Which Of The Following Is A Prokaryotic Cell
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
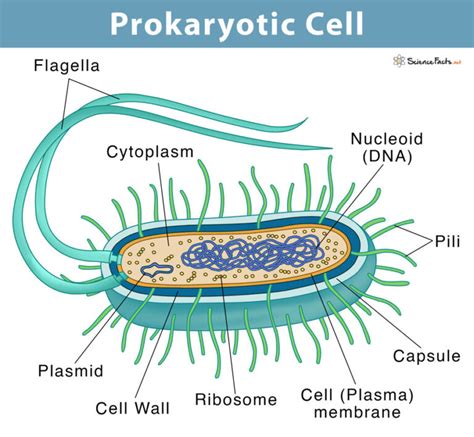
Table of Contents
Delving into the Microscopic World: Which of the Following is a Prokaryotic Cell?
Understanding the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is crucial in biology. This comprehensive guide will explore the defining characteristics of prokaryotic cells, enabling you to confidently identify them from a given list. We'll examine the key structural components, evolutionary significance, and diverse examples of prokaryotic life, ultimately answering the question: which of the following is a prokaryotic cell?
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. This distinguishes them significantly from eukaryotic cells, which possess a nucleus and a complex internal membrane system. The term "prokaryote" itself originates from the Greek words "pro" (before) and "karyon" (kernel), referring to the absence of a defined nucleus. Their genetic material, primarily a single circular chromosome, resides in a region called the nucleoid, which is not enclosed by a membrane.
Key Features of Prokaryotic Cells: A Detailed Look
Several key features characterize prokaryotic cells:
-
Absence of Membrane-Bound Organelles: Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells lack membrane-enclosed compartments such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Metabolic processes occur in the cytoplasm or on the cell membrane.
-
Smaller Size: Prokaryotic cells are generally much smaller than eukaryotic cells, typically ranging from 0.1 to 5 micrometers in diameter. This small size contributes to their efficient nutrient uptake and waste removal.
-
Circular Chromosome: The genetic material in prokaryotic cells is organized into a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region. They may also possess smaller, circular DNA molecules called plasmids, which often carry genes conferring antibiotic resistance or other advantageous traits.
-
Ribosomes: Prokaryotic cells possess ribosomes, responsible for protein synthesis. However, prokaryotic ribosomes (70S) are smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes (80S). This difference is exploited by some antibiotics that specifically target prokaryotic ribosomes, inhibiting protein synthesis in bacterial cells without affecting human cells.
-
Cell Wall: Most prokaryotic cells possess a rigid cell wall outside the plasma membrane. The composition of the cell wall differs between bacterial and archaeal cells. Bacterial cell walls typically contain peptidoglycan, a unique polymer providing structural support and protection. Archaeal cell walls lack peptidoglycan but may contain other polysaccharides or proteins.
-
Capsule (Optional): Some prokaryotic cells have a capsule, a sticky outer layer composed of polysaccharides or proteins. The capsule protects the cell from dehydration, aids in attachment to surfaces, and can contribute to pathogenicity in some bacteria.
-
Flagella (Optional): Many prokaryotic cells possess flagella, long, whip-like appendages used for motility. Prokaryotic flagella are simpler in structure than eukaryotic flagella.
-
Pili (Optional): Pili are shorter, hair-like appendages found on the surface of some prokaryotic cells. They play roles in attachment to surfaces, conjugation (transfer of genetic material between cells), and motility.
Differentiating Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea
The domain Prokaryota encompasses two distinct groups: Bacteria and Archaea. While both are prokaryotic, they exhibit significant differences in their genetic makeup, cellular structure, and metabolism.
-
Bacteria: Bacteria are the most widespread prokaryotes, inhabiting a wide range of environments, from soil and water to the human body. They exhibit diverse metabolic strategies, including photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, and respiration. Bacterial cell walls typically contain peptidoglycan.
-
Archaea: Archaea are often found in extreme environments, such as hot springs, salt lakes, and acidic environments. They share some similarities with eukaryotes in their genetic machinery and ribosomal structure, but their cell walls lack peptidoglycan and often contain other unique polysaccharides or proteins. Archaea exhibit diverse metabolic capabilities, including methanogenesis (production of methane).
Examples of Prokaryotic Cells: A Diverse World
The diversity of prokaryotic life is immense. Let’s explore some examples:
-
Escherichia coli (E. coli): A common bacterium found in the intestines of humans and animals. Most strains are harmless, but some can cause illness.
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae: A bacterium that can cause pneumonia, meningitis, and other infections.
-
Cyanobacteria (Blue-green algae): Photosynthetic bacteria that play a vital role in the global carbon cycle.
-
Halophiles: Archaea that thrive in extremely salty environments.
-
Methanogens: Archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of their metabolism. They are often found in anaerobic environments, such as swamps and the digestive tracts of animals.
-
Thermophiles: Archaea that thrive in extremely hot environments, such as hot springs and hydrothermal vents.
-
Acidophiles: Archaea that thrive in extremely acidic environments.
Identifying Prokaryotic Cells: A Practical Approach
When faced with a list of cells, consider these characteristics to identify prokaryotic cells:
- Absence of a nucleus: Look for the absence of a clearly defined membrane-bound nucleus.
- Small size: Prokaryotic cells are typically much smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- Simple structure: Prokaryotic cells lack the complex internal membrane system found in eukaryotic cells.
- Cell wall composition: The presence of peptidoglycan (in bacteria) or other unique polysaccharides (in archaea) can be indicative of prokaryotic cells.
- Genetic material: The presence of a single, circular chromosome in the nucleoid region is a key characteristic of prokaryotic cells.
By carefully examining these features, you can accurately identify prokaryotic cells from a list of potential candidates. Remember to consider the specific characteristics of bacteria and archaea to make a more precise classification.
The Significance of Prokaryotic Cells: An Ecological Perspective
Prokaryotic cells play crucial roles in various ecological processes:
-
Nutrient cycling: Prokaryotes are essential for nutrient cycling in ecosystems. They decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the environment. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants.
-
Symbiotic relationships: Many prokaryotes form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. For example, certain bacteria in the human gut aid in digestion.
-
Bioremediation: Prokaryotes are used in bioremediation, the use of microorganisms to clean up pollutants. They can break down various harmful substances, such as oil spills and industrial waste.
-
Food production: Prokaryotes are involved in the production of various foods, such as yogurt, cheese, and sauerkraut, through fermentation processes.
Conclusion: Understanding the Prokaryotic World
Understanding the characteristics of prokaryotic cells is fundamental to appreciating the diversity and importance of microbial life. By recognizing their key features—absence of a membrane-bound nucleus, smaller size, simpler structure, and unique cell wall compositions—you can confidently identify prokaryotic cells from any given list. The vast diversity and ecological significance of these microscopic organisms highlight their fundamental role in shaping our world. Their adaptability, metabolic versatility, and ubiquity underscore their continued importance in biological research and applications across various fields. From understanding fundamental biological processes to developing novel biotechnological solutions, the prokaryotic world offers a treasure trove of knowledge waiting to be explored.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Difference Between A Square And Rhombus
May 09, 2025
-
1 424 Rounded To The Nearest Hundredth
May 09, 2025
-
Conjugate Of A Complex Number In Polar Form
May 09, 2025
-
Arteries And Veins Fill In The Blank
May 09, 2025
-
48 As A Product Of Prime Factors
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Prokaryotic Cell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.