What Is The Prime Factorization Of 65
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
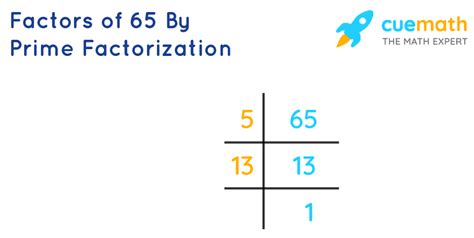
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 65? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 65?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the concept behind it unlocks a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical principles and their applications. This article will not only provide the answer but also delve into the intricacies of prime numbers, factorization, and the significance of this process in various mathematical fields.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 65, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it cannot be divided evenly by any other number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The sequence continues infinitely, a fact that has captivated mathematicians for centuries. The study of prime numbers is a cornerstone of number theory, with many unsolved problems and ongoing research continuing to drive advancements in the field.
Distinguishing Prime Numbers from Composite Numbers
It's crucial to differentiate prime numbers from composite numbers. Composite numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that have more than two divisors. For example, 6 is a composite number because it's divisible by 1, 2, 3, and 6. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite; it's a unique case in number theory.
The Concept of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Every composite number can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers, a fundamental theorem in number theory known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This means there's only one way to represent a composite number as a product of primes (ignoring the order of the factors). This unique representation is incredibly valuable in various mathematical applications.
Why is Prime Factorization Important?
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has far-reaching implications across several mathematical areas:
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization forms the backbone of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components is the foundation of secure online transactions and data protection. RSA encryption, a widely used algorithm, relies on this principle.
-
Number Theory Research: Prime factorization is a key area of ongoing research in number theory. Uncovering patterns and properties of prime numbers is essential to furthering our understanding of fundamental mathematical structures. Conjectures such as the Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, are deeply connected to the distribution and properties of prime numbers.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization concepts extend into abstract algebra, providing insights into the structure of rings and fields. The unique factorization property is crucial in various algebraic structures.
-
Simplifying Fractions: In basic arithmetic, prime factorization is instrumental in simplifying fractions. By finding the prime factors of the numerator and denominator, we can identify common factors and reduce the fraction to its simplest form.
-
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Prime factorization simplifies the process of finding the LCM and GCD of two or more numbers. This has applications in various areas, from scheduling tasks to solving problems involving ratios and proportions.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 65
Now, let's apply the concept of prime factorization to the number 65. We need to find the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal 65.
One approach is to systematically check for prime divisors, starting with the smallest prime number, 2. Since 65 is not divisible by 2 (it's an odd number), we move to the next prime number, 3. 65 is not divisible by 3. Next, we try 5. 65 divided by 5 is 13. Therefore, we have:
65 = 5 x 13
Both 5 and 13 are prime numbers. We've successfully expressed 65 as a product of its prime factors. This is the unique prime factorization of 65. There are no other sets of prime numbers that will multiply to give 65.
Alternative Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
While the method above is straightforward for smaller numbers like 65, other methods exist for larger composite numbers:
-
Factor Tree: This visual method involves repeatedly branching down until all factors are prime numbers.
-
Division Method: This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly until the result is 1.
-
Algorithms: For extremely large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are employed to find prime factorizations efficiently. These algorithms are essential in cryptography and other applications dealing with large numbers.
Advanced Concepts Related to Prime Factorization
The study of prime numbers and factorization extends far beyond the basics. Here are some more advanced concepts:
-
The Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm provides an efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
-
Mersenne Primes: These are prime numbers of the form 2<sup>p</sup> - 1, where p is a prime number. The search for Mersenne primes is an ongoing area of research, with discoveries regularly pushing the boundaries of known prime numbers.
-
Twin Primes: These are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The twin prime conjecture, which posits an infinite number of twin primes, remains unproven.
-
Goldbach's Conjecture: This conjecture states that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes. Despite extensive testing, this conjecture also remains unproven.
Conclusion: The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 65, while seemingly simple (5 x 13), illustrates a fundamental concept in number theory with significant implications across various mathematical fields. Understanding prime numbers and factorization is not merely an academic exercise; it's a foundational principle underpinning many critical applications in computer science, cryptography, and pure mathematics. The exploration of prime numbers and their properties continues to inspire mathematical research and advancements, showcasing the enduring power of seemingly simple mathematical concepts. The unique factorization theorem assures us that every composite number can be broken down into this fundamental building block, providing a deep and elegant structure to the seemingly infinite world of numbers. So, the next time you encounter a number, remember the power and beauty hidden within its prime factorization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Five Letter Words Starting With Sta
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 32 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Liters Is 3 Gallons
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Do You Calculate The Perimeter Of A Triangle
Mar 10, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is Incorrect
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 65 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
