Write 45 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
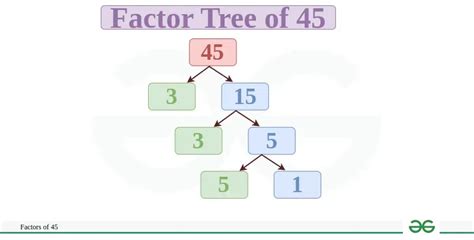
Table of Contents
Writing 45 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This seemingly simple process unlocks a wealth of understanding about numbers and their properties, revealing patterns and relationships that are fundamental to various mathematical applications. This article will delve into the prime factorization of 45, providing a detailed explanation and exploring its broader significance within mathematics. We'll go beyond simply stating the answer, examining the methods used, the importance of prime numbers, and the practical applications of this fundamental concept.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we embark on the factorization of 45, let's clarify some key definitions:
-
Prime Number: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other integers.
-
Composite Number: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. In other words, it can be expressed as a product of two or more smaller integers. For example, 4, 6, 9, 10, and 12 are composite numbers.
-
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This representation is unique for every composite number, meaning there's only one way to express it as a product of primes (disregarding the order of the factors).
Methods for Prime Factorization
Several methods can be employed to find the prime factorization of a number. Let's explore a few, focusing on their application to the number 45:
1. Factor Tree Method
This is a visually intuitive approach, particularly useful for smaller numbers like 45.
-
Start with the number: Begin with 45 at the top of your factor tree.
-
Find two factors: Find any two factors of 45. A simple choice is 5 and 9. Write these below 45, connected by branches.
-
Continue factoring: 9 is not a prime number; it can be further factored into 3 and 3. 5 is a prime number, so we stop branching from it.
-
Identify prime factors: The branches lead to the prime factors: 3, 3, and 5.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 45 using the factor tree method is 3 x 3 x 5, or 3² x 5.
(Illustrative Factor Tree would be visually represented here if this were a visual medium.)
2. Division Method
This method is more systematic and well-suited for larger numbers.
-
Divide by the smallest prime number: Start by dividing 45 by the smallest prime number, which is 2. Since 45 is not divisible by 2, we move to the next prime number, 3.
-
Repeated division: 45 ÷ 3 = 15. 15 is divisible by 3, resulting in 5.
-
Prime factor identification: 5 is a prime number, and the division process stops.
The prime factors obtained are 3, 3, and 5. Thus, the prime factorization of 45 is 3² x 5.
The Prime Factorization of 45: 3² x 5
The prime factorization of 45 is definitively 3² x 5. This means that 45 can be expressed as the product of two 3's and one 5. This representation is unique; no other combination of prime numbers will multiply to give 45.
Significance and Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has profound implications across various mathematical disciplines and practical applications:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization is crucial for finding the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD represents the largest number that divides all given numbers, while the LCM is the smallest number divisible by all given numbers. Finding these values simplifies calculations in many areas, including fraction simplification and solving algebraic equations.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers play a vital role in modern cryptography, forming the basis of many encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors underpins the security of these systems.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Prime factorization is essential in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography, computer science, and coding theory. Modular arithmetic involves operations on remainders after division by a certain number (the modulus).
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization and prime numbers are fundamental concepts in abstract algebra, a field that deals with algebraic structures like groups, rings, and fields. Prime ideals, a generalization of prime numbers, play a significant role in advanced algebraic studies.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is, of course, central to number theory itself. Many open problems and unsolved conjectures in number theory relate directly or indirectly to the properties of prime numbers and their distribution.
Beyond 45: Exploring Further
While we've focused on 45, the principles of prime factorization apply to any composite number. Let's briefly consider a few examples to illustrate the broader application:
- Prime factorization of 100: 2² x 5²
- Prime factorization of 120: 2³ x 3 x 5
- Prime factorization of 360: 2³ x 3² x 5
Observe how the prime factorization uniquely represents each number as a product of its prime constituents.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, despite its apparent simplicity, is a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications in mathematics and beyond. The process of breaking down a composite number into its prime factors offers valuable insights into the structure and properties of numbers, ultimately impacting various fields from cryptography to abstract algebra. Understanding the prime factorization of a number like 45, therefore, is not merely an exercise in arithmetic; it's a stepping stone to appreciating the deeper elegance and power of number theory. The unique representation offered by prime factorization allows for elegant solutions to complex problems, solidifying its importance as a cornerstone of mathematical exploration. The ability to readily perform prime factorization is a crucial skill for anyone pursuing advanced mathematical studies or working in fields reliant on number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Two Purines Bases In Dna Are
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of Eight
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Element Does Not Contain Any Neutrons
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is One Fifth As A Percentage
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Is Greater 2 5 Or 1 3
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write 45 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
