Write An Inverse Variation Equation That Relates X And Y
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
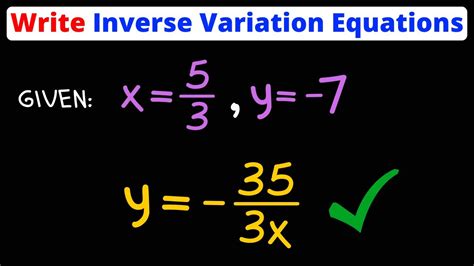
Table of Contents
- Write An Inverse Variation Equation That Relates X And Y
- Table of Contents
- Understanding and Applying Inverse Variation Equations: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is Inverse Variation?
- Key Characteristics of Inverse Variation
- How to Write an Inverse Variation Equation
- Examples of Inverse Variation Equations
- Solving Problems Using Inverse Variation Equations
- Real-World Applications of Inverse Variation
- Identifying Inverse Variation in Word Problems
- Beyond the Basics: Joint and Combined Variation
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Understanding and Applying Inverse Variation Equations: A Comprehensive Guide
Inverse variation, a fundamental concept in algebra, describes a relationship where one variable increases while the other decreases proportionally. Mastering inverse variation equations is crucial for numerous applications in physics, engineering, and everyday life. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of inverse variation, equipping you with the knowledge to construct, solve, and interpret these equations effectively.
What is Inverse Variation?
Inverse variation, also known as inverse proportionality, signifies that two variables are inversely related. This means that as one variable increases, the other decreases at a constant rate, and vice versa. The product of the two variables remains constant. This constant is often represented by the letter 'k' and is known as the constant of variation.
The core principle: If y varies inversely with x, then the equation representing their relationship is:
y = k/x
where:
- y is the dependent variable
- x is the independent variable
- k is the constant of variation (a non-zero constant)
Key Characteristics of Inverse Variation
- Reciprocal Relationship: The variables are reciprocals of each other, meaning their product is always a constant.
- Hyperbolic Graph: When plotted on a Cartesian coordinate system, an inverse variation produces a hyperbola. This curve approaches but never touches the x and y axes.
- Constant Product: The defining characteristic is the constant product of the variables (xy = k). This allows for easy determination of the constant of variation.
How to Write an Inverse Variation Equation
Constructing an inverse variation equation involves identifying the variables and determining the constant of variation. Let's walk through the process with step-by-step examples.
Step 1: Identify the Variables
First, clearly identify the dependent and independent variables. The problem statement usually provides this information. For example:
- "The time it takes to travel a certain distance varies inversely with the speed." Here, time (t) is the dependent variable, and speed (s) is the independent variable.
Step 2: Determine the Constant of Variation (k)
To find 'k', you need at least one pair of values for x and y. Substitute these values into the equation y = k/x and solve for k. For instance:
-
If y = 10 when x = 5, then:
10 = k/5
k = 50
Step 3: Write the Equation
Once 'k' is found, substitute its value into the general inverse variation equation y = k/x to obtain the specific equation that describes the relationship between x and y. In our example, the equation becomes:
y = 50/x
Examples of Inverse Variation Equations
Let's explore a variety of examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: Travel Time and Speed
The time (t) it takes to travel a fixed distance of 100 miles varies inversely with the speed (s). If it takes 2 hours to travel at a speed of 50 mph, write the equation relating time and speed.
- Variables: t (dependent), s (independent)
- Constant of variation (k): t = k/s; 2 = k/50; k = 100
- Equation: t = 100/s
Example 2: Pressure and Volume (Boyle's Law)
Boyle's Law in physics states that the pressure (P) of a gas varies inversely with its volume (V) at a constant temperature. If the pressure is 2 atmospheres when the volume is 5 liters, find the equation relating pressure and volume.
- Variables: P (dependent), V (independent)
- Constant of variation (k): P = k/V; 2 = k/5; k = 10
- Equation: P = 10/V
Example 3: Intensity of Light and Distance
The intensity (I) of light from a source varies inversely with the square of the distance (d) from the source. If the intensity is 10 lumens at a distance of 2 meters, determine the equation relating intensity and distance.
- Variables: I (dependent), d (independent)
- Constant of variation (k): I = k/d²; 10 = k/2²; k = 40
- Equation: I = 40/d² (Note the squared term reflecting the inverse square relationship)
Solving Problems Using Inverse Variation Equations
Once you have the inverse variation equation, you can use it to solve for unknown values of x or y. Simply substitute the known value and solve for the unknown.
Example 4: Using the Travel Time Equation
Using the equation t = 100/s from Example 1, find the time it takes to travel the 100 miles at a speed of 25 mph.
Substitute s = 25 into the equation:
t = 100/25 = 4 hours
Example 5: Using the Pressure-Volume Equation
Using the equation P = 10/V from Example 2, find the pressure when the volume is 2 liters.
Substitute V = 2 into the equation:
P = 10/2 = 5 atmospheres
Real-World Applications of Inverse Variation
Inverse variation plays a significant role in various real-world phenomena:
- Physics: Boyle's Law (gas pressure and volume), Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation (gravitational force and distance), the intensity of light and distance from a source.
- Engineering: Calculating gear ratios (speed and torque), designing circuits (voltage and current in certain circumstances), analyzing stress and strain in materials.
- Economics: Supply and demand (price and quantity), labor productivity (output per worker).
- Everyday Life: Cooking times (cooking time and oven temperature), travel time (speed and distance), the number of workers needed to complete a task (number of workers and time to completion).
Identifying Inverse Variation in Word Problems
Word problems often present inverse variation scenarios indirectly. Look for keywords and phrases that indicate an inverse relationship:
- "varies inversely with"
- "is inversely proportional to"
- "decreases as...increases"
- "increases as...decreases"
- Situations where the product of two quantities remains constant.
Beyond the Basics: Joint and Combined Variation
While this guide focuses on simple inverse variation, it's important to be aware of more complex variations:
- Joint Variation: A variable varies jointly with two or more other variables if it is directly proportional to their product. For example, z = kxy.
- Combined Variation: A variable varies directly with one variable and inversely with another. For example, z = kx/y.
Understanding these variations expands your problem-solving capabilities in various contexts.
Conclusion
Inverse variation is a crucial mathematical concept with numerous practical applications. By understanding its principles, learning to construct and solve inverse variation equations, and recognizing its presence in word problems, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle complex problems across various fields. Remember the key characteristics: reciprocal relationship, hyperbolic graph, and constant product. Practice is key to mastering this important topic!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Function Of A Lacteal Is To Absorb
Mar 24, 2025
-
If Meiosis Did Not Occur In Sexually Reproducing Organisms
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Lateral Surface Area Of A Rectangular Prism
Mar 24, 2025
-
Acids Turn Litmus Paper What Color
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Mixed Number For 11 3
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write An Inverse Variation Equation That Relates X And Y . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
