What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Rectangle
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
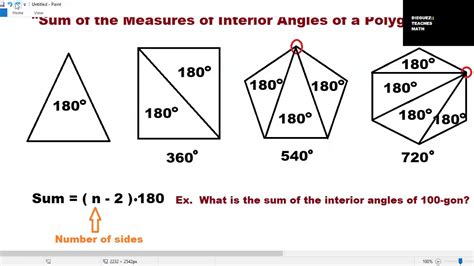
Table of Contents
What is the Sum of Interior Angles of a Rectangle? A Deep Dive into Geometry
The seemingly simple question, "What is the sum of the interior angles of a rectangle?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, its principles, and its applications. While the answer itself is straightforward – 360 degrees – understanding why this is true requires delving into the fundamental properties of rectangles and quadrilaterals, and ultimately, the broader concept of polygon angle sums. This article will not only answer the titular question but also equip you with a comprehensive understanding of the underlying geometrical principles.
Understanding Rectangles: A Foundation in Geometry
Before tackling the sum of interior angles, let's solidify our understanding of what constitutes a rectangle. A rectangle is a quadrilateral, meaning it's a closed two-dimensional shape with four sides. However, it's a special type of quadrilateral with specific properties that distinguish it from others like squares, parallelograms, and trapezoids. These defining characteristics include:
- Four right angles: Each of the four interior angles measures exactly 90 degrees. This is the crucial property that directly relates to the sum of its interior angles.
- Opposite sides are equal and parallel: The lengths of opposite sides are equal, and these sides are parallel to each other. This property contributes to the rectangle's stability and symmetry.
- Diagonals bisect each other: The diagonals of a rectangle (lines connecting opposite corners) intersect at their midpoints. This property further highlights the symmetry inherent in the shape.
These properties are not independent; they are interconnected and define the unique characteristics of a rectangle. Understanding these properties is essential for grasping why the sum of its interior angles is always 360 degrees.
The Sum of Interior Angles: A General Formula and its Application to Rectangles
The sum of interior angles isn't unique to rectangles; it's a property applicable to all polygons. A general formula exists to calculate this sum, dependent solely on the number of sides (n) of the polygon:
(n - 2) * 180°
For a rectangle, n = 4 (it has four sides). Substituting this into the formula, we get:
(4 - 2) * 180° = 2 * 180° = 360°
This formula elegantly demonstrates that the sum of interior angles is directly related to the number of sides. The more sides a polygon has, the larger the sum of its interior angles. This formula holds true for all polygons, from triangles (n=3, sum = 180°) to complex shapes with numerous sides.
For rectangles, however, the fact that each angle is already known to be 90 degrees provides an alternative, simpler way to calculate the sum:
90° + 90° + 90° + 90° = 360°
This direct addition method emphasizes the unique characteristic of rectangles – the presence of four right angles.
Visualizing the Angle Sum: Triangulation and Proof
We can visually demonstrate the 360-degree sum using triangulation. A rectangle can be divided into two triangles by drawing a diagonal line connecting opposite vertices. Each triangle has an interior angle sum of 180 degrees. Since the rectangle is comprised of two triangles, the total sum of its interior angles is 180° + 180° = 360°.
This triangulation method offers a visual and intuitive proof of the angle sum. It's not only applicable to rectangles but also to other quadrilaterals, highlighting the underlying geometrical relationship between triangles and other polygons.
Beyond Rectangles: Exploring Other Quadrilaterals
While the sum of interior angles is 360 degrees for all quadrilaterals, including rectangles, the individual angle measurements vary depending on the type of quadrilateral. Let's briefly compare rectangles with other quadrilaterals:
- Squares: A square is a special case of a rectangle where all four sides are equal in length. The sum of its interior angles remains 360°, with each angle measuring 90°.
- Parallelograms: A parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length. The sum of its interior angles is 360°, but unlike rectangles, its angles aren't necessarily right angles. Opposite angles are equal, but adjacent angles are supplementary (add up to 180°).
- Trapezoids: A trapezoid has only one pair of parallel sides. The sum of its interior angles is still 360°, but the individual angles can vary significantly depending on the shape of the trapezoid.
Practical Applications: Where the 360° Sum Matters
The seemingly theoretical concept of the sum of interior angles in rectangles has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Architecture and Construction: Understanding the angle relationships in rectangles is fundamental to building structures. From designing walls and windows to calculating roof angles, accurate angle measurements ensure stability and structural integrity.
- Engineering: Engineers rely on geometric principles to design and build various structures, machinery, and systems. Accurate calculations of angles are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and efficiency of these systems.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: In computer graphics and game development, the properties of rectangles and their angle sums are used extensively in creating two-dimensional and three-dimensional models and environments.
- Cartography and Surveying: The principles of geometry, including the angle sums of polygons, are essential for creating accurate maps and surveying land.
Advanced Concepts: Extending the Understanding
The concept of angle sums extends beyond simple polygons. The understanding of interior angles can be further developed through exploring:
- Exterior angles: The exterior angles of a polygon are the angles formed by extending one side of the polygon. The sum of exterior angles of any polygon is always 360°.
- Irregular polygons: While the formula (n-2) * 180° applies to all polygons, calculating the individual angles of irregular polygons requires additional information about the lengths of their sides.
- Non-Euclidean geometry: In non-Euclidean geometries (like spherical geometry), the sum of interior angles of a polygon can differ from the Euclidean formula.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Sum
The seemingly simple answer – 360 degrees – to the sum of interior angles in a rectangle opens a vast world of geometrical concepts and practical applications. Understanding this fundamental principle isn't just about memorizing a number; it's about grasping the underlying principles of geometry, its interconnectedness, and its significance in various fields. From the simple elegance of the formula to the practical implications in architecture and beyond, the 360° sum of a rectangle's interior angles serves as a cornerstone of geometrical understanding. This comprehensive exploration hopefully provided a deeper appreciation for this seemingly simple yet profoundly significant concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Template Strand 3 To 5
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of The Arm Of The Microscope
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Amount Of Energy In Food Is Measured In
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Is Greater 1 3 Or 2 5
Mar 19, 2025
-
Gay Lussacs Law Real Life Example
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Rectangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
