What Is The Similarity Between A Compound And A Mixture
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
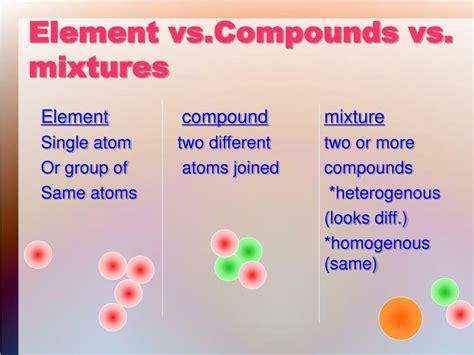
Table of Contents
What's the Similarity Between a Compound and a Mixture? A Deep Dive into Chemical Composition
Understanding the fundamental differences between compounds and mixtures is crucial for anyone studying chemistry. While they might seem similar at first glance – both involve combining different substances – a closer examination reveals key distinctions in their composition, properties, and behavior. However, before we delve into the differences, let's explore the surprising similarities between compounds and mixtures. This seemingly counterintuitive approach offers a valuable perspective, highlighting the nuances of chemical interactions.
The Overarching Similarity: The Combination of Substances
The most fundamental similarity between compounds and mixtures lies in their very nature: they are both formed by combining two or more substances. This is the unifying principle that links these two seemingly disparate categories of matter. Whether it’s the intricate bonding in a compound or the simple physical intermingling in a mixture, the foundational act of combining elements or compounds remains the same. This overarching similarity is often overlooked in the rush to highlight the significant differences, but recognizing it provides a valuable framework for understanding both concepts more effectively.
A Deeper Look at the Combining Process
While the act of combining is shared, the manner in which the combination occurs differentiates compounds and mixtures significantly. In compounds, the constituent elements undergo a chemical transformation, resulting in the formation of new substances with unique properties. In contrast, mixtures involve a physical combination where the individual components retain their original properties. This difference in the combining process is critical in determining the overall characteristics of the resulting substance. We'll expand on these differences extensively in the following sections, but understanding this fundamental distinction in the how of combining is key to grasping the similarity in the what of combining.
Exploring the Subtleties: Where Compounds and Mixtures Converge
The similarity between compounds and mixtures extends beyond the simple act of combination. Let's investigate some subtle, yet crucial, overlaps:
1. Both Can Be Separated (Under Different Conditions):
While the methods differ drastically, both compounds and mixtures can be separated into their constituent parts. Compounds require chemical processes such as electrolysis or chemical reactions to break the bonds holding them together. Mixtures, on the other hand, can be separated by physical methods such as filtration, distillation, evaporation, chromatography, or magnetism. The contrasting methods reflect the fundamental difference in their bonding and intermolecular forces, but the end result – the separation of components – serves as a point of convergence.
2. Both Can Exhibit Variable Composition (to a Degree):
While this point might seem contradictory, especially considering the fixed ratios in compounds, it deserves closer examination. Compounds, although having a fixed ratio of elements, can exist in different isotopic forms, leading to slight variations in overall mass. For example, water (H₂O) can have varying isotopic compositions (e.g., D₂O, heavy water), altering its overall physical properties marginally. Mixtures, by their very nature, exhibit widely variable compositions, depending on the ratio of their components. The critical difference lies in the scale and cause of this variability. The variability in compounds is subtle and based on isotopic variations, while in mixtures, it is often significant and determined by the proportions of the components mixed.
3. Both Can Exist in Different Phases:
Compounds and mixtures can exist in any of the three common phases of matter: solid, liquid, or gas. For example, water (a compound) can exist as ice (solid), liquid water, or steam (gas). Similarly, a mixture of sand and water can exist in any of these phases depending on the temperature. This shared ability to exist in various phases further underscores the underlying similarity – both represent aggregated forms of matter. The specific properties and behavior within each phase will differ depending on whether it’s a compound or a mixture, but the possibility of existing in all phases is a shared trait.
4. Both Can Undergo Physical Changes:
Both compounds and mixtures can undergo physical changes without altering their chemical composition. These changes might include changes in state (melting, boiling, freezing), changes in shape, or changes in size. For instance, melting an ice cube (a compound) is a physical change, as is dissolving salt (a compound) in water (a compound creating a mixture). Similarly, separating the components of a mixture by filtration is a physical change. The key is that no chemical bonds are broken or formed during these processes. This ability to undergo various physical transformations without altering the fundamental chemical identity is a unifying characteristic.
A Comparative Look: Highlighting the Key Differences
While the similarities are interesting and reveal the underlying unity in chemical composition, the differences between compounds and mixtures are far more significant and define their distinct identities.
| Feature | Compound | Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fixed ratio of elements | Variable ratio of components |
| Formation | Chemical reaction, bond formation | Physical combination, no new substance formed |
| Separation | Chemical methods (electrolysis, etc.) | Physical methods (filtration, distillation, etc.) |
| Properties | Unique properties different from components | Retains properties of individual components |
| Representation | Chemical formula (e.g., H₂O) | No single formula, varying composition |
Case Studies: Illustrating Compound vs. Mixture Behavior
Let's consider some specific examples to solidify our understanding of the differences:
1. Water (H₂O) vs. Salt Water:
-
Water (H₂O): A compound formed by a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. It has a fixed ratio of 2:1 (hydrogen to oxygen) and unique properties distinct from hydrogen and oxygen gases. Electrolysis can decompose water into its constituent elements.
-
Salt Water: A mixture of salt (NaCl) and water (H₂O). The salt dissolves in the water but retains its chemical identity. Simple methods like evaporation can separate the salt and water.
2. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) vs. Air:
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A compound with a fixed ratio of one carbon atom to two oxygen atoms. It has distinct properties, different from carbon and oxygen.
-
Air: A mixture of various gases (primarily nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide). The gases retain their individual properties, and physical methods like fractional distillation can separate them.
3. Sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) vs. Sugar Water:
-
Sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁): A compound with a specific molecular formula and distinct properties.
-
Sugar Water: A mixture of sugar dissolved in water. The sugar retains its identity, and the water acts as a solvent. Evaporation can recover the sugar.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Similarity and Difference
The seemingly paradoxical similarity between compounds and mixtures offers a fascinating insight into the world of chemistry. While both involve combining substances, the how of combination fundamentally distinguishes them. Understanding both the similarities and differences is crucial for appreciating the full spectrum of chemical interactions and the diverse forms matter can take. By recognizing the subtle overlaps and the significant distinctions, we develop a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the building blocks of the universe around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
63 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
-
X 2 X 3 X 2 X 3
Mar 25, 2025
-
Two Stroke Engine Four Stroke Engine Difference
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is Ph Of Pure Water
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Acute Angles Are In An Acute Triangle
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Similarity Between A Compound And A Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
