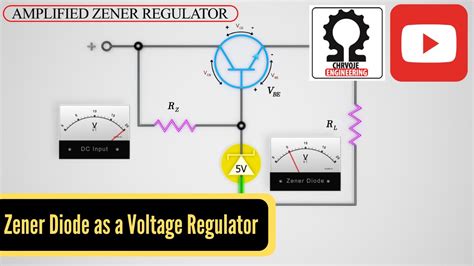
Table of Contents
Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator: A Deep Dive into its Working Principles
The humble Zener diode, often overlooked amidst the plethora of modern semiconductor devices, plays a crucial role in electronic circuits as a voltage regulator. Its ability to maintain a relatively constant voltage across its terminals, even when the current or input voltage fluctuates, makes it an invaluable component in countless applications. This article delves deep into the working principles of a Zener diode as a voltage regulator, exploring its characteristics, advantages, limitations, and various circuit configurations.
Understanding the Zener Effect
Before diving into voltage regulation, let's grasp the fundamental principle behind the Zener diode's operation: the Zener effect. This phenomenon, discovered by Clarence Zener, describes the breakdown voltage of a heavily doped p-n junction diode. Unlike a standard diode that conducts significantly only when forward-biased, a Zener diode is specifically designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region.
When a reverse bias voltage is applied across a Zener diode, the electric field across the depletion region increases. At a specific voltage, called the Zener breakdown voltage (Vz), a significant increase in current occurs. This is not a destructive breakdown like in other diodes; rather, it's a controlled avalanche effect where electrons gain enough energy to ionize atoms, creating more charge carriers and sustaining the current. This allows the diode to maintain a nearly constant voltage across its terminals, even with varying current.
The Zener Diode's I-V Characteristic Curve
The I-V (current-voltage) characteristic curve of a Zener diode vividly illustrates its unique behavior. The curve shows a steep, almost vertical section around the Zener voltage (Vz). This signifies the diode's ability to maintain a constant voltage despite current fluctuations within its operating range. Outside this region, the curve slopes more gradually, indicating a less stable voltage regulation. Understanding this curve is key to selecting the appropriate Zener diode for a specific application.
Zener Diode as a Simple Voltage Regulator
One of the simplest applications of a Zener diode is as a shunt regulator. In this configuration, the Zener diode is connected in parallel with the load, and a series resistor limits the current flowing through the diode.
Circuit Diagram:
Imagine a simple circuit with a variable DC power supply (Vin), a series resistor (Rs), a Zener diode (Vz), and a load (RL) all connected in series. The Zener diode is connected in parallel with the load.
Working Principle:
- When Vin increases: The voltage across the Zener diode tries to exceed Vz. However, the Zener diode clamps the voltage to Vz. The excess current flows through the Zener diode.
- When Vin decreases: The voltage across the Zener diode falls, but the Zener diode maintains the voltage across the load at approximately Vz. The current through the Zener diode reduces.
- Series Resistor (Rs) Importance: The series resistor (Rs) is crucial because it limits the current flowing through the Zener diode during voltage spikes. Without it, excessive current could damage the diode. Rs is selected based on the desired load current and the Zener diode's power dissipation capability.
Calculations:
The design of this simple Zener regulator involves calculating the appropriate value of Rs. We need to consider the maximum and minimum input voltages (Vin(max) and Vin(min)), the Zener voltage (Vz), the load current (IL), and the Zener diode's maximum current (Iz(max)).
The crucial formula to determine Rs is:
Rs = (Vin(max) - Vz) / (IL + Iz(max))
Selecting a sufficiently high Iz(max) ensures the Zener diode operates safely within its specifications.
Advantages and Limitations of Zener Diode Regulators
Zener diode regulators, while simple and effective for many applications, have both advantages and limitations:
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Zener diode regulators are simple to design and implement, requiring minimal components.
- Low cost: Zener diodes are inexpensive and readily available.
- Fast response: They offer relatively fast response times to input voltage variations.
Limitations:
- Power dissipation: A significant portion of the input power is dissipated as heat in the Zener diode, especially at higher currents. This necessitates using Zener diodes with appropriate power ratings.
- Efficiency: Their efficiency is low because the Zener diode dissipates considerable power.
- Line and load regulation: The voltage regulation provided by simple Zener regulators is not perfect; it's affected by both input voltage and load current changes.
- Temperature sensitivity: The Zener voltage (Vz) is temperature-dependent, which can affect the regulated voltage stability.
- Limited current capacity: Zener diodes have limited current capacity, restricting the maximum load current that can be regulated effectively.
Improving Zener Diode Regulator Performance
Several techniques can improve the performance of Zener diode regulators, addressing some of the limitations discussed earlier:
Using a Current Limiting Resistor:
A precisely calculated current-limiting resistor ensures the Zener diode operates within its safe current limits.
Using a Transistor for Improved Current Capacity:
By incorporating a transistor, we can significantly increase the load current handling capability of the regulator. The Zener diode regulates the base-emitter voltage of the transistor, which in turn controls the collector current flowing to the load. This configuration dramatically boosts the current capacity beyond the Zener's limits.
Employing a Temperature-Stable Zener Diode:
Temperature-stable Zener diodes minimize voltage variations due to temperature changes. These diodes use special construction techniques to reduce the temperature sensitivity.
Incorporating Negative Feedback:
Negative feedback mechanisms further improve line and load regulation. This typically involves incorporating operational amplifiers (op-amps) to enhance the stability and precision of the regulated voltage.
Advanced Zener Diode Regulator Circuits
Beyond the basic shunt regulator, more advanced circuits utilize Zener diodes for more sophisticated voltage regulation:
Zener Diode with Transistor as a Series Regulator:
In this configuration, the transistor acts as a series pass element, increasing the current-handling capacity significantly. The Zener diode still provides voltage reference.
Zener Diode with Op-Amp for Precision Regulation:
Combining a Zener diode with an op-amp creates a precise and stable voltage regulator with better line and load regulation. The op-amp provides negative feedback, ensuring that the output voltage remains remarkably constant despite input voltage or load current variations.
Applications of Zener Diode Voltage Regulators
Zener diode voltage regulators find widespread applications in various electronic systems, including:
- Over-voltage protection: They protect sensitive circuits from damage due to excessive voltage.
- Reference voltage sources: They provide stable reference voltages for other circuits.
- Power supplies: They are used in various power supply designs to maintain a constant output voltage.
- Clipping circuits: In audio applications, Zener diodes can be used to clip signal peaks, protecting speakers and amplifiers from overload.
- Surge suppressors: They can be employed in surge protection circuits to absorb voltage spikes.
Conclusion
Zener diodes are versatile components that offer a simple yet effective method for voltage regulation. While their performance is limited by inherent characteristics like power dissipation and temperature sensitivity, advanced circuit designs address these shortcomings, achieving high precision and current capacity. Understanding the fundamental working principles, advantages, and limitations of Zener diode regulators is crucial for selecting and designing appropriate circuits for various applications. The simplicity, low cost, and readily available nature of Zener diodes continue to make them a vital component in the world of electronics. They are a foundational element in understanding more advanced voltage regulation techniques and represent a critical stepping stone in the field of power electronics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Working . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
