Which Chamber Of The Heart Has The Thickest Muscular Wall
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
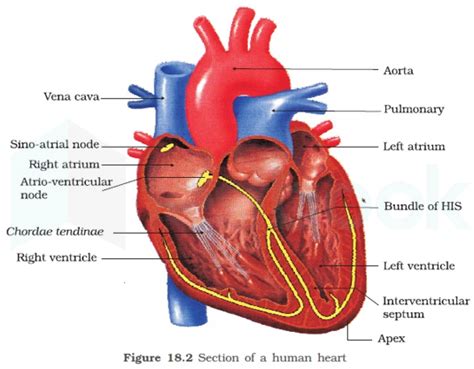
Table of Contents
Which Chamber of the Heart Has the Thickest Muscular Wall?
The human heart, a tireless powerhouse, is a marvel of biological engineering. Composed of four chambers – two atria and two ventricles – each plays a crucial role in the continuous circulation of blood throughout the body. While all chambers possess muscular walls, one stands out for its significantly greater thickness: the left ventricle. This article delves deep into the reasons behind this anatomical distinction, exploring the physiological demands placed upon the left ventricle and the consequences of its robust structure.
The Anatomy of the Heart: A Closer Look
Before we examine the thickness of the left ventricle's wall, it's crucial to understand the overall structure of the heart. The heart is a muscular organ roughly the size of a fist, located slightly left of the center of the chest. Its four chambers are interconnected and work in a coordinated sequence to efficiently pump blood.
The Atria: Receiving Chambers
The two atria – the right atrium and the left atrium – are the receiving chambers of the heart. They receive deoxygenated blood (right atrium) from the body via the vena cava and oxygenated blood (left atrium) from the lungs via the pulmonary veins. Their muscular walls are relatively thin, reflecting their role as low-pressure chambers. Their primary function is to collect incoming blood and gently pass it on to the ventricles.
The Ventricles: Pumping Powerhouses
The ventricles – the right ventricle and the left ventricle – are the powerful pumping chambers of the heart. They receive blood from the atria and propel it out to the rest of the body (left ventricle) and to the lungs (right ventricle). The significant difference in wall thickness between the two ventricles is directly related to the vastly different pressures they must overcome to perform their functions.
The Left Ventricle: A Champion of Pressure
The left ventricle possesses the thickest muscular wall of all four chambers. This is because it is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the systemic circulation – the entire body, except for the lungs. This circulation requires significantly higher pressure than the pulmonary circulation, which is handled by the right ventricle. The systemic circulation encompasses a much larger network of blood vessels and experiences significantly higher resistance.
Systemic Circulation vs. Pulmonary Circulation: A Pressure Differential
The systemic circulation necessitates a much higher pressure to overcome the resistance of the vast network of blood vessels that supply every organ and tissue in the body. This necessitates a considerably stronger pump, which is reflected in the robust musculature of the left ventricle.
In contrast, the pulmonary circulation, handled by the right ventricle, only needs to pump blood to the lungs. The lungs present significantly less resistance to blood flow, demanding a lower pressure and thus a thinner ventricular wall.
The Role of Myocardial Thickness
The thickness of the myocardial wall (the heart muscle) in the left ventricle is directly proportional to the pressure it must generate. The greater the pressure required, the thicker the muscle needs to be to handle the increased workload. This increased thickness allows for stronger contractions, efficiently pumping blood against the higher resistance encountered in systemic circulation.
Physiological Consequences of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
While the substantial thickness of the left ventricle is crucial for its function, excessive thickening – a condition known as left ventricular hypertrophy – can be detrimental to heart health. This often arises from chronic conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure), narrowing of the heart valves (valvular stenosis), or congenital heart defects. Sustained high pressure forces the left ventricle to work harder, causing it to thicken beyond its normal capacity.
Left ventricular hypertrophy can lead to various complications, including:
- Heart failure: The thickened heart muscle may become less efficient at pumping blood, leading to heart failure.
- Arrhythmias: Changes in the heart's electrical signals can lead to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias).
- Sudden cardiac death: In severe cases, left ventricular hypertrophy can increase the risk of sudden cardiac death.
Diagnosing Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
- Echocardiogram: A non-invasive ultrasound test that produces images of the heart's structure and function. This is a primary tool for assessing left ventricular wall thickness.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the heart's electrical activity and can reveal characteristic changes associated with left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Cardiac MRI: A more advanced imaging technique providing detailed images of the heart's anatomy and function.
Maintaining Cardiovascular Health: Preventing Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is critical in preventing left ventricular hypertrophy and other cardiovascular issues. This involves:
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves overall cardiovascular health.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium is crucial.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the heart.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can negatively impact cardiovascular health.
- Blood pressure control: Regularly monitoring and controlling blood pressure is essential in preventing hypertension, a major risk factor for left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
The Interplay of Structure and Function: A Perfect Balance
The remarkable thickness of the left ventricle's muscular wall is a testament to the intricate design of the human heart. It's a direct consequence of the physiological demands placed upon this chamber to effectively pump oxygenated blood throughout the entire body. Understanding this anatomical distinction highlights the crucial relationship between structure and function in maintaining cardiovascular health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regularly consulting with healthcare professionals are essential for preserving the integrity of this vital organ and preventing the development of conditions like left ventricular hypertrophy. The heart's ability to adapt to the demands placed upon it is remarkable, but this adaptability has limits. Sustained stress on the heart necessitates proactive measures to maintain its optimal function and overall well-being. Through a conscious effort toward healthy lifestyle choices, we can help to ensure that this incredible organ continues to function efficiently and reliably throughout our lives. The power of prevention lies in understanding the intricate mechanics of this vital organ, and taking the necessary steps to safeguard its health.
Further Research and Exploration
The intricate workings of the heart continue to fascinate scientists and researchers. Ongoing studies are constantly unraveling more complex details about the heart's structure, function, and the mechanisms that govern its response to various stressors and diseases. Future research will undoubtedly further elucidate the interplay between the left ventricle's structure, its response to disease, and the development of more effective treatments for cardiovascular conditions. Understanding the unique demands placed on the left ventricle continues to be a key focus in the quest to improve cardiovascular health outcomes globally. The advancements in medical technology and research methods pave the way for a deeper understanding of cardiac physiology and pave the path for innovation in the treatment and prevention of heart-related diseases. The ongoing effort to uncover the intricate secrets of the heart underscores its importance as a critical organ and highlights the importance of maintaining its health throughout one's lifetime.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is The Biogeochemical Cycle Important
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Common Factor Of 60
Mar 18, 2025
-
Words That Have The Oi Sound
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Are The Process Of Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Related
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Moles In 22g Of Co2
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Chamber Of The Heart Has The Thickest Muscular Wall . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
