How Do You Calculate The Perimeter Of A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
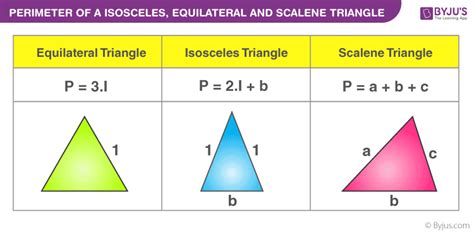
Table of Contents
How Do You Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle? A Comprehensive Guide
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle might seem like a simple task, especially compared to more complex geometric calculations. However, understanding the different approaches and nuances involved allows for a deeper grasp of fundamental geometric principles and lays the groundwork for tackling more advanced problems. This comprehensive guide explores various methods for calculating the perimeter of a triangle, catering to different levels of mathematical understanding and providing practical examples to solidify your knowledge.
Understanding the Basics: What is Perimeter?
Before diving into the calculations, let's establish a clear understanding of what perimeter means. The perimeter of any polygon, including a triangle, is the total distance around its exterior. In simpler terms, it's the sum of the lengths of all its sides. For a triangle, this means adding the lengths of its three sides to obtain the total perimeter.
Method 1: The Straightforward Approach: Adding the Sides
This is the most fundamental and widely applicable method. If you know the lengths of all three sides of the triangle, calculating the perimeter is straightforward addition.
Formula:
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c
Where:
- 'a', 'b', and 'c' represent the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Example:
Let's say we have a triangle with sides of length 5 cm, 7 cm, and 10 cm. The perimeter would be:
P = 5 cm + 7 cm + 10 cm = 22 cm
Method 2: Using Coordinates (Distance Formula)
When the vertices of a triangle are represented by coordinates on a Cartesian plane (x-y coordinate system), the distance formula helps determine the length of each side before calculating the perimeter.
Distance Formula:
The distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given by:
d = √[(x2 - x1)² + (y2 - y1)²]
Example:
Consider a triangle with vertices A(1, 2), B(4, 6), and C(7, 2).
-
Find the distance between A and B (side AB):
dAB = √[(4 - 1)² + (6 - 2)²] = √(3² + 4²) = √25 = 5 units
-
Find the distance between B and C (side BC):
dBC = √[(7 - 4)² + (2 - 6)²] = √(3² + (-4)²) = √25 = 5 units
-
Find the distance between C and A (side CA):
dCA = √[(1 - 7)² + (2 - 2)²] = √((-6)² + 0²) = √36 = 6 units
-
Calculate the perimeter:
P = dAB + dBC + dCA = 5 units + 5 units + 6 units = 16 units
Method 3: Equilateral Triangles: A Special Case
An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all three sides of equal length. Calculating its perimeter is simplified considerably.
Formula:
Perimeter (P) = 3 * s
Where:
- 's' represents the length of one side of the equilateral triangle.
Example:
If an equilateral triangle has sides of length 8 cm, its perimeter is:
P = 3 * 8 cm = 24 cm
Method 4: Isosceles Triangles: Another Special Case
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. While the calculation is still the sum of all three sides, knowing that two sides are equal can streamline the process.
Formula:
Perimeter (P) = 2 * s + b
Where:
- 's' represents the length of each of the two equal sides.
- 'b' represents the length of the base (the unequal side).
Example:
An isosceles triangle has two sides of 9 cm each, and a base of 6 cm. Its perimeter is:
P = 2 * 9 cm + 6 cm = 24 cm
Method 5: Using Heron's Formula (When Only Side Lengths are Known)
Heron's formula is a powerful tool for calculating the area of a triangle when only the lengths of its three sides are known. While not directly calculating the perimeter, it demonstrates a more advanced approach to triangle geometry. However, once you have the area, it doesn't directly lead to the perimeter without knowing more. You still need the side lengths to calculate the perimeter separately.
Heron's Formula (for Area):
Area (A) = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
Where:
- 'a', 'b', and 'c' are the lengths of the three sides.
- 's' is the semi-perimeter: s = (a + b + c) / 2
Method 6: Trigonometry and the Law of Cosines (Solving for Missing Sides)
If you know only two sides and the angle between them, you can utilize the Law of Cosines to determine the length of the third side, and then calculate the perimeter.
Law of Cosines:
c² = a² + b² - 2ab * cos(C)
Where:
- 'a' and 'b' are the lengths of two known sides.
- 'C' is the angle between sides 'a' and 'b'.
- 'c' is the length of the third side (the one you're solving for).
Example:
Let's say you know sides 'a' = 4 cm and 'b' = 6 cm, and the angle C between them is 60°.
-
Use the Law of Cosines to find 'c':
c² = 4² + 6² - 2 * 4 * 6 * cos(60°) = 16 + 36 - 48 * 0.5 = 28 c = √28 = 2√7 cm
-
Calculate the perimeter:
P = a + b + c = 4 cm + 6 cm + 2√7 cm ≈ 16.29 cm
Method 7: Trigonometry and the Law of Sines (Solving for Missing Sides and Angles)
The Law of Sines is useful when you have one side and two angles of a triangle. You can solve for the other sides and then calculate the perimeter.
Law of Sines:
a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C)
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle extends beyond theoretical geometry. It has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Construction: Determining the amount of fencing needed for a triangular plot of land, calculating the length of materials for a triangular roof frame.
- Engineering: Designing triangular bracing structures, calculating the lengths of support beams in bridges or buildings.
- Surveying: Measuring distances between points using triangulation techniques, mapping out irregular terrains.
- Navigation: Determining the shortest distance between locations using triangulation.
- Art and Design: Creating designs with specific proportions, such as in logos or artwork.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While the methods discussed above cover the fundamentals, there are more advanced concepts you can explore:
- Triangle Inequality Theorem: This theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. This is crucial when determining if a given set of side lengths can form a valid triangle.
- Types of Triangles (Scalene, Isosceles, Equilateral): Understanding the properties of different types of triangles allows for more efficient calculation methods and problem-solving.
- Area Calculation Methods: Various methods exist for calculating the area of a triangle, such as using base and height, Heron's formula, or trigonometric functions.
Conclusion
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry with diverse applications. Whether you're dealing with simple side lengths or using coordinates and trigonometric functions, understanding the various approaches and their contexts equips you with a powerful set of tools for solving a wide range of geometric problems. The key is to choose the most appropriate method based on the given information and apply the formula accurately. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for mastering this essential geometric skill. Remember to always double-check your calculations and consider the practical context of the problem to ensure accurate results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of These Statements Is True
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 2 5 As A Percent
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Tall Is 36 Inches In Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
1 75 Liters Equals How Many Ml
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 15 Yards
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Calculate The Perimeter Of A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
