Which Element Does Not Contain Any Neutrons
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
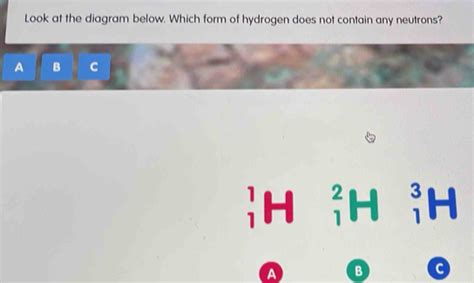
Table of Contents
Which Element Does Not Contain Any Neutrons?
The question of which element contains no neutrons is a deceptively simple one that leads us down a fascinating path exploring the very nature of atomic structure and the periodic table. While the vast majority of atoms contain neutrons in their nuclei, there is one element that exists with a naturally occurring isotope that bucks this trend. Let's delve into the details, exploring the roles of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and finally uncover the answer to our intriguing question.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we can identify the element lacking neutrons, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental building blocks of atoms:
-
Protons: Positively charged particles residing within the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the atomic number of an element and dictates its place on the periodic table. It is the fundamental characteristic that distinguishes one element from another.
-
Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also found within the atom's nucleus. Neutrons play a crucial role in stabilizing the nucleus, particularly in heavier elements where the repulsive forces between positively charged protons are strong.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, resulting in a net charge of zero. Electrons are involved in chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of an element.
Isotopes: Variations on a Theme
Most elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with varying numbers of neutrons. These variations in neutron count influence the atom's mass but don't alter its chemical behavior significantly. For example, carbon-12 (⁶C), carbon-13 (¹³C), and carbon-14 (¹⁴C) are all isotopes of carbon, each containing 6 protons but differing in their neutron count (6, 7, and 8 neutrons, respectively).
The Exceptional Case: Protium (Hydrogen-1)
The answer to our question lies with the simplest element: hydrogen. Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes:
-
Protium (¹H): This is the most common isotope of hydrogen, comprising about 99.98% of naturally occurring hydrogen. It contains one proton and zero neutrons. This is the exception that proves the rule – a stable atom without any neutrons.
-
Deuterium (²H or D): Containing one proton and one neutron.
-
Tritium (³H or T): Containing one proton and two neutrons; a radioactive isotope.
While deuterium and tritium are stable isotopes in the sense that they do not spontaneously decay, it's protium, the most abundant form of hydrogen, that uniquely lacks neutrons.
The Role of Neutrons in Nuclear Stability
The presence or absence of neutrons significantly impacts nuclear stability. For lighter elements, the neutron-to-proton ratio is close to 1:1. However, as the atomic number increases, the required number of neutrons increases more rapidly than the number of protons to overcome the strong repulsive forces between the positively charged protons within the nucleus. Without sufficient neutrons to act as a "nuclear glue," the nucleus becomes unstable and prone to radioactive decay.
This explains why heavier elements typically require a higher neutron-to-proton ratio for stability. The extra neutrons help to counteract the repulsive forces between protons, preventing the nucleus from disintegrating.
Why Protium Exists Without Neutrons
The stability of protium, despite its lack of neutrons, is attributable to its extremely small nucleus. The repulsive forces between the single proton are minimal, requiring no additional neutrons for stabilization. In contrast, heavier elements with multiple protons necessitate a significant neutron presence to maintain nuclear stability.
Implications and Applications
The unique properties of protium, particularly its lack of neutrons, have implications in several scientific fields:
-
Nuclear Fusion: Protium is a key component in nuclear fusion reactions, such as those occurring in the sun. Its simplicity contributes to the efficiency of these reactions.
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: Deuterium (²H) is used extensively in NMR spectroscopy as a labeling agent. Its different NMR properties compared to protium allow researchers to distinguish and track specific molecules or parts of molecules during experiments.
-
Isotope Studies: The differing abundances of protium, deuterium, and tritium can provide insights into various natural processes, including climate change research and hydrology studies.
Beyond Protium: Neutron-deficient Nuclei
While protium is the only naturally occurring element with a stable isotope lacking neutrons, it's important to note that artificially created isotopes of other elements can also exist with a very low number of neutrons or even a neutron deficiency. These isotopes are typically radioactive and highly unstable, with extremely short half-lives. Their creation usually occurs in high-energy particle accelerators or nuclear reactors. The study of these neutron-deficient nuclei contributes to our understanding of nuclear forces and decay processes.
Conclusion: The Unique Simplicity of Hydrogen
The question of which element doesn't contain neutrons highlights the fascinating nuances of atomic structure and the interplay between protons and neutrons in maintaining nuclear stability. While most elements rely on neutrons for nuclear stability, the simplest element, hydrogen, exists in a stable form – protium – completely lacking neutrons. This unique characteristic of protium has significant scientific implications across various fields and underscores the rich diversity of the elements in the periodic table. The study of isotopes and nuclear structure continues to expand our understanding of matter at its most fundamental level, unveiling more intricacies of the atomic world. The simple answer to our initial question – hydrogen – opens a door to a complex and compelling world of nuclear physics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Planets Closest To The Sun Are Known As The
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Purpose Of The Filament
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 10 And 11
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Is A Solution Different From A Mixture
Mar 18, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 3
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Element Does Not Contain Any Neutrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
