What Is The Prime Factorization Of 105
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
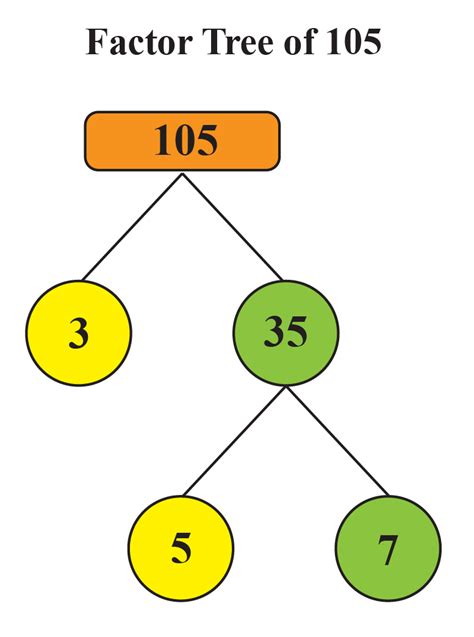
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 105? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Finding the prime factorization of a number might seem like a simple mathematical exercise, but it's a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications in number theory, cryptography, and even computer science. This article will explore the prime factorization of 105, explaining the process step-by-step, and then delve deeper into the broader concepts of prime numbers and factorization, illustrating their significance and applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the factorization of 105, let's establish a firm understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Prime numbers are only divisible by 1 and themselves.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This fundamental theorem of arithmetic has been proven, ensuring a limitless supply of these building blocks of numbers.
- Uniqueness: The prime factorization of any number is unique (except for the order of factors). This property is crucial in various mathematical applications.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number (a number that is not prime) as a product of its prime factors. Every composite number can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This uniqueness is a cornerstone of number theory.
For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3). This means that 12 can be built solely by multiplying the prime numbers 2 and 3.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 105: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 105. We'll use a method called the factor tree.
-
Start with the number 105.
-
Find the smallest prime number that divides 105. The smallest prime number is 2, but 105 is not divisible by 2 (it's an odd number). The next prime number is 3. 105 divided by 3 is 35. So, we can write: 105 = 3 x 35
-
Now, consider the factor 35. 35 is not divisible by 3. However, it is divisible by 5 (another prime number). 35 divided by 5 is 7. So, we can write: 35 = 5 x 7
-
Finally, we have reached prime factors. Both 5 and 7 are prime numbers.
Therefore, the complete prime factorization of 105 is 3 x 5 x 7. We can represent this concisely as 3¹ x 5¹ x 7¹.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, despite seeming like a simple mathematical concept, has surprisingly broad applications across numerous fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime factorization forms the basis of many modern encryption algorithms, such as RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman). RSA relies on the fact that multiplying two large prime numbers is computationally easy, while factoring the resulting product back into its prime components is extremely difficult. This asymmetry is what makes RSA secure for protecting sensitive data. The difficulty of factoring large numbers is a crucial aspect of the security of online transactions and data protection.
2. Number Theory
In number theory, prime factorization is a fundamental tool for studying various properties of numbers, such as divisibility, congruences, and the distribution of prime numbers. Understanding prime factorization is essential for solving complex problems related to number patterns and relationships.
3. Computer Science
Prime numbers play a vital role in algorithms related to hashing, data structures, and random number generation. Efficient algorithms for finding prime numbers and factoring numbers are crucial for the performance of many computer programs. Prime numbers are also important in ensuring the security of cryptographic protocols used in computer networks.
4. Modular Arithmetic
Prime numbers are especially important in modular arithmetic, where calculations are performed within a specific modulus (a remainder after division). This field has applications in cryptography, error detection, and coding theory. The properties of prime numbers allow for efficient calculations and error detection mechanisms.
5. Abstract Algebra
The concept of prime factorization extends into abstract algebra, where it relates to the factorization of polynomials and ideals in rings. This field is fundamental to many advanced mathematical concepts and has applications in various scientific disciplines.
Beyond the Factor Tree: Other Factorization Methods
While the factor tree method is visually intuitive, especially for smaller numbers like 105, other methods exist for finding prime factorization, particularly for larger numbers:
-
Trial Division: This method involves systematically testing for divisibility by prime numbers, starting with the smallest prime number (2) and progressing upwards. This method can be quite time-consuming for very large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It's efficient for generating a list of primes within a range, which is useful when attempting to factorize a number.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: This is a probabilistic algorithm for integer factorization. It's particularly useful for finding smaller prime factors of a large composite number.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): This is currently the most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers and is commonly used for breaking cryptographic systems based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 105, as seemingly simple as it might appear (3 x 5 x 7), reveals a deeper mathematical truth: the fundamental building blocks of numbers are prime numbers. Understanding the concept of prime factorization and the various methods for determining it is not only crucial for advanced mathematical study but also has significant practical applications in fields like cryptography and computer science. The seemingly simple act of breaking down a number into its prime constituents holds the key to unlocking sophisticated security protocols, enabling efficient algorithms, and driving advances in numerous scientific disciplines. The world of prime numbers and factorization is vast, intricate, and continues to be a vibrant area of mathematical exploration and innovation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm Of 3 And 4 And 5
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is 81 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 09, 2025
-
When Diluting An Acid With Water
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Opposite Of Heavy
Mar 09, 2025
-
In Which Of The Following Organelles Does Photosynthesis Take Place
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 105 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
