What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 11
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
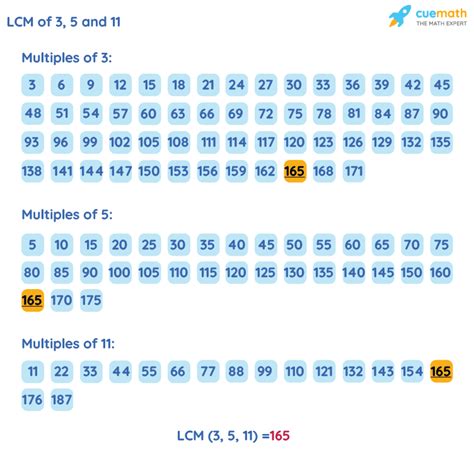
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 3 and 11? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in algebra and beyond. This article will explore the LCM of 3 and 11 in detail, explaining the process, different methods of calculation, and the broader significance of LCMs in mathematics and other fields. We’ll also touch upon related concepts and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before diving into the specific LCM of 3 and 11, let's establish a clear understanding of what an LCM is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14... and multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 11
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 3 and 11. Since 3 and 11 are both prime numbers (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves), finding their LCM is relatively straightforward. There are several methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method is to list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, ...
- Multiples of 11: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, ...
By examining the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in both lists is 33. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 11 is 33.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or numbers with multiple factors. Prime factorization involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is already a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 11: 11 (11 is also a prime number)
To find the LCM using prime factorization, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations of the numbers. In this case, we have only 3 and 11 as prime factors, each raised to the power of 1. Therefore, the LCM is 3 x 11 = 33.
Method 3: Formula for Two Numbers
For two numbers, a and b, there's a simple formula to calculate their LCM:
LCM(a, b) = (|a * b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where GCD(a, b) represents the greatest common divisor of a and b.
Since 3 and 11 are prime numbers and have no common factors other than 1, their GCD is 1. Therefore:
LCM(3, 11) = (3 * 11) / 1 = 33
The Significance of LCM
The concept of LCM isn't just an abstract mathematical exercise; it holds practical significance in various areas:
Fraction Operations
LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To perform these operations, we need to find the LCM of the denominators and then convert the fractions to equivalent fractions with the LCM as the common denominator. For instance, adding 1/3 and 1/11 requires finding the LCM of 3 and 11 (which is 33), converting the fractions to 11/33 and 3/33 respectively, and then adding them to get 14/33.
Scheduling Problems
LCM finds applications in scheduling problems. Imagine two buses that depart from the same station at regular intervals. One bus departs every 3 hours, and the other departs every 11 hours. The LCM (33 hours) determines when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
Cyclical Events
LCM helps to understand and predict cyclical events. If event A repeats every 3 days and event B repeats every 11 days, the LCM (33 days) indicates when both events will occur on the same day.
Number Theory
In number theory, the LCM plays a significant role in various theorems and proofs related to divisibility, prime numbers, and modular arithmetic.
Computer Science
LCM finds applications in algorithms related to scheduling tasks, resource allocation, and optimizing processes.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For example, let's find the LCM of 3, 11, and 5:
Method 1: Listing Multiples becomes less efficient with more numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization remains effective. The prime factorization of 3, 11, and 5 are 3, 11, and 5 respectively. Therefore, the LCM is 3 x 11 x 5 = 165.
Method 3: There's no direct formula for more than two numbers, but you can find the LCM sequentially. First, find the LCM of 3 and 11 (which is 33), then find the LCM of 33 and 5 (which is 165).
Conclusion: The Ubiquity of LCM
The least common multiple, seemingly a simple mathematical concept, plays a surprisingly significant role in various aspects of mathematics and its applications. Understanding how to calculate the LCM, whether for two numbers or more, is essential for anyone studying mathematics or working in fields that involve numerical analysis and problem-solving. The specific example of finding the LCM of 3 and 11, although straightforward, serves as a fundamental building block for understanding more complex LCM calculations and their broader applications across diverse disciplines. Mastering this concept empowers you with a versatile tool for tackling a wide range of problems efficiently and effectively. Remember, understanding the underlying principles and choosing the most appropriate method for a given scenario will enhance your mathematical proficiency and problem-solving capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 36 Inches In Feet
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 18 And 9
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Is 63 Kilograms
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Much Bones Does A Shark Have
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Millimeters Are In 1 M
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 11 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
