Which Type Of Plastids Store Food
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
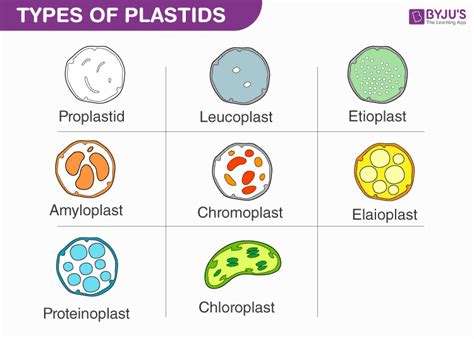
Table of Contents
Which Type of Plastids Store Food? A Deep Dive into the World of Plant Cell Organelles
Plastids are essential double-membrane-bound organelles found in plant cells and some other eukaryotic organisms. These versatile organelles play crucial roles in various cellular processes, including photosynthesis, storage of various substances, and pigment synthesis. While many types of plastids exist, a key function of some is the storage of food reserves, vital for the plant's survival and growth. This article will delve into the specific types of plastids responsible for food storage, examining their structure, function, and the types of food substances they accumulate.
The Amazing World of Plastids: A Brief Overview
Before focusing on food-storing plastids, let's briefly explore the diverse world of plastids. These organelles are broadly classified into several types, each specialized for a particular function:
-
Chloroplasts: These are the most well-known plastids, responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, the green pigment that captures light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the plant's primary source of energy.
-
Chromoplasts: These plastids are responsible for the synthesis and storage of carotenoid pigments, giving fruits, flowers, and leaves their characteristic yellow, orange, or red colors. While they may contain some stored food reserves, their primary role is not food storage.
-
Leucoplasts: These are colorless plastids, lacking pigments. They are involved in storing various substances, and this group includes the plastids responsible for food storage. We will explore the different types of leucoplasts in detail below.
-
Gerontoplasts: These are senescent chloroplasts, essentially aged chloroplasts undergoing degradation. They are not directly involved in food storage.
-
Etioplasts: These are immature chloroplasts found in plants grown in the dark. They develop into chloroplasts upon exposure to light. They do not have a significant role in food storage.
Leucoplasts: The Primary Food Storage Plastids
Leucoplasts are the main players in food storage within plant cells. Unlike chloroplasts with their vibrant green color, leucoplasts are colorless, reflecting their lack of photosynthetic pigments. Their structure, however, is similar to other plastids, featuring a double membrane and an internal membrane system. Depending on the type of substance they store, leucoplasts are further classified into several types:
1. Amyloplasts: The Starch Storages
Amyloplasts are specialized leucoplasts that store starch. Starch is a complex carbohydrate composed of glucose units, representing a crucial energy reserve for the plant. Amyloplasts are particularly abundant in storage organs such as roots (e.g., potatoes), tubers, and seeds. The starch grains within amyloplasts are highly organized structures, with characteristic layering patterns that reflect the way glucose units are deposited.
Key features of amyloplasts:
- Abundant in storage tissues: These plastids are strategically located in tissues dedicated to storing energy reserves.
- Starch grain formation: The precise arrangement of starch within amyloplasts is a fascinating example of cellular organization.
- Dynamic nature: Amyloplasts can be dynamic, changing size and starch content depending on the plant's metabolic needs.
2. Elaioplasts: The Lipid Reservoirs
Elaioplasts are leucoplasts specialized in storing lipids, or fats. These fats provide another significant energy reserve for the plant, particularly important during periods of low photosynthetic activity or during seed germination. Elaioplasts are commonly found in seeds and other plant tissues requiring energy-rich reserves.
Key features of elaioplasts:
- Lipid droplet accumulation: The lipid storage within elaioplasts is organized as distinct droplets.
- Important for seed germination: The stored lipids are crucial for fueling the initial growth of seedlings.
- Distribution across plant tissues: While concentrated in seeds, they may also be present in other parts of the plant.
3. Proteinoplasts: Protein Storage Specialists
Proteinoplasts are leucoplasts specialized for storing proteins. These proteins serve as building blocks for various cellular structures and enzymes, and their storage in proteinoplasts ensures a readily available source of these essential molecules. Proteinoplasts are especially common in seeds, providing essential amino acids for seedling development.
Key features of proteinoplasts:
- Crystalline protein inclusion: Proteins often appear as crystalline structures within proteinoplasts.
- Essential for seedling growth: The stored proteins are crucial for the rapid growth of seedlings after germination.
- Diverse protein content: Proteinoplasts can store a variety of proteins with different functions.
The Interplay Between Plastid Types and Plant Life Cycle
The different types of plastids, including the food-storing leucoplasts, play crucial roles throughout a plant's life cycle. During seed development, for example, amyloplasts, elaioplasts, and proteinoplasts accumulate significant reserves to support the germination process and early seedling growth. In mature plants, amyloplasts in storage organs maintain energy reserves, while in other tissues, chloroplasts focus on photosynthesis. As plants age, some plastids may undergo changes, such as chloroplasts transforming into gerontoplasts. This complex interplay of plastid types ensures that plants efficiently use resources for growth, reproduction, and survival.
Factors Affecting Food Storage in Plastids
Several factors influence the amount and type of food stored in plastids:
- Genetics: The genetic makeup of the plant determines the capacity of its cells to produce and store specific food reserves.
- Environmental conditions: Factors such as light intensity, temperature, water availability, and nutrient levels significantly impact the accumulation of food reserves in plastids.
- Developmental stage: The developmental stage of the plant influences the activity of plastids and their storage capacity.
- Hormonal regulation: Plant hormones play a crucial role in regulating the processes of food synthesis and storage within plastids.
The Importance of Food Storage Plastids in Human Life
The food-storing plastids in plants are not only essential for plant survival but also have a significant impact on human life. Many staple crops, including potatoes, rice, corn, and wheat, rely heavily on amyloplasts for starch storage, providing a fundamental source of carbohydrates in the human diet. Furthermore, seeds rich in lipids stored in elaioplasts and proteins stored in proteinoplasts are crucial sources of essential nutrients. Understanding the biology of food-storing plastids is therefore crucial for improving crop yields and ensuring food security.
Conclusion: A Vital Component of Plant Life
The various types of plastids, particularly the leucoplasts specialized for food storage (amyloplasts, elaioplasts, and proteinoplasts), are essential components of plant cells. Their role in storing energy reserves in the form of starch, lipids, and proteins is vital for plant growth, development, and survival. This intricate cellular machinery is not only crucial for plants themselves but also significantly contributes to the human food supply. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complex processes involved in plastid development, function, and regulation, paving the way for improvements in agriculture and our understanding of plant biology. This deeper understanding is crucial for addressing global challenges related to food security and sustainable agriculture. The fascinating world of plastids continues to hold many secrets, and future research promises to unveil even more about their vital contributions to plant life and our own.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
John Drives To His Workplace And Back Home
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Division Of Cytoplasm Called
Mar 25, 2025
-
3 1 8 As A Decimal
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is A Factor Of 5
Mar 25, 2025
-
List Three Similarities Between Dna And Rna
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Type Of Plastids Store Food . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
