Composition Of Functions Examples With Answers
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
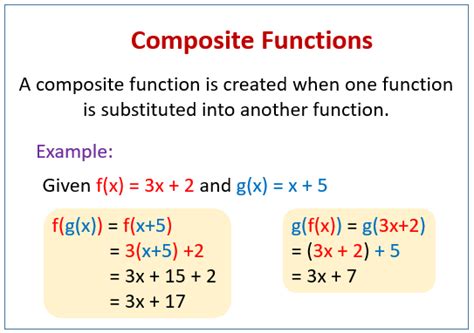
Table of Contents
Composition of Functions: Examples with Detailed Answers
Understanding composition of functions is crucial for anyone studying algebra, calculus, or any field that utilizes mathematical functions. It's a fundamental concept that builds a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical operations. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the concept of function composition, providing numerous examples with detailed solutions to solidify your understanding. We'll explore various types of functions and demonstrate how to compose them effectively. By the end, you'll be confident in your ability to tackle composition problems of varying complexity.
What is Composition of Functions?
Function composition is a mathematical operation that combines two or more functions to create a new function. The output of one function becomes the input of the next. This is often represented as (f ∘ g)(x), which reads as "f composed with g of x," or "f of g of x." It essentially means we apply function g to x first, and then apply function f to the result.
Formally: The composition of two functions, f and g, is defined as:
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x))
This means we substitute the expression for g(x) into the function f wherever we see x.
Examples of Composition of Functions
Let's delve into a series of examples with detailed step-by-step solutions to illustrate the process of function composition.
Example 1: Linear Functions
Let f(x) = 2x + 1 and g(x) = x - 3. Find (f ∘ g)(x) and (g ∘ f)(x).
Solution:
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x - 3) = 2(x - 3) + 1 = 2x - 6 + 1 = 2x - 5
In this case, we substituted (x - 3) for x in the function f(x).
(g ∘ f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g(2x + 1) = (2x + 1) - 3 = 2x - 2
Here, we substituted (2x + 1) for x in the function g(x). Note that (f ∘ g)(x) and (g ∘ f)(x) are generally not equal. The order of composition matters!
Example 2: Quadratic and Linear Functions
Let f(x) = x² and g(x) = x + 2. Find (f ∘ g)(x) and (g ∘ f)(x).
Solution:
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x + 2) = (x + 2)² = x² + 4x + 4
(g ∘ f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g(x²) = x² + 2
Again, we observe that the order of composition significantly impacts the resulting function.
Example 3: Evaluating a Composition at a Specific Point
Let f(x) = √x and g(x) = x - 4. Find (f ∘ g)(9).
Solution:
First, we find the composition (f ∘ g)(x):
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x - 4) = √(x - 4)
Now, we substitute x = 9:
(f ∘ g)(9) = √(9 - 4) = √5
Example 4: Composition with Trigonometric Functions
Let f(x) = sin(x) and g(x) = 2x. Find (f ∘ g)(π/4).
Solution:
First, find the composition:
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(2x) = sin(2x)
Now substitute x = π/4:
(f ∘ g)(π/4) = sin(2 * π/4) = sin(π/2) = 1
Example 5: Composition with More Complex Functions
Let f(x) = (x + 1)/(x - 1) and g(x) = 1/x. Find (f ∘ g)(x) and specify the domain.
Solution:
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(1/x) = ((1/x) + 1)/((1/x) - 1)
To simplify, multiply the numerator and denominator by x:
(f ∘ g)(x) = (1 + x)/(1 - x)
Domain: The domain of (f ∘ g)(x) is all real numbers except x = 1 (because this makes the denominator zero) and x = 0 (because g(x) is undefined at x = 0). Therefore, the domain is (-∞, 0) U (0, 1) U (1, ∞).
Example 6: Composition Involving Absolute Value Functions
Let f(x) = |x| and g(x) = x - 5. Find (f ∘ g)(x) and (g ∘ f)(x).
Solution:
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x - 5) = |x - 5|
(g ∘ f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g(|x|) = |x| - 5
Example 7: Composition of Polynomial Functions
Let f(x) = x³ + 2x and g(x) = x² - 1. Find (f ∘ g)(2).
Solution:
First, find (f ∘ g)(x):
(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x² - 1) = (x² - 1)³ + 2(x² - 1) = x⁶ - 3x⁴ + 3x² - 1 + 2x² - 2 = x⁶ - 3x⁴ + 5x² - 3
Now, substitute x = 2:
(f ∘ g)(2) = 2⁶ - 3(2⁴) + 5(2²) - 3 = 64 - 48 + 20 - 3 = 33
Understanding the Domain and Range of Composite Functions
The domain of a composite function (f ∘ g)(x) is the set of all x values such that x is in the domain of g(x), and g(x) is in the domain of f(x). In simpler terms, you need to consider the restrictions on both the inner and outer functions.
The range of a composite function is the set of all possible output values of (f ∘ g)(x). This often requires careful analysis of the functions involved.
Applications of Composition of Functions
Composition of functions isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has significant applications in various fields:
- Physics: Modeling complex systems often involves composing functions representing different physical processes.
- Computer Science: Composition is essential in functional programming, where functions are treated as first-class citizens.
- Economics: Modeling economic relationships may involve composing functions to represent different economic factors.
- Engineering: Designing and analyzing systems often requires composing functions to represent different components.
Conclusion
Mastering function composition is a key skill for success in mathematics and related fields. Through consistent practice and understanding of the underlying principles, you can confidently tackle complex compositions and appreciate their practical applications. Remember to always pay close attention to the order of composition and the domains of the individual functions to avoid errors. The examples provided here, along with the detailed solutions, offer a strong foundation for further exploration and problem-solving. Continue practicing with diverse function types to build your proficiency and confidence in this essential mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Temperature At Which A Liquid Changes To A Gas
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Rectangle Has How Many Sides
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Factors Of 55
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Stage Of Mitosis Is Essentially The Reverse Of Prophase
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Blood An Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Composition Of Functions Examples With Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
