Which Terms Are Used To Identify Pure Substances
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
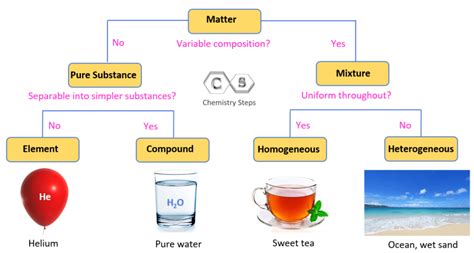
Table of Contents
Which Terms Are Used to Identify Pure Substances?
The world around us is a complex mixture of substances, but understanding the fundamental building blocks—pure substances—is crucial in chemistry and many other scientific disciplines. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the terminology used to identify pure substances, exploring their characteristics, classifications, and the subtle nuances that distinguish them from mixtures. We'll also touch upon practical applications and examples to solidify your understanding.
Defining Pure Substances: A Foundation
A pure substance is defined as a form of matter that has a constant chemical composition and consistent properties throughout a sample. This means that no matter where you take a sample from a specific pure substance (provided it's not contaminated), its chemical makeup and physical properties will remain identical. This contrasts sharply with mixtures, where the composition varies depending on the sample location.
The key characteristic of a pure substance is its uniformity. This uniformity extends to both its macroscopic properties (observable with the naked eye or simple instruments) and its microscopic properties (at the atomic or molecular level).
Distinguishing Pure Substances from Mixtures: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between pure substances and mixtures is fundamental. Here's a table highlighting their key differences:
| Feature | Pure Substance | Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Constant and uniform throughout the sample | Variable, depending on the sample location |
| Properties | Consistent physical and chemical properties | Properties vary depending on composition |
| Separation | Cannot be separated into simpler components by physical methods | Can be separated into its components by physical methods |
| Melting/Boiling Point | Sharp, well-defined melting and boiling points | Range of melting and boiling points |
Classifying Pure Substances: Elements and Compounds
Pure substances fall into two primary categories:
-
Elements: These are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are composed of only one type of atom. The periodic table organizes and displays all known elements. Examples include:
- Oxygen (O): A crucial element for respiration and combustion.
- Hydrogen (H): The lightest element, a component of water and many organic compounds.
- Gold (Au): A valuable metal prized for its inertness and beauty.
- Iron (Fe): A strong and versatile metal used in construction and manufacturing.
-
Compounds: These are pure substances formed by the chemical combination of two or more different elements in fixed proportions. The properties of a compound are distinctly different from the properties of its constituent elements. Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances (their constituent elements) only through chemical means. Examples include:
- Water (H₂O): Composed of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, essential for life.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Table salt, formed from sodium and chlorine atoms.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A greenhouse gas crucial in the carbon cycle.
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): A simple sugar vital for energy metabolism.
Identifying Compounds: Chemical Formulas and Nomenclature
Compounds are precisely identified using chemical formulas. These formulas indicate the types of atoms present and their relative ratios within the compound. For example, H₂O indicates that one molecule of water contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical nomenclature provides a systematic way of naming compounds based on their composition and structure. Understanding chemical formulas and nomenclature is critical for accurately identifying and describing compounds.
Exploring the Properties of Pure Substances
Pure substances exhibit characteristic properties that are consistent and predictable. These properties can be classified as:
-
Physical Properties: These are properties that can be observed or measured without changing the chemical composition of the substance. Examples include:
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid transitions to a liquid.
- Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid transitions to a gas.
- Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance.
- Color: The visual appearance of a substance.
- Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
- Conductivity: The ability of a substance to conduct electricity or heat.
-
Chemical Properties: These describe how a substance reacts with other substances. Observing chemical properties requires a chemical change (a reaction) that alters the substance's composition. Examples include:
- Reactivity with acids: How a substance reacts when exposed to acids.
- Flammability: The ability of a substance to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Oxidation: The tendency of a substance to react with oxygen.
- Decomposition: The breaking down of a substance into simpler components.
The consistent and predictable nature of these properties is a hallmark of pure substances and aids in their identification and characterization.
Advanced Concepts: Allotropes and Isotopes
The world of pure substances gets even more nuanced when we consider:
-
Allotropes: These are different structural modifications of the same element. While composed of the same type of atom, allotropes differ in their arrangement and bonding, leading to distinct physical and chemical properties. For example, carbon exists as diamond (strong, hard), graphite (soft, slippery), and fullerenes (unique molecular structures).
-
Isotopes: These are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. Isotopes have the same chemical properties but slightly different physical properties due to their different masses. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
Practical Applications and Examples
The identification of pure substances is crucial in numerous fields:
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: The purity of drugs is paramount for safety and efficacy. Impurities can lead to adverse effects or reduced effectiveness. Rigorous techniques are used to ensure the purity of pharmaceutical compounds.
-
Materials Science: Developing new materials often involves understanding the properties of pure substances and how they interact. The characteristics of pure metals and their alloys are crucial in engineering applications.
-
Environmental Science: Identifying pollutants and contaminants requires precise determination of the chemical composition of samples. Pure substances serve as benchmarks against which the purity of environmental samples is compared.
-
Food Science: The purity of food ingredients influences food safety, quality, and nutritional value. The analysis of pure substances allows for the detection of adulteration and ensures quality control.
Conclusion: The Importance of Precise Identification
Accurately identifying pure substances relies on a combination of careful observation, precise measurements, and an understanding of their inherent properties. From the simple elements on the periodic table to complex organic compounds, consistent terminology, precise chemical formulas, and rigorous analytical techniques are indispensable tools for characterizing these fundamental building blocks of matter. Understanding pure substances is a cornerstone of scientific progress and crucial across numerous fields. The knowledge presented here provides a solid foundation for anyone seeking to delve deeper into the fascinating world of chemistry and materials science.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Are In 12 Gallons
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are All Of The Factors Of 63
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Blood A Mixture Or Compound
Mar 19, 2025
-
Composition Of Functions Examples With Answers
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Neon A Metal Or Nonmetal
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Terms Are Used To Identify Pure Substances . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
