What Wavelength Does Chlorophyll A Absorb
Juapaving
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
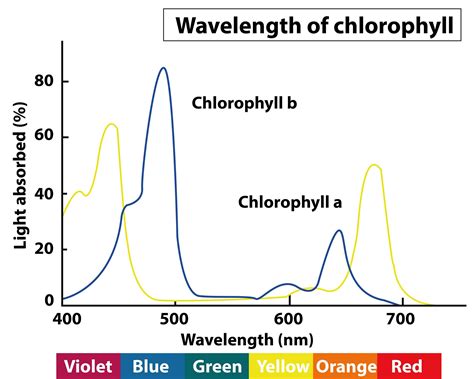
Table of Contents
What Wavelength Does Chlorophyll a Absorb? A Deep Dive into Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll a, the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, plays a vital role in capturing light energy from the sun. Understanding the specific wavelengths of light it absorbs is crucial to comprehending the process of photosynthesis and its importance for life on Earth. This article delves deep into the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a, exploring its intricacies and implications.
The Basics of Chlorophyll a and Photosynthesis
Before diving into the specifics of wavelength absorption, let's briefly revisit the fundamentals. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, is a cornerstone of most ecosystems. This remarkable process relies heavily on chlorophyll, a group of green pigments found within chloroplasts—the cellular powerhouses of plant cells.
Chlorophyll a is the most abundant type of chlorophyll, serving as the primary light-harvesting pigment. It's characterized by its unique chemical structure, containing a porphyrin ring with a magnesium ion at its center. This structure is crucial for absorbing light energy. Different types of chlorophyll, like chlorophyll b and carotenoids, act as accessory pigments, expanding the range of wavelengths absorbed and transferring that energy to chlorophyll a.
Chlorophyll a's Absorption Spectrum: Peak Absorption and Action Spectrum
Chlorophyll a exhibits a distinct absorption spectrum, meaning it absorbs light most effectively at certain wavelengths. Its absorption spectrum isn't a simple, smooth curve; rather, it displays two prominent peaks.
The Two Major Absorption Peaks
-
Peak 1: Around 430 nm (Blue Light): Chlorophyll a strongly absorbs blue light, a portion of the visible light spectrum. This absorption corresponds to high-energy photons.
-
Peak 2: Around 662 nm (Red Light): The second peak of absorption lies in the red portion of the visible spectrum, also corresponding to high energy photons, though not as high as blue light.
This dual-peak absorption is critical. The absorption of both blue and red light ensures that a wide range of the sun's energy is effectively captured.
The Action Spectrum: Photosynthetic Efficiency Across Wavelengths
While the absorption spectrum shows how much light chlorophyll a absorbs at different wavelengths, the action spectrum reveals how efficiently that absorbed light is used in photosynthesis. The action spectrum generally mirrors the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a, with peaks in the blue and red regions indicating high photosynthetic activity. However, subtle differences may exist due to the involvement of accessory pigments and the efficiency of energy transfer within the photosynthetic apparatus.
Why Chlorophyll a Appears Green: The Relationship Between Absorption and Reflection
The color of chlorophyll a, a deep green, is a direct consequence of its absorption spectrum. Chlorophyll a absorbs blue and red light effectively, but it reflects green light. This reflected green light is what we perceive when we see plants. In essence, the green light is the portion of the visible spectrum that is not efficiently absorbed by chlorophyll a.
Factors Affecting Chlorophyll a's Absorption
Several factors can influence the precise wavelengths absorbed by chlorophyll a:
-
Solvent Effects: The solvent in which chlorophyll a is dissolved can slightly alter its absorption spectrum. Different solvents can interact differently with the chlorophyll molecule, causing minor shifts in the absorption peaks.
-
Temperature: Temperature changes can also impact chlorophyll a's absorption. Higher temperatures can sometimes lead to subtle shifts in the absorption spectrum, although the effect is typically not dramatic.
-
pH: The acidity or alkalinity (pH) of the surrounding environment can also slightly influence the absorption spectrum. Changes in pH may affect the chlorophyll molecule's conformation and its interaction with light.
-
Protein Binding: In vivo (within the plant cell), chlorophyll a is often bound to proteins within photosystems. This binding can influence the chlorophyll's absorption properties, slightly modifying its absorption spectrum compared to chlorophyll in solution.
The Role of Accessory Pigments: Expanding the Light-Harvesting Range
Chlorophyll a isn't the sole pigment involved in photosynthesis. Accessory pigments, such as chlorophyll b and carotenoids, play a crucial role by absorbing wavelengths that chlorophyll a doesn't absorb efficiently. Chlorophyll b, for example, absorbs more strongly in the blue and orange-yellow regions. Carotenoids absorb in the blue-green and violet regions, also protecting chlorophyll a from damage caused by excessive light energy. These accessory pigments broaden the range of light energy captured and transfer this energy to chlorophyll a for use in photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll a and the Photosystems: Organization and Energy Transfer
Within the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, chlorophyll a is organized into photosystems—complex protein-pigment complexes. These photosystems efficiently capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy.
-
Photosystem II (PSII): PSII primarily utilizes light energy absorbed by chlorophyll a (and accessory pigments) to split water molecules, releasing electrons and oxygen.
-
Photosystem I (PSI): PSI also employs chlorophyll a (and accessory pigments) to capture light energy. The electrons, initially excited in PSII, are passed through an electron transport chain and ultimately reach PSI, where they are further energized to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
The precise arrangement and interactions of chlorophyll a molecules within these photosystems are crucial for efficient energy transfer and the overall success of photosynthesis.
Applications and Significance: Beyond Photosynthesis
Understanding the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a has broad implications beyond basic biology. This knowledge is applied in diverse fields:
-
Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and remote sensing techniques utilize the absorption properties of chlorophyll a to assess plant health, monitor vegetation growth, and study ecosystem dynamics. By measuring the reflectance of different wavelengths, scientists can estimate chlorophyll a concentrations and gain insights into plant productivity.
-
Agriculture: Knowledge of chlorophyll a's absorption spectrum helps optimize agricultural practices. For instance, understanding how light affects chlorophyll a helps in designing efficient lighting systems for greenhouses and optimizing crop yields.
-
Biotechnology and Biofuel Research: Chlorophyll a's role in photosynthesis is central to research aimed at developing biofuels and other sustainable energy solutions. Harnessing photosynthetic processes efficiently depends on understanding the detailed mechanisms of light absorption and energy conversion.
Conclusion: The Importance of Chlorophyll a's Absorption Spectrum
Chlorophyll a’s primary absorption at around 430 nm (blue light) and 662 nm (red light) is fundamental to the process of photosynthesis, which sustains virtually all life on Earth. This precise absorption spectrum, along with the action of accessory pigments and the intricate organization within photosystems, enables highly efficient light harvesting and energy conversion. The knowledge of chlorophyll a’s absorption characteristics has applications across multiple scientific disciplines, ranging from ecology and agriculture to biotechnology and remote sensing, highlighting its enduring significance in our understanding of the natural world. Further research into the subtleties of chlorophyll a's absorption and its interactions within the photosynthetic apparatus continues to refine our understanding and unlock new applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Calculate The Rf Value
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is Difference Between Power And Energy
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 118 Inches
Mar 30, 2025
-
Rusting Of Iron Is A Chemical Change True Or False
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Wavelength Does Chlorophyll A Absorb . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
