Write The Prime Factorization Of 50
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
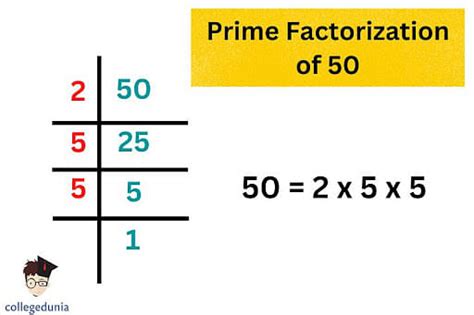
Table of Contents
Prime Factorization of 50: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves breaking down a composite number into its prime number constituents. Understanding this process is crucial for various mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to cryptography. This article will explore the prime factorization of 50 in detail, delving into the underlying concepts and illustrating its significance in mathematics. We'll also touch upon related concepts and offer practical examples.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before we delve into the prime factorization of 50, let's establish a solid foundation by defining key terms:
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Note that 1 is not considered a prime number.
Composite Numbers: Products of Primes
A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Essentially, a composite number can be factored into smaller positive integers. All composite numbers can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. This is the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, a cornerstone of number theory.
The Prime Factorization Process: Finding the Building Blocks
The process of prime factorization involves systematically identifying the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, produce the original composite number. There are several methods for achieving this, including:
- Factor Trees: A visual method where you repeatedly branch out until you're left with only prime numbers.
- Division Method: Repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until the quotient is 1.
The Prime Factorization of 50: Step-by-Step
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 50 using both the factor tree and division methods.
Method 1: The Factor Tree
- Start with the number 50.
- Find two factors of 50. A simple choice is 2 and 25. We write these as branches from 50.
- 2 is a prime number, so we circle it.
- 25 is composite. Its factors are 5 and 5. We branch these from 25.
- Both 5s are prime numbers, so we circle them.
The factor tree would look like this:
50
/ \
2 25
/ \
5 5
Therefore, the prime factorization of 50 is 2 x 5 x 5, which can be written as 2 x 5².
Method 2: The Division Method
- Start with the number 50.
- Divide 50 by its smallest prime factor, which is 2. 50 ÷ 2 = 25.
- The quotient is 25. The smallest prime factor of 25 is 5. 25 ÷ 5 = 5.
- The quotient is 5, which is a prime number.
This method gives us the same result: 2 x 5 x 5 or 2 x 5².
Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number isn't just an academic exercise; it has practical applications across various fields:
1. Simplifying Fractions
Prime factorization is crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. By finding the prime factors of both the numerator and the denominator, you can identify common factors and cancel them out.
Example: Simplify the fraction 50/75.
First, find the prime factorization of 50: 2 x 5² Then, find the prime factorization of 75: 3 x 5²
50/75 = (2 x 5²) / (3 x 5²) = 2/3
2. Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
Prime factorization simplifies finding the LCM and GCD of two or more numbers.
- LCM: The smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
- GCD: The largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
Example: Find the LCM and GCD of 50 and 75.
Prime factorization of 50: 2 x 5² Prime factorization of 75: 3 x 5²
- GCD: The common prime factors are 5². Therefore, GCD(50, 75) = 25.
- LCM: To find the LCM, take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations: 2 x 3 x 5² = 150. Therefore, LCM(50, 75) = 150.
3. Cryptography
Prime factorization plays a vital role in modern cryptography, particularly in the RSA algorithm, a widely used public-key cryptosystem. The security of RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors. This computational challenge protects sensitive data transmitted over the internet.
4. Modular Arithmetic and Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental to many concepts in modular arithmetic and advanced number theory. It underpins theorems related to congruences, Fermat's Little Theorem, and other essential results.
Exploring Further: Related Concepts
Let's explore some closely related concepts:
1. Unique Prime Factorization Theorem (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic)
This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, up to the order of the factors. This uniqueness is crucial for many mathematical operations.
2. Perfect Numbers
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding itself). Prime factorization helps in identifying potential perfect numbers. For example, 6 (2 x 3) is a perfect number because its proper divisors (1, 2, and 3) sum to 6.
3. Mersenne Primes
Mersenne primes are prime numbers that are one less than a power of 2 (2<sup>p</sup> - 1, where p is a prime number). Finding Mersenne primes is a significant area of research in number theory.
Conclusion: The Power of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization reveals a deep connection to the fundamental building blocks of numbers. Understanding this process is essential for a strong foundation in mathematics and opens doors to further exploration of number theory and its applications in various fields, from simplifying everyday calculations to securing sensitive data in the digital age. The prime factorization of 50, while seemingly trivial on its own, serves as a perfect illustration of these profound mathematical concepts. Its simplicity allows for a clear understanding of the core principles, paving the way for more advanced exploration of the world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Can An Event Be Independent And Mutually Exclusive
Mar 16, 2025
-
How To Find Out Perimeter Of A Rectangle
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 11
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Two Types Of Currents
Mar 16, 2025
-
Alternative Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Prime Factorization Of 50 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
