Write 80 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
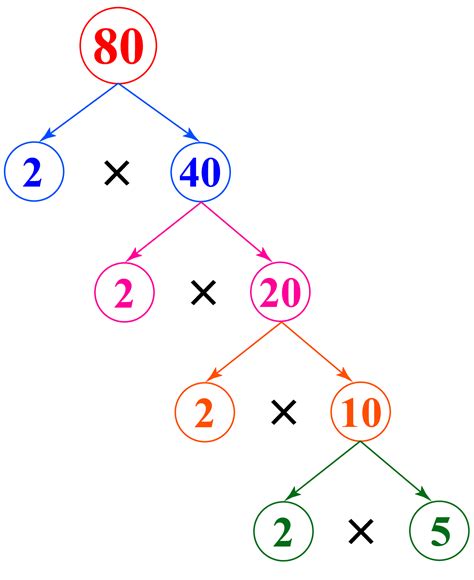
Table of Contents
Writing 80 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the prime factorization of a number is a fundamental concept in number theory. It's the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). This process is crucial in various mathematical applications, including cryptography and simplifying fractions. This article will delve deep into how to write 80 as a product of its prime factors, exploring different methods and highlighting the importance of prime factorization.
Understanding Prime Factorization
Before we tackle the specific example of 80, let's solidify the understanding of prime factorization. The fundamental theorem of arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (disregarding the order of the factors). This unique representation is called the prime factorization of the number. This theorem is the cornerstone of many number theory concepts.
For instance:
- 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3 Here, 2 and 3 are the prime factors of 12.
- 35 = 5 x 7 Here, 5 and 7 are the prime factors of 35.
- 100 = 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 = 2² x 5² Here, 2 and 5 are the prime factors of 100.
The process of finding the prime factorization involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until the result is 1.
Method 1: Factor Tree Method
The factor tree method is a visual approach that's particularly helpful for beginners. It's a systematic way to break down a number into its prime factors. Let's apply this method to 80:
- Start with the number 80.
- Find the smallest prime factor. The smallest prime factor of 80 is 2.
- Divide 80 by 2: 80 / 2 = 40
- Repeat the process with 40. The smallest prime factor of 40 is 2.
- Divide 40 by 2: 40 / 2 = 20
- Repeat with 20. The smallest prime factor of 20 is 2.
- Divide 20 by 2: 20 / 2 = 10
- Repeat with 10. The smallest prime factor of 10 is 2.
- Divide 10 by 2: 10 / 2 = 5
- The result is 5, which is a prime number.
Now, let's represent this visually as a factor tree:
80
/ \
2 40
/ \
2 20
/ \
2 10
/ \
2 5
Therefore, the prime factorization of 80 using the factor tree method is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 = 2⁴ x 5.
Method 2: Division Method
The division method is a more concise approach, particularly useful for larger numbers. It involves systematically dividing the number by its prime factors until you reach 1.
- Start with the number 80.
- Divide by the smallest prime factor (2): 80 / 2 = 40
- Divide the result (40) by the smallest prime factor (2): 40 / 2 = 20
- Divide the result (20) by the smallest prime factor (2): 20 / 2 = 10
- Divide the result (10) by the smallest prime factor (2): 10 / 2 = 5
- The result (5) is a prime number.
This process can be organized in a table:
| Number | Prime Factor | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 80 | 2 | 40 |
| 40 | 2 | 20 |
| 20 | 2 | 10 |
| 10 | 2 | 5 |
| 5 | 5 | 1 |
Therefore, the prime factorization of 80 using the division method is 2⁴ x 5.
Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of finding prime factors has far-reaching implications across numerous mathematical fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization is essential for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. By identifying common prime factors in the numerator and denominator, you can effectively reduce the fraction.
-
Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization forms the basis for efficiently determining the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. These concepts are crucial in various mathematical calculations.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are the foundation of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors is the key to the security of these systems.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Prime factorization plays a significant role in modular arithmetic, which is used extensively in computer science and cryptography.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization underpins many concepts in abstract algebra, a branch of mathematics dealing with algebraic structures.
-
Number Theory Research: Prime factorization is a continuous area of research in number theory, with ongoing efforts to develop more efficient algorithms for factoring large numbers.
Advanced Techniques for Prime Factorization
For very large numbers, the methods described above can become cumbersome. More advanced techniques, often implemented using computer algorithms, are employed:
-
Trial Division: This is a basic algorithm that systematically tests for divisibility by prime numbers. While simple, it's computationally expensive for very large numbers.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that's more efficient than trial division for finding small factors.
-
Quadratic Sieve and General Number Field Sieve: These are advanced algorithms used for factoring very large numbers, often employed in cryptography research.
Conclusion
Writing 80 as a product of its prime factors – 2⁴ x 5 – is a straightforward exercise that illustrates a fundamental concept in mathematics. While simple for smaller numbers, prime factorization is a powerful tool with broad applications across various mathematical disciplines and fields like computer science and cryptography. Mastering prime factorization not only strengthens your mathematical foundation but also provides a stepping stone for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts. Whether using the factor tree or division method, understanding the process and its significance is key to appreciating its value in the wider world of mathematics and beyond. The unique representation of any number as a product of its prime factors, as stated by the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, underlines the elegance and power of this fundamental mathematical operation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 10 And 20
Mar 17, 2025
-
Depression In Freezing Point Is A Colligative Property
Mar 17, 2025
-
Words That Starts With R And Ends With R
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lcm Of 12 9 And 6
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Are A Group Of Kangaroos Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write 80 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
