What Number Is A Multiple Of 3
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
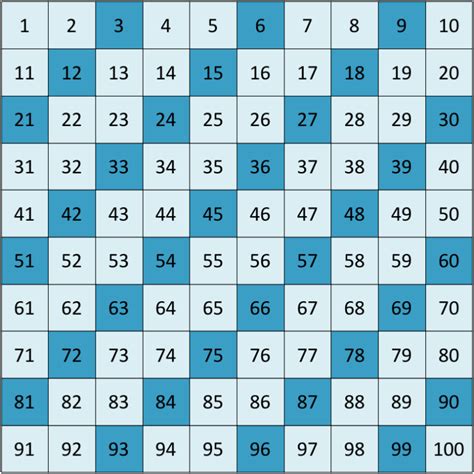
Table of Contents
What Number is a Multiple of 3? A Deep Dive into Divisibility and its Applications
The seemingly simple question, "What number is a multiple of 3?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, divisibility rules, and practical applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the concept of multiples of 3, delve into efficient methods for identifying them, and demonstrate their relevance in everyday life and advanced mathematical concepts.
Understanding Multiples
Before we dive into the specifics of multiples of 3, let's establish a foundational understanding of the term "multiple." A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer (a whole number, including zero and negative numbers). For example:
- Multiples of 2: 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, -2, -4, -6... (obtained by multiplying 2 by 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, -1, -2, -3...)
- Multiples of 5: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, -5, -10, -15... (obtained by multiplying 5 by 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, -1, -2, -3...)
Therefore, a multiple of 3 is any number that results from multiplying 3 by an integer.
Identifying Multiples of 3: The Divisibility Rule
The most straightforward way to determine if a number is a multiple of 3 is to divide it by 3. If the division results in a whole number (no remainder), then the number is a multiple of 3. However, for larger numbers, this method can be tedious. Fortunately, there's a handy divisibility rule:
The Divisibility Rule for 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
Let's illustrate this with some examples:
- Is 12 a multiple of 3? 1 + 2 = 3. 3 is divisible by 3, so 12 is a multiple of 3.
- Is 45 a multiple of 3? 4 + 5 = 9. 9 is divisible by 3, so 45 is a multiple of 3.
- Is 783 a multiple of 3? 7 + 8 + 3 = 18. 18 is divisible by 3, so 783 is a multiple of 3.
- Is 251 a multiple of 3? 2 + 5 + 1 = 8. 8 is not divisible by 3, so 251 is not a multiple of 3.
This divisibility rule significantly simplifies the process of identifying multiples of 3, particularly for larger numbers. It avoids the need for long division, making it a valuable tool for quick mental calculations.
Why Does the Divisibility Rule for 3 Work?
The divisibility rule for 3 stems from the properties of modular arithmetic. Without delving too deeply into the mathematical intricacies, the essence lies in the fact that any power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.) leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 3. This means that each digit in a number contributes its face value to the sum of its digits when considering divisibility by 3.
Applications of Multiples of 3
The concept of multiples of 3, though seemingly basic, has significant applications across various fields:
1. Everyday Life:
-
Counting and Grouping: Multiples of 3 are frequently used in everyday counting and grouping tasks. For example, arranging items in rows of three, calculating the total cost of three identical items, or determining the number of groups of three students in a class.
-
Time: Dividing time into three equal parts (e.g., splitting a 3-hour project into three 1-hour segments) relies on the concept of multiples of 3.
2. Mathematics:
-
Number Theory: Multiples of 3 are fundamental in number theory, playing a role in concepts like prime numbers, modular arithmetic, and divisibility rules. Understanding multiples of 3 is a stepping stone to more complex mathematical concepts.
-
Algebra and Equations: Solving algebraic equations often involves finding multiples of 3 or determining if a variable represents a multiple of 3.
-
Geometry: Multiples of 3 appear in geometric patterns and calculations, such as determining the area of a triangle (base * height / 2 – this often results in multiples of 3 depending on base and height values)
3. Computer Science:
-
Algorithms and Programming: Divisibility checks, including those for multiples of 3, are frequently incorporated into computer programs for tasks such as data validation, array manipulation, and game development.
-
Data Structures: Efficient data structures often leverage concepts of divisibility to optimize memory allocation and search algorithms.
4. Other Fields:
-
Engineering: Multiples of 3 can be relevant in engineering calculations and designs, particularly in situations involving symmetry or equal divisions.
-
Music: Musical intervals and chord progressions often involve multiples of 3, reflecting the inherent mathematical structures in music theory.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Scenarios
While the divisibility rule provides a straightforward method for identifying multiples of 3, some situations require a deeper understanding.
1. Large Numbers:
For extremely large numbers, even adding the digits can become time-consuming. In such cases, repeated application of the divisibility rule can be beneficial. You can sum the digits, and if the result is still large, sum its digits until you reach a single-digit number. If this final number is 3, 6, or 9, the original number is a multiple of 3.
2. Negative Numbers:
The divisibility rule for 3 applies equally to negative numbers. If the sum of the digits of a negative number is divisible by 3, the number itself is a multiple of 3. For example, -27: 2 + 7 = 9; 9 is divisible by 3, thus -27 is a multiple of 3.
3. Decimal Numbers:
The divisibility rule for 3 doesn't directly apply to decimal numbers (numbers with a decimal point). To determine if a decimal number is a multiple of 3, you can either convert it to a fraction and then check the numerator's divisibility by 3, or you can ignore the decimal point and apply the divisibility rule to the whole number part. If the whole number part is a multiple of 3, and the fractional part is also a multiple of 3, the number is a multiple of 3.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Multiples of 3
The seemingly simple concept of multiples of 3 has far-reaching implications in various fields. From everyday calculations to advanced mathematical concepts, understanding this fundamental principle is crucial for efficient problem-solving and a deeper appreciation of the structure and patterns within numbers. The divisibility rule offers a powerful tool for identifying multiples of 3 quickly and efficiently, simplifying numerous tasks and paving the way for exploring more complex mathematical ideas. Mastering this concept enhances numerical fluency and opens doors to a richer understanding of the mathematical world. The versatility and practicality of understanding multiples of 3 underscore its enduring significance in mathematics and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Number Is A Multiple Of 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
