What Is The Prime Factorization Of 156
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
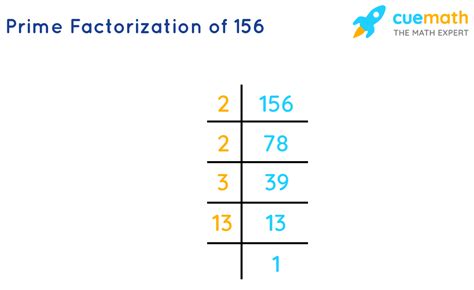
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 156? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 156?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. Understanding prime factorization isn't just about finding the answer for a single number; it's about grasping fundamental concepts that underpin much of mathematics and computer science. This article will not only provide the prime factorization of 156 but also explore the broader concepts of prime numbers, factorization methods, and their real-world applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before diving into the factorization of 156, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, a prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The infinitude of primes – the fact that there are infinitely many prime numbers – is a cornerstone theorem in number theory, first proven by Euclid.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Uniqueness: Every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be expressed as a unique product of primes (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic).
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
Several methods can be used to find the prime factorization of a number. Let's explore a few common techniques:
1. The Factor Tree Method
This is a visual and intuitive method, especially helpful for smaller numbers like 156. You start by breaking down the number into any two factors, and then continue breaking down those factors until you're left with only prime numbers.
Let's apply this to 156:
156
/ \
2 78
/ \
2 39
/ \
3 13
The prime factorization of 156 is therefore 2 x 2 x 3 x 13, or 2² x 3 x 13.
2. Repeated Division by Prime Numbers
This method involves systematically dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible. You continue dividing by prime numbers until you reach 1.
For 156:
- Divide 156 by 2: 156 ÷ 2 = 78
- Divide 78 by 2: 78 ÷ 2 = 39
- Divide 39 by 3: 39 ÷ 3 = 13
- 13 is a prime number.
This confirms that the prime factorization of 156 is 2² x 3 x 13.
3. Using Algorithms (for Larger Numbers)
For significantly larger numbers, manual methods become impractical. Sophisticated algorithms are used in computer science to find prime factorizations. These algorithms, such as the Pollard rho algorithm and the general number field sieve, are complex but highly efficient for handling very large numbers. Understanding these algorithms requires a deeper dive into computational number theory.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The concept of prime factorization might seem abstract, but it has profound implications across various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime factorization is the cornerstone of many modern encryption methods. RSA encryption, one of the most widely used public-key cryptosystems, relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The security of RSA depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring the product of two large prime numbers. Breaking RSA encryption would require finding the prime factors of a massive number, a task currently beyond the capabilities of even the most powerful computers for appropriately sized keys.
2. Number Theory
Prime factorization is central to numerous theorems and problems in number theory. It's intimately linked to concepts like the distribution of primes, modular arithmetic, and the Riemann Hypothesis – one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics.
3. Computer Science
Efficient algorithms for prime factorization are crucial for various aspects of computer science. From cryptography to data compression and error correction codes, the ability to work with prime numbers efficiently is essential.
4. Mathematics Education
Understanding prime factorization builds a strong foundation in number sense and mathematical reasoning. It helps students develop critical thinking skills and appreciate the underlying structure of numbers.
Beyond 156: Exploring Further
While we've focused on the prime factorization of 156, the principles discussed apply to any integer. Let's briefly consider some related concepts:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides all of the integers without a remainder. Prime factorization helps determine the GCD efficiently.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all of the integers without a remainder. Prime factorization is also useful for finding the LCM.
- Divisibility Rules: These rules provide shortcuts for determining whether a number is divisible by a certain prime number (e.g., a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3).
Conclusion
The prime factorization of 156, 2² x 3 x 13, is more than just a mathematical result. It serves as a gateway to understanding prime numbers, factorization methods, and their far-reaching applications in cryptography, computer science, and number theory. The seemingly simple process of breaking down a number into its prime components reveals a deep and elegant structure that underlies much of the mathematical world. By understanding prime factorization, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and power of mathematics. Whether you're a student exploring the fundamentals of number theory or a professional working in a field that relies on computational mathematics, a firm grasp of prime factorization is invaluable. Continue to explore the fascinating world of numbers; the journey of mathematical discovery is endless!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Words That End In Ing
Mar 24, 2025
-
Angular Velocity Of Earth Around Sun
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Ni2
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Mixture
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 4 6 And 10
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 156 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
