What Is The Prime Factorization For 135
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
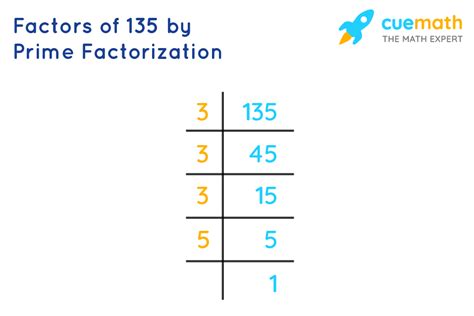
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization for 135? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Finding the prime factorization of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching applications in cryptography, computer science, and beyond. This article delves deep into the prime factorization of 135, explaining the process step-by-step, exploring the underlying mathematical principles, and showcasing its relevance in various fields.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 135, let's establish a solid understanding of the core concepts involved.
What are Prime Numbers?
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. 2 is the only even prime number; all other prime numbers are odd.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal the original number. Every composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 135: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 135 using a systematic approach:
-
Start with the smallest prime number: The smallest prime number is 2. However, 135 is an odd number, so it's not divisible by 2.
-
Move to the next prime number: The next prime number is 3. We check if 135 is divisible by 3. The sum of the digits of 135 (1 + 3 + 5 = 9) is divisible by 3, indicating that 135 is divisible by 3. Performing the division, we get 135 ÷ 3 = 45.
-
Continue the process: Now we work with 45. Again, 45 is divisible by 3 (4 + 5 = 9). Dividing 45 by 3, we get 15.
-
Repeat until you reach a prime number: 15 is also divisible by 3, resulting in 5.
-
The final prime number: 5 is a prime number. We have reached the end of our factorization.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 135 is 3 x 3 x 3 x 5, which can also be written as 3³ x 5.
Visualizing Prime Factorization: Factor Trees
A helpful visual aid for prime factorization is the factor tree. Here's how to create a factor tree for 135:
135
/ \
3 45
/ \
3 15
/ \
3 5
The factor tree branches out, showing each division step until we reach only prime numbers at the end of each branch. The prime factors are then read from the bottom of the tree: 3, 3, 3, and 5.
Applications of Prime Factorization
While seemingly simple, prime factorization has significant applications in various fields:
1. Cryptography: RSA Algorithm
The RSA algorithm, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, heavily relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of RSA depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring extremely large semiprimes (numbers that are the product of two large prime numbers). Breaking RSA encryption requires factoring these massive numbers, a task that becomes computationally prohibitive with sufficiently large primes.
2. Computer Science: Hashing and Data Structures
Prime numbers play a crucial role in designing efficient hashing functions and data structures. Choosing prime numbers for hash table sizes helps minimize collisions and improves the performance of hash-based algorithms. Prime numbers offer better distribution of data within the hash table.
3. Number Theory: Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The prime factorization of 135 is a direct consequence of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (disregarding the order of the factors). This theorem is a cornerstone of number theory, providing a foundation for many other results and theorems.
4. Mathematics Education: Building Number Sense
Understanding prime factorization helps build a strong foundation in number sense and mathematical reasoning. It enhances the ability to work with numbers efficiently, comprehend divisibility rules, and solve various mathematical problems.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Let's delve into some related concepts to further enrich your understanding of prime factorization and its implications:
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. Prime factorization simplifies finding the GCD. By finding the prime factorization of each number, we can identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers to determine the GCD.
For example, let's find the GCD of 135 and 75.
- Prime factorization of 135: 3³ x 5
- Prime factorization of 75: 3 x 5²
The common prime factors are 3 and 5. The lowest power of 3 is 3¹, and the lowest power of 5 is 5¹. Therefore, the GCD(135, 75) = 3 x 5 = 15.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of the integers. Similar to the GCD, prime factorization provides a straightforward method for finding the LCM. We identify the prime factors of each number and take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations.
For the same example, the LCM of 135 and 75 would be:
- Prime factorization of 135: 3³ x 5
- Prime factorization of 75: 3 x 5²
The highest power of 3 is 3³, and the highest power of 5 is 5². Therefore, the LCM(135, 75) = 3³ x 5² = 27 x 25 = 675.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of finding the prime factorization of a number like 135 reveals a deep connection to fundamental mathematical principles and has far-reaching implications across diverse fields. From the security of online transactions to the efficiency of computer algorithms, prime factorization is a cornerstone of modern technology and mathematical understanding. Understanding this concept not only enhances mathematical skills but also provides a glimpse into the elegant structure and power of number theory. The prime factorization of 135—3³ x 5—is more than just a calculation; it's a testament to the fundamental building blocks of mathematics and their pervasive influence on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Correct Name For N2o3
Mar 14, 2025
-
50 Is 25 Of What Number
Mar 14, 2025
-
Slogans On The Topic Save Water
Mar 14, 2025
-
Whats The Lcm Of 4 And 10
Mar 14, 2025
-
Lateral Area Formula For A Rectangular Prism
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization For 135 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
