Write 40 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
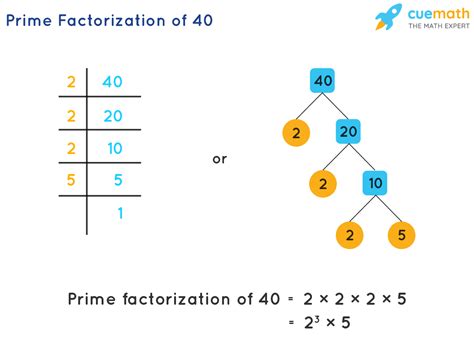
Table of Contents
Writing 40 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, the process of breaking down a number into its prime number components, is a fundamental concept in number theory. It's a cornerstone of various mathematical applications, from cryptography to simplifying fractions. This article will meticulously explore the prime factorization of 40, demonstrating the process step-by-step and then extending the discussion to encompass broader concepts within prime factorization and its practical uses.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before diving into the factorization of 40, let's establish a clear understanding of the key terms:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Note that 1 is not considered a prime number.
Prime Factorization: This is the process of expressing a composite number (a number that is not prime) as a product of its prime factors. Each composite number has a unique prime factorization, meaning there's only one way to represent it as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors).
Factorizing 40: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's break down 40 into its prime factors. We can use a factor tree method or repeated division.
Method 1: Factor Tree
-
Start with 40: Begin by finding any two factors of 40. A simple choice is 4 and 10.
40 / \ 4 10 -
Continue Factoring: Now, factor each of these numbers. 4 can be factored into 2 x 2, and 10 can be factored into 2 x 5.
40 / \ 4 10 / \ / \ 2 2 2 5 -
Identify Prime Factors: All the numbers at the bottom of the tree (2, 2, 2, and 5) are prime numbers. Therefore, the prime factorization of 40 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 5, or 2³ x 5.
Method 2: Repeated Division
-
Start with 40: Begin by dividing 40 by the smallest prime number, which is 2. 40 ÷ 2 = 20.
-
Continue Dividing: Continue dividing the result by the smallest prime number possible. 20 ÷ 2 = 10; 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
-
Stop at a Prime Number: Since 5 is a prime number, we stop here.
-
Write the Prime Factorization: The prime factors are the numbers we divided by (2, 2, 2, and 5). Therefore, the prime factorization of 40 is 2³ x 5.
Both methods yield the same result: 40 = 2³ x 5
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The fact that 40 has only one prime factorization (2³ x 5) is not a coincidence. This is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, a cornerstone of number theory. This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (disregarding the order of the factors). This uniqueness is crucial in many mathematical applications.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, while seemingly simple, has profound applications across various fields:
-
Cryptography: Modern encryption methods, particularly RSA cryptography, heavily rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring huge numbers with hundreds of digits.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers is simplified using prime factorization. To reduce a fraction to its simplest form, you find the GCD of the numerator and denominator. Prime factorization makes finding the GCD much easier.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is central to many number theory concepts, including modular arithmetic, which finds applications in computer science and cryptography. It helps in understanding the properties of numbers and their relationships.
-
Solving Diophantine Equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions to polynomial equations. Prime factorization techniques can be helpful in solving certain types of Diophantine equations.
Beyond 40: Exploring Other Factorizations
Let's extend our understanding by looking at a few more examples of prime factorization:
-
Factorizing 72:
Following the same methods as with 40, we find that 72 = 2³ x 3².
-
Factorizing 105:
105 = 3 x 5 x 7
-
Factorizing 252:
252 = 2² x 3² x 7
These examples illustrate the versatility of prime factorization across different numbers. The process remains consistent, regardless of the number's size or complexity.
Identifying Prime Factors: Helpful Techniques
While small numbers are easy to factor, larger numbers require more strategic approaches. Here are some helpful techniques:
-
Trial Division: Systematically try dividing the number by prime numbers, starting with the smallest (2, 3, 5, 7, etc.).
-
Divisibility Rules: Knowing divisibility rules for small prime numbers (e.g., a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3) can speed up the process.
-
Factorization Algorithms: For extremely large numbers, specialized algorithms like the quadratic sieve and the general number field sieve are used. These algorithms are computationally intensive but are essential for breaking some encryption methods.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of writing 40 as a product of its prime factors (2³ x 5) opens the door to a vast and fascinating world of number theory and its applications. Understanding prime factorization is crucial for anyone interested in mathematics, computer science, or cryptography. Its importance extends beyond simple calculations, reaching into the core of many advanced mathematical and computational techniques. By mastering this fundamental concept, we unlock a deeper understanding of the structure and properties of numbers themselves. From simple examples like 40 to astronomically large numbers, the principles remain consistent, highlighting the power and elegance of prime factorization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Latitude And Longitude Of Delhi India
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Is The Cell Membrane Said To Be Selectively Permeable
Mar 19, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Ending In Eat
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Hardest Tissue In The Body
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is Prime Factorization Of 84
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write 40 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
