What's The Square Root Of 16
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
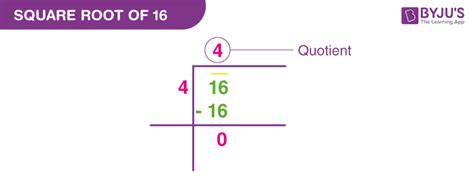
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 16? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Their Applications
The question, "What's the square root of 16?" seems deceptively simple. A quick glance might offer the immediate answer: 4. However, a deeper exploration reveals a fascinating world of mathematical concepts, historical context, and practical applications far beyond this seemingly basic calculation. This article will delve into the intricacies of square roots, focusing on the square root of 16 as a springboard for understanding broader mathematical principles and their relevance in various fields.
Understanding Square Roots: The Fundamental Concept
Before we tackle the square root of 16 specifically, let's establish a solid understanding of what a square root actually is. In essence, the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), equals the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. This is often represented mathematically as √9 = 3. The symbol "√" is known as the radical symbol.
The concept of square roots is intrinsically linked to the idea of squaring a number. Squaring a number involves multiplying it by itself. So, squaring 3 (3²) results in 9. The square root, therefore, is the inverse operation of squaring.
Solving the Puzzle: What's the Square Root of 16?
Now, let's return to our original question: What's the square root of 16? Applying the definition, we are looking for a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. The answer is undeniably 4, because 4 x 4 = 16. Therefore, √16 = 4.
However, this seemingly simple answer opens up a more nuanced understanding of square roots. While 4 is the principal square root of 16, it's crucial to acknowledge that -4 is also a valid solution, as (-4) x (-4) = 16. This introduces the concept of positive and negative square roots. While in many practical applications we focus on the positive square root, understanding the existence of both positive and negative solutions is essential for a complete mathematical understanding.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Different Number Systems
The concept of square roots extends beyond the realm of simple integers. Let's consider different number systems:
-
Real Numbers: The square roots of 16 (4 and -4) are both real numbers. Real numbers encompass all numbers that can be plotted on a number line, including rational (like fractions and integers) and irrational numbers (like π and √2).
-
Complex Numbers: When dealing with the square root of negative numbers, we enter the realm of complex numbers. For example, the square root of -16 involves the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1. The square root of -16 would be expressed as ±4i. This demonstrates that the concept of square roots extends to more abstract number systems.
-
Irrational Numbers: Many square roots are irrational numbers—numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. For instance, the square root of 2 (√2) is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.414. Understanding the difference between rational and irrational numbers enhances the appreciation of the richness and complexity of the number system.
Historical Context: A Journey Through Time
The concept of square roots has ancient roots, literally! Evidence suggests that mathematicians in ancient civilizations like Babylon and Egypt were familiar with calculating square roots, albeit using different methods than those used today. The Babylonian method, for example, involved iterative approximations to reach a solution. These early understandings laid the groundwork for the sophisticated mathematical tools we use today.
The development of mathematical notation played a crucial role in making square roots easier to understand and work with. The adoption of the radical symbol "√" and the understanding of algebraic notation significantly simplified the representation and calculation of square roots.
Practical Applications: Square Roots in the Real World
Far from being a purely theoretical concept, square roots have numerous practical applications in various fields:
-
Geometry and Physics: Calculating distances, areas, and volumes frequently involves square roots. Finding the length of a diagonal of a square or the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle relies heavily on the Pythagorean theorem, which utilizes square roots. In physics, square roots are essential for calculations involving velocity, acceleration, and energy.
-
Engineering and Architecture: Structural engineers utilize square roots in stress and strain calculations to ensure the stability and safety of buildings and other structures. Architects also utilize square roots in designing aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound buildings.
-
Finance and Investment: In finance, square roots are used in calculating standard deviation and variance, which are crucial metrics for assessing risk in investments. Understanding these concepts helps investors make informed decisions.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Square roots are extensively used in computer graphics and game development for calculations related to 2D and 3D transformations, rotations, and distances. They are fundamental to creating realistic and immersive gaming experiences.
-
Statistics and Data Analysis: Square roots are integral to statistical analysis, particularly in calculating standard deviation and correlation coefficients. These calculations are essential for understanding and interpreting data in various fields, from medicine and social sciences to business and economics.
Advanced Concepts: Beyond the Basic Square Root
The exploration of square roots opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Nth Roots: The concept of square roots extends to nth roots. The nth root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself n times, equals the original number. For example, the cube root (3rd root) of 8 is 2 because 2 x 2 x 2 = 8.
-
Radical Equations: These equations involve variables under radical symbols. Solving radical equations requires specific techniques, often involving squaring both sides of the equation to eliminate the radical.
-
Approximating Square Roots: For irrational square roots, approximation techniques are necessary. Methods like the Babylonian method or Newton-Raphson method provide efficient ways to calculate approximate values of square roots.
-
Complex Numbers and Their Applications: As previously mentioned, venturing into complex numbers unlocks a whole new world of mathematical possibilities. Complex numbers find applications in diverse areas such as electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, and signal processing.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Square Roots
The seemingly simple question, "What's the square root of 16?" has led us on a journey through fundamental mathematical concepts, historical context, and practical applications. The answer, while easily obtained, serves as a gateway to a far richer and more complex mathematical landscape. From the basic operations of squaring and finding square roots to the exploration of complex numbers and their diverse applications, understanding square roots illuminates the power and versatility of mathematics in various aspects of our lives. The seemingly elementary square root of 16, therefore, stands as a testament to the profound impact of mathematical principles on our understanding of the world around us. The exploration continues, with countless opportunities to delve deeper into the fascinating world of numbers and their applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cuanto Es 15 Inches En Centimetros
May 09, 2025
-
The Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 8
May 09, 2025
-
Is 5 7 A Rational Number
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find Minors Of Matrix
May 09, 2025
-
This Is The Process Of Copying Dna To Rna
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.