Which Of The Following Is False
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
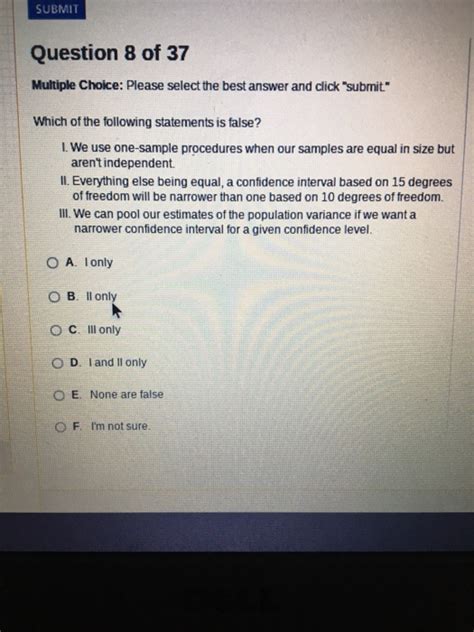
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is False: Mastering the Art of Identifying Incorrect Statements
Identifying false statements is a crucial skill applicable across various fields, from standardized testing and academic pursuits to critical thinking in everyday life and professional decision-making. This ability hinges on careful analysis, logical reasoning, and a deep understanding of the subject matter. This article delves into the strategies and techniques for effectively discerning false statements, exploring common pitfalls and offering practical examples to enhance your critical thinking prowess.
Understanding the Nature of False Statements
Before we delve into strategies, it's crucial to understand what constitutes a false statement. A false statement, simply put, is a claim that doesn't align with reality or established facts. This can manifest in several ways:
-
Factual Inaccuracies: The statement presents information that is demonstrably incorrect or unsupported by evidence. This is the most straightforward type of false statement.
-
Logical Fallacies: The statement uses flawed reasoning, even if the individual components might seem plausible. This often involves errors in deduction, induction, or other forms of logical argumentation.
-
Misleading Information: The statement might be technically true but presented in a way that distorts the reality or creates a false impression. This often involves omitting crucial details or using ambiguous language.
-
Contradictions: The statement contradicts itself or other established facts within the same context.
-
Ambiguity and Vagueness: The statement uses language that is unclear, imprecise, or open to multiple interpretations, making it impossible to assess its truthfulness definitively.
Strategies for Identifying False Statements
Identifying a false statement often requires a multi-pronged approach. Here's a breakdown of effective strategies:
1. Fact-Checking and Verification:
This is the cornerstone of identifying false statements. Whenever you encounter a claim, especially if it seems unusual or controversial, immediately cross-reference it with reliable sources. Reputable sources include peer-reviewed academic journals, established news organizations, and government websites. Avoid relying solely on social media or unverified online sources.
Example: A statement claiming that "The Earth is flat" can be easily debunked by consulting numerous scientific sources providing overwhelming evidence of the Earth's spherical shape.
2. Analyzing the Logic and Reasoning:
Examine the structure of the statement itself. Look for logical fallacies, such as:
- Hasty Generalization: Drawing a broad conclusion based on limited evidence.
- Appeal to Authority: Accepting a claim as true solely because an authority figure asserts it, without considering other evidence.
- Appeal to Emotion: Manipulating emotions rather than presenting rational arguments.
- False Dilemma (Either/Or Fallacy): Presenting only two options when more exist.
- Straw Man Fallacy: Misrepresenting an opponent's argument to make it easier to attack.
- Ad Hominem: Attacking the person making the claim instead of addressing the claim itself.
Example: A statement like, "All politicians are corrupt because I know one who is dishonest," represents a hasty generalization. The experience with one individual doesn't necessarily reflect the entire group.
3. Examining the Source's Credibility:
Consider the source of the information. Is it a reputable organization, an expert in the field, or an anonymous online commenter? The credibility of the source significantly impacts the reliability of the information it presents. Consider factors like the source's track record, potential biases, and transparency.
Example: A statement about climate change made by a renowned climatologist carries more weight than a statement made by someone with no relevant expertise.
4. Identifying Contradictions and Inconsistencies:
Look for internal contradictions within the statement itself or inconsistencies with other known facts. A statement that contradicts established knowledge or its own claims is likely false.
Example: A statement saying, "The sun rises in the west and sets in the east" immediately contradicts our understanding of celestial mechanics.
5. Paying Attention to Ambiguity and Vagueness:
Be wary of statements that are unclear, imprecise, or open to multiple interpretations. Such statements are difficult to evaluate for truthfulness and are often intentionally vague to avoid scrutiny.
Example: A statement like, "The economy is doing better," is vague. "Better" is subjective and needs further specification regarding which aspects of the economy are improving.
6. Contextual Understanding:
Consider the context in which the statement is presented. The meaning and truthfulness of a statement can depend heavily on its surrounding information and the intended audience.
Example: The statement, "It's cold today," could be true in a snowy region but false in a tropical climate.
7. Seeking Multiple Perspectives:
Before accepting or rejecting a statement, consult various perspectives and sources. This helps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the topic and reduces the likelihood of being misled by biased information.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to favor information that confirms pre-existing beliefs and disregard information that contradicts them.
- Cognitive Biases: A wide range of mental shortcuts and heuristics that can distort our judgment and lead to inaccurate conclusions.
- Emotional Reasoning: Allowing emotions to cloud judgment and influence the assessment of truthfulness.
- Overconfidence: Believing one's own judgments are always correct without sufficient evidence.
Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
The ability to identify false statements is vital in various scenarios:
-
News Literacy: Discerning accurate news from misinformation and propaganda is crucial in today's media landscape. Developing critical thinking skills is essential to avoid being misled by biased or fabricated news stories.
-
Academic Integrity: Students must be able to identify plagiarism and false claims in academic writing to maintain ethical standards.
-
Scientific Inquiry: Scientists constantly evaluate hypotheses and evidence to identify inconsistencies and errors. The process of scientific inquiry inherently involves identifying and rejecting false claims.
-
Financial Decisions: In finance, understanding fraudulent claims and misleading investment strategies is critical for protecting one's assets.
-
Health and Wellness: Identifying false health claims and misleading medical information is crucial for making informed decisions about one's health and well-being.
-
Social Media: Social media is rife with misinformation and disinformation. Developing critical thinking skills is paramount to navigating this complex environment safely.
Conclusion: Cultivating Critical Thinking
Identifying false statements is not merely a skill; it's a crucial aspect of critical thinking. By mastering the strategies discussed in this article—fact-checking, logical analysis, source evaluation, and awareness of cognitive biases—you equip yourself to navigate the complexities of information, make informed decisions, and contribute to a more informed and discerning society. Consistent practice and self-reflection are key to refining this essential skill and enhancing your ability to differentiate truth from falsehood. Remember that skepticism, while crucial, should be balanced with open-mindedness and a willingness to learn and update one's understanding based on credible evidence. The pursuit of truth requires diligence, critical thought, and a commitment to reasoned judgment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is False . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
