What Is The Common Factor Of 60
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
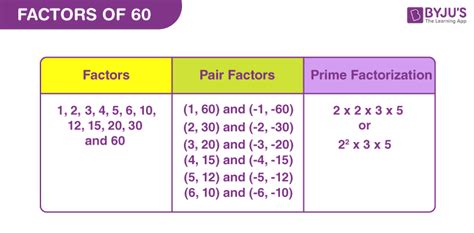
Table of Contents
What are the Common Factors of 60? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of a number, like 60, is a fundamental concept in number theory with applications across various fields, from cryptography to computer science. This article will not only answer the question "What are the common factors of 60?" but will also explore the broader context of factors, divisors, prime factorization, and their significance. We'll delve into different methods for finding factors, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential mathematical concept.
Understanding Factors and Divisors
Before we jump into the specifics of 60, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides that number without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Finding the Factors of 60: A Systematic Approach
There are several ways to identify the factors of 60. Let's explore the most common methods:
1. The Pairwise Method
This method involves systematically considering pairs of numbers that multiply to give 60. We start with 1 and work our way up:
- 1 x 60 = 60
- 2 x 30 = 60
- 3 x 20 = 60
- 4 x 15 = 60
- 5 x 12 = 60
- 6 x 10 = 60
This gives us the factors 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, and 60.
2. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a powerful technique. It involves breaking down a number into its prime factors—numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). The prime factorization of 60 is:
2² x 3 x 5
This tells us that 60 is composed of two 2s, one 3, and one 5. From this prime factorization, we can derive all the factors:
- Factors of 60 are derived from combinations of these prime factors and 1:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 5
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 2 x 5 = 10
- 3 x 5 = 15
- 2 x 2 x 3 = 12
- 2 x 2 x 5 = 20
- 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
- 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 = 60
This method ensures we don't miss any factors.
3. Division Method
This is a straightforward approach. We systematically divide 60 by each whole number, starting from 1, to check for divisibility:
- 60 ÷ 1 = 60
- 60 ÷ 2 = 30
- 60 ÷ 3 = 20
- 60 ÷ 4 = 15
- 60 ÷ 5 = 12
- 60 ÷ 6 = 10
- 60 ÷ 10 = 6
- 60 ÷ 12 = 5
- 60 ÷ 15 = 4
- 60 ÷ 20 = 3
- 60 ÷ 30 = 2
- 60 ÷ 60 = 1
This method, although slightly longer, is also reliable and leads to the same set of factors.
Common Factors and Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
When dealing with multiple numbers, we often look for common factors. These are factors shared by all the numbers in question. For example, let's find the common factors of 60 and 72.
The factors of 60 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, 60. The factors of 72 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 72.
The common factors of 60 and 72 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
The greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), is the largest of these common factors. In this case, the GCF of 60 and 72 is 12.
Applications of Factors and GCF
The concepts of factors and GCF have significant applications across various fields:
1. Simplifying Fractions
Finding the GCF is crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 60/72 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF (12), resulting in the simplified fraction 5/6.
2. Solving Problems Involving Measurement
Factors are important when working with measurement units. For instance, if you have a rectangular piece of land measuring 60 meters by 72 meters, finding the common factors helps determine possible square tile sizes that can perfectly cover the area without cutting any tiles. The largest possible square tile size would be determined by the GCF (12 meters).
3. Cryptography
Prime factorization plays a vital role in modern cryptography. The security of many encryption algorithms, such as RSA, relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors.
4. Computer Science
Factors are used in algorithms related to data structures and optimization problems. Efficient algorithms often exploit the properties of factors and prime factorization to improve performance.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Factors
Understanding the factors of a number, like 60, is far more than just a basic arithmetic exercise. It opens the door to more complex mathematical concepts and reveals the underlying structure of numbers. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, the applications of factors and related concepts are pervasive and impactful. By mastering the various methods of finding factors and grasping the significance of prime factorization, we gain a powerful tool for solving problems across multiple disciplines. The seemingly simple question "What are the common factors of 60?" thus unlocks a deeper understanding of number theory and its diverse applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Elements Are In Water
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is Meant By Translational Kinetic Energy
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is Salt A Compound Mixture Or Element
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 24 And 14
Mar 18, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 2 And 8
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Common Factor Of 60 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
