Volume Is The Amount Of Space A
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
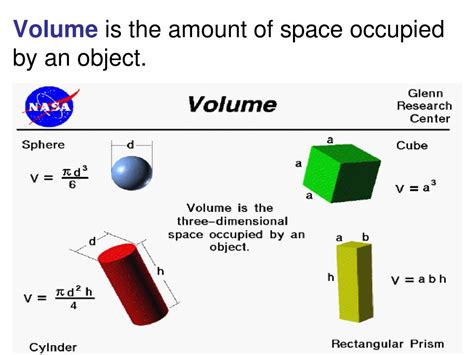
Table of Contents
Volume: The Amount of Space an Object Occupies
Volume, in its simplest definition, is the amount of three-dimensional space occupied by a substance or shape. It's a fundamental concept in geometry, physics, and various other scientific fields. Understanding volume is crucial for everything from calculating the capacity of a container to understanding the properties of matter. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of volume, exploring its calculation, units of measurement, and practical applications.
Understanding the Concept of Volume
Imagine filling a box with small cubes. The number of cubes needed to completely fill the box represents its volume. This simple analogy highlights the core idea: volume measures the internal capacity of an object or the space it encloses. Unlike area, which is a two-dimensional measurement, volume is a three-dimensional measurement, encompassing length, width, and height.
Distinguishing Volume from Other Measures
It's important to differentiate volume from other related concepts like:
-
Mass: Mass measures the amount of matter in an object, while volume measures the space it occupies. A kilogram of feathers will have a much larger volume than a kilogram of lead, even though their masses are equal.
-
Density: Density is the ratio of mass to volume. It describes how compactly matter is packed within a given space. A high-density material like gold will have a relatively small volume for a given mass, compared to a low-density material like wood.
-
Capacity: Capacity often refers to the volume a container can hold. While closely related to volume, capacity emphasizes the container's ability to contain a substance.
Units of Volume Measurement
The units used to measure volume vary depending on the context and the system of measurement employed. The most common units include:
-
Cubic meter (m³): The standard unit of volume in the International System of Units (SI). It represents the volume of a cube with sides of one meter each.
-
Cubic centimeter (cm³): A smaller unit, often used for measuring the volume of smaller objects or liquids. One cubic centimeter is equivalent to one milliliter (ml).
-
Liter (L): A common unit for measuring liquid volume. One liter is equal to 1000 cubic centimeters or 0.001 cubic meters.
-
Gallon (gal): A unit of volume commonly used in the United States and some other countries. Its exact size varies depending on the country.
-
Cubic foot (ft³): Used primarily in the imperial system, often for measuring larger volumes.
-
Cubic inch (in³): Another imperial unit, suitable for smaller volumes.
Converting Between Units
Converting between different units of volume involves using conversion factors. For example:
- 1 m³ = 1,000,000 cm³
- 1 L = 1000 cm³ = 1000 ml
- 1 gal ≈ 3.785 L
Accurate conversions are crucial in many scientific and engineering applications.
Calculating the Volume of Different Shapes
The method for calculating volume depends heavily on the shape of the object. Here's a breakdown of common shapes and their respective volume formulas:
1. Cube and Rectangular Prism (Cuboid)
These are the simplest shapes to calculate volume for. The formula is:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
For a cube, all three dimensions are equal.
2. Sphere
The volume of a sphere is given by the formula:
Volume = (4/3)πr³
where 'r' is the radius of the sphere and 'π' (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
3. Cylinder
The volume of a cylinder is calculated using:
Volume = πr²h
where 'r' is the radius of the base and 'h' is the height of the cylinder.
4. Cone
The volume of a cone is:
Volume = (1/3)πr²h
Again, 'r' represents the radius of the base and 'h' represents the height.
5. Pyramid
The volume of a pyramid is given by:
Volume = (1/3)Bh
where 'B' is the area of the base and 'h' is the height of the pyramid. The formula for 'B' will vary depending on the shape of the base (square, triangle, etc.).
6. Irregular Shapes
Calculating the volume of irregularly shaped objects can be more challenging. One common method is water displacement. By submerging the object in a container of water and measuring the change in water level, the volume of the object can be determined. Another method involves using integration techniques in calculus.
Applications of Volume Measurement
Volume measurement plays a crucial role in numerous fields:
1. Engineering and Construction
Calculating volumes is essential for designing structures, estimating material quantities, and determining the capacity of reservoirs, tanks, and pipes. Accurate volume calculations ensure efficient resource management and structural integrity.
2. Medicine and Healthcare
Volume measurements are crucial in various medical applications, including determining dosages of medications, analyzing blood samples, and assessing organ sizes. Accurate volume measurement ensures proper medical treatment and diagnosis.
3. Environmental Science
Measuring the volume of pollutants in water bodies or the volume of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is critical for environmental monitoring and protection. This data informs environmental policies and conservation efforts.
4. Manufacturing and Industry
Volume calculations are vital in manufacturing processes, helping determine the size and capacity of containers, packaging, and production equipment. Accurate volume measurements ensure efficient production and minimize waste.
5. Meteorology and Oceanography
Measuring the volume of rainfall, snow, or ocean currents is important for understanding weather patterns, predicting natural disasters, and managing water resources. These volume measurements provide insights into climate change and its impacts.
6. Food and Beverage Industry
Volume measurement is fundamental in food and beverage production, ensuring accurate packaging, portion control, and efficient distribution. Accurate volume ensures consistency and quality control.
Advanced Concepts in Volume
Beyond the basic calculations, more advanced concepts related to volume include:
-
Volume integrals: Calculus provides methods for calculating the volumes of complex shapes using integration techniques.
-
Differential volume elements: Infinitesimally small volumes are used in advanced calculations to determine the volume of intricate objects.
-
Volume in higher dimensions: The concept of volume can be extended to higher dimensions beyond the three-dimensional space we experience.
-
Archimedes' principle: This principle relates the volume of a submerged object to the buoyant force it experiences.
Conclusion
Volume, a fundamental concept in science and engineering, encompasses the amount of three-dimensional space occupied by an object or substance. Understanding its calculation, units, and applications is crucial across various fields. From simple geometric shapes to complex irregular objects, mastering the concept of volume is essential for solving problems and understanding the world around us. The ability to accurately measure and calculate volume is a key skill that contributes to advancements in technology, medicine, environmental science, and countless other areas. As we continue to explore the complexities of the universe, the concept of volume remains a cornerstone of our scientific understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 2 8 As A Percent
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is 95 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Subatomic Particle That Has No Charge
Mar 18, 2025
-
Does A Circle Have A Corner
Mar 18, 2025
-
Why Do We Look Like Our Parents
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Volume Is The Amount Of Space A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
