What Is Prime Factorization Of 84
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
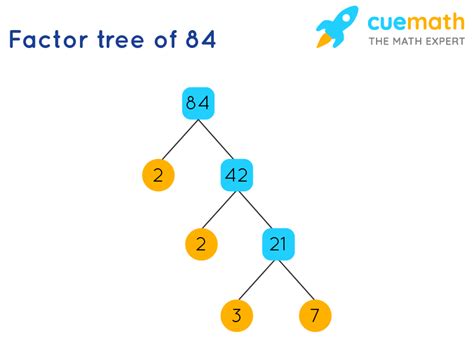
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 84? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Understanding this process unlocks deeper insights into number properties and forms the basis for various mathematical applications. This article will explore the prime factorization of 84 in detail, covering the fundamental concepts, the step-by-step process, and its broader significance in mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before diving into the prime factorization of 84, let's clarify some essential terms:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. In essence, it's a number that can be factored into smaller positive integers. The number 84, which we'll be focusing on, is a composite number.
Prime Factorization: This process involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Each prime factor will only appear once in this representation. This unique factorization is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, a crucial theorem in number theory.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 84: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several methods to find the prime factorization of a number. Let's explore a common approach using a factor tree:
Step 1: Find the Smallest Prime Factor
The smallest prime number is 2. We check if 84 is divisible by 2. Since 84 is an even number, it's divisible by 2.
84 ÷ 2 = 42
Step 2: Continue Factoring
Now, we focus on the result, 42. Is 42 divisible by 2? Yes, it is.
42 ÷ 2 = 21
Step 3: Move to the Next Prime
21 is not divisible by 2. The next prime number is 3. Is 21 divisible by 3? Yes, it is.
21 ÷ 3 = 7
Step 4: Identify the Prime Factor
The result, 7, is itself a prime number. This signifies that we have reached the end of our factorization.
Step 5: Write the Prime Factorization
By combining the prime factors obtained in each step, we find the prime factorization of 84:
2 x 2 x 3 x 7 = 2² x 3 x 7
This demonstrates that 84 can be expressed as the product of the prime numbers 2, 2, 3, and 7. The exponent 2 indicates that the prime factor 2 appears twice in the factorization.
Alternative Methods for Prime Factorization
While the factor tree method is visually intuitive, other approaches exist, particularly useful for larger numbers:
Division Method: This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until you reach 1. Let's demonstrate with 84:
- 84 ÷ 2 = 42
- 42 ÷ 2 = 21
- 21 ÷ 3 = 7
- 7 ÷ 7 = 1
The prime factors are the divisors used: 2, 2, 3, and 7, leading to the same prime factorization: 2² x 3 x 7.
Using a Prime Factorization Calculator: For larger numbers, online prime factorization calculators can streamline the process. These tools use optimized algorithms to efficiently determine the prime factors. However, understanding the manual methods remains crucial for grasping the underlying concepts.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
Beyond its inherent mathematical interest, prime factorization holds significant applications in various fields:
Cryptography: Prime factorization is fundamental to many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components underpins the security of systems like RSA encryption, protecting sensitive data online.
Number Theory Research: Prime factorization plays a vital role in advanced number theory research. Questions related to prime distribution, gaps between primes, and the search for large prime numbers are actively explored by mathematicians worldwide.
Computer Science: Algorithms related to prime factorization are used in areas such as computer security, random number generation, and efficient data structures.
Coding Theory: Prime numbers and prime factorization find applications in coding theory, particularly in error-correcting codes used in data transmission and storage.
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in abstract algebra, underpinning the study of rings, fields, and modular arithmetic.
Exploring the Divisors of 84 using Prime Factorization
Understanding the prime factorization of 84 also allows us to easily determine all of its divisors. A divisor is a number that divides another number without leaving a remainder.
To find all divisors, we consider all possible combinations of the prime factors (2, 2, 3, and 7):
- 1 (the trivial divisor)
- 2
- 3
- 7
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 2 x 7 = 14
- 3 x 7 = 21
- 2 x 2 x 3 = 12
- 2 x 2 x 7 = 28
- 2 x 3 x 7 = 42
- 2 x 2 x 3 x 7 = 84
Therefore, the divisors of 84 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 12, 14, 21, 28, 42, and 84.
Prime Factorization and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
Prime factorization is a powerful tool for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
Let's find the GCD of 84 and another number, say 126.
First, we find the prime factorization of 126:
126 = 2 x 3² x 7
Now, we compare the prime factorizations of 84 (2² x 3 x 7) and 126 (2 x 3² x 7):
- Both numbers share a factor of 2.
- Both numbers share a factor of 3.
- Both numbers share a factor of 7.
To find the GCD, we take the lowest power of each common prime factor:
GCD(84, 126) = 2¹ x 3¹ x 7¹ = 42
Therefore, the greatest common divisor of 84 and 126 is 42.
Prime Factorization and the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Similarly, prime factorization helps us find the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
Let's find the LCM of 84 and 126 using their prime factorizations:
84 = 2² x 3 x 7 126 = 2 x 3² x 7
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
LCM(84, 126) = 2² x 3² x 7 = 4 x 9 x 7 = 252
Therefore, the least common multiple of 84 and 126 is 252.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 84, expressed as 2² x 3 x 7, is more than just a simple mathematical result. It exemplifies a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications in various fields. Understanding prime factorization allows us to delve deeper into the structure of numbers, solve problems related to divisors and multiples, and appreciate its crucial role in advanced mathematical concepts and applications in computer science and cryptography. The seemingly simple act of factoring a number reveals the elegance and power of fundamental mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Secondary Structure Of Dna
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Multiples Of 40
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 60 And 24
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Is Frequency And Amplitude Related
Mar 19, 2025
-
Square Root Of 80 In Simplest Radical Form
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 84 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
